Credit: Dr Ulrike Kappler
Just a few changes to an enzyme’s amino acids can be enough to dramatically change its function, enabling microbes to inhabit wildly different environments.
University of Queensland microbiologist Associate Professor Ulrike Kappler, led by an international team of researchers, made this discovery when investigating how Haemophilus influenzae bacteria colonise the human respiratory system.
“This disease-causing bacterium is supremely adapted to living in humans, so much so that they cannot survive anywhere else,” Dr Kappler said.
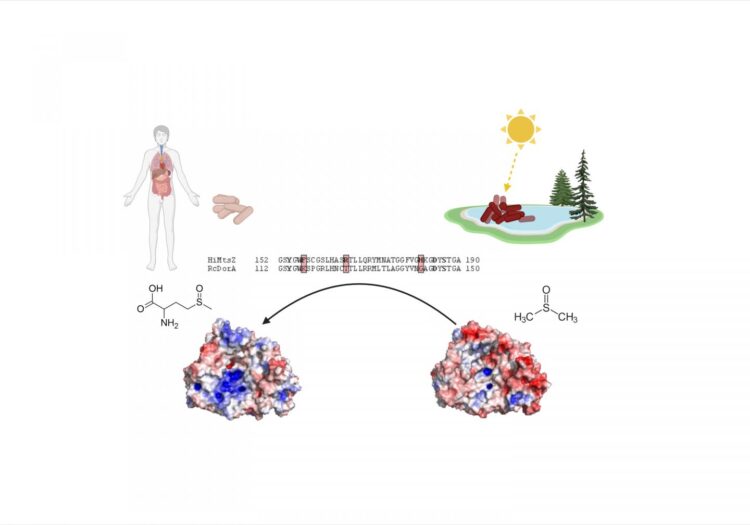
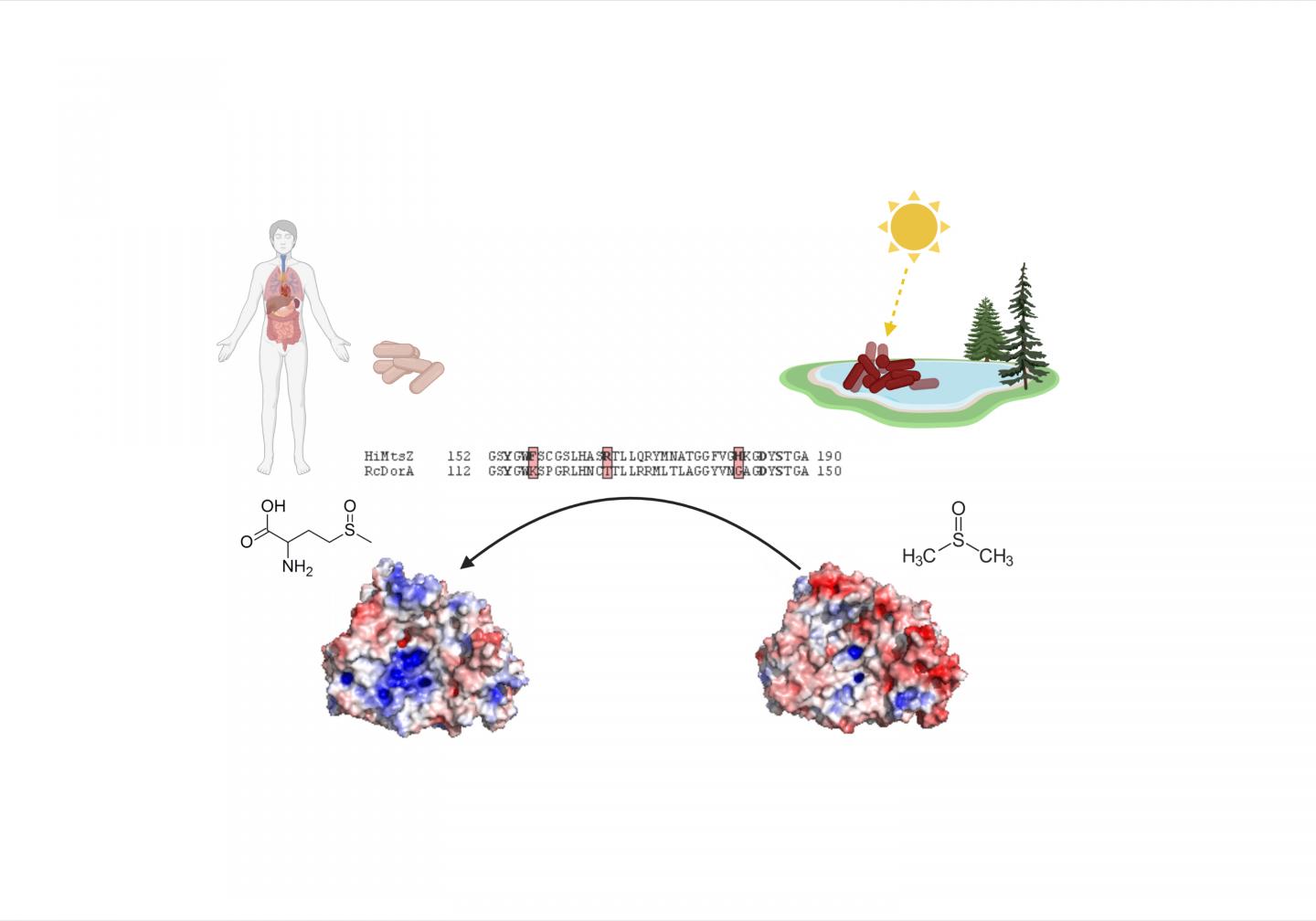
“It turns out that one enzyme, MtsZ, is the key player in this adaptation.
“But, surprisingly, close relatives of this protein, which promotes Haemophilus survival exclusively inside humans, help other species of bacteria to survive exclusively in lakes.
“How could closely related enzymes help one bacterial species live exclusively in humans and another to live only in lakes?
“The answer is a matter of minute amino acid changes.”
The research shows that a sequence difference of just three amino acids, a difference of less than 0.25 per cent of the MtsZ enzyme sequence, changes the functionality of the enzyme between bacteria living in lakes compared with those living in humans.
“It the natural world, tiny differences can lead to enormous functional changes – for example, humans and chimpanzees aren’t exactly the same despite being 99 percent genetically similar,” Dr Kappler said.
“We’re just now realising that this can be the case for enzymes as well.
“The slight changes in this enzyme enable the lake-dwelling bacteria to live on decaying algae and generate energy.
“Contrast this with Haemophilus, which uses MtsZ to scavenge amino acids from the human body and use them for bacterial growth and replication.
“Now that we understand the unique structure of this enzyme in Haemophilus, we hope to develop ways to inhibit its specific function and remedy chronic respiratory conditions associated with this bacterium.”
###
The paper is published in Journal of Biological Chemistry (DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100672) and includes collaborating researchers from the USA, Germany and Australia.
Media Contact
A/Prof Ulrike Kappler
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.