Labeling proteins with ubiquitin paves new road to cell regulation research
Credit: K. Lang / TUM
Human cells have a sophisticated regulatory system at their disposal: labeling proteins with the small molecule ubiquitin. In a first, a team from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has succeeded in marking proteins with ubiquitin in a targeted manner, in test tubes as well as in living cells. The procedure opens the door to exploring the inner workings of this vital regulatory system.
Plants, fungi, animals and even humans have it: the protein ubiquitin. It comprises a sequence of 76 amino acids, making it a relatively small biomolecule. But its influence is far-reaching: the type, position, and number of ubiquitin molecules bound to proteins determine their stability, function, and location within the cell.
“Virtually every process in the cell is directly or indirectly affected by ubiquitin. That is why malfunctions of this labeling mechanism are associated with the development and progression of cancer and many other severe diseases,” explains Kathrin Lang, Professor of Synthetic Biochemistry at the Technical University of Munich.
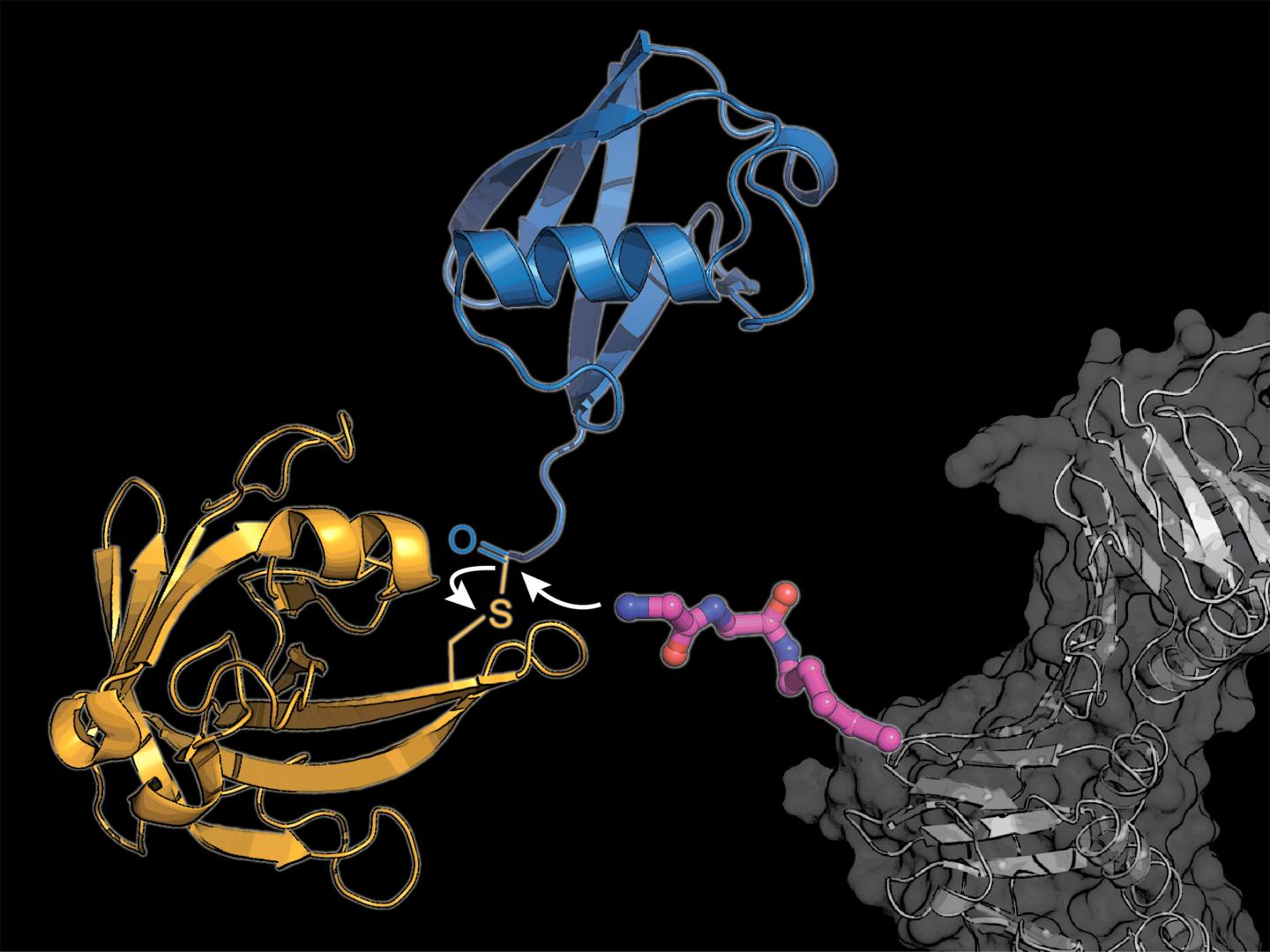
The discovery of the important role this cellular regulatory system plays in the controlled degradation of proteins was acknowledged with the 2004 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. But, in many cases the details of how ubiquitin modifications affect the function of cells remains unclear. Kathrin Lang’s team has now developed a method for attaching ubiquitin labels to targeted proteins – a key to exploring the system.
A bacterial enzyme creates new compounds
Lang’s team uses two tricks to circumvent the complicated natural system: They incorporate a novel modified amino acid, at which the bacteria-derived enzyme sortase can attach ubiquitin or a ubiquitin-similar molecule.
“The biggest challenge was to align the various steps – the incorporation of the unnatural amino acid into a target protein and the transfer of ubiquitin by the enzyme sortase – in such a way that they will work not only in the test tube but also in living cells,” recalls Maximilian Fottner, the lead author of the study.
In the meantime, the researchers at the Technical University of Munich have optimized and patented their new method for many different cellular proteins. “We have already entered into collaborations with physicians and cell biologists who now want to work with us to study the effects of ubiquitin markers on the development of cancer and neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s at the molecular level,” says Prof. Lang.
###
In its research, Kathrin Lang’s team collaborated with the groups of Prof. Ville R. I. Kaila, Chair of Computational Biocatalysis of the Technical University of Munich and the group of Dr. Anja Bremm from the Goethe University in Frankfurt am Main.
The research was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) as part of the Excellence Cluster Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich (CIPSM), the International Research Training Group GRK 1721, and the Collaborative Research Centers SFB 1309, SFB 1035 and the priority program SPP 1623. Kathrin Lang is Fellow of the TUM Institute for Advanced Study as part of her Rudolf Mößbauer Tenure Track Professorship.
Publication:
Site-specific ubiquitylation and SUMOylation using genetic-code expansion and sortase
Maximilian Fottner, Andreas-David Brunner, Verena Bittl, Daniel Horn-Ghetko,
Alexander Jussupow , Ville R. I. Kaila, Anja Bremm and Kathrin Lang
Nature Chemical Biology, 15, 276-284 (2019) – DOI: 10.1038/s41589-019-0227-4
Media Contact
Dr. Andreas Battenberg
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




