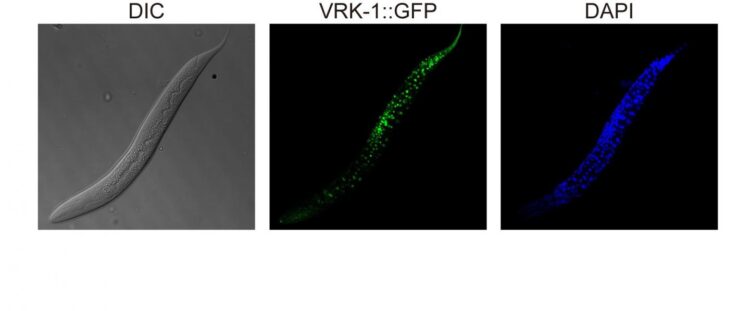
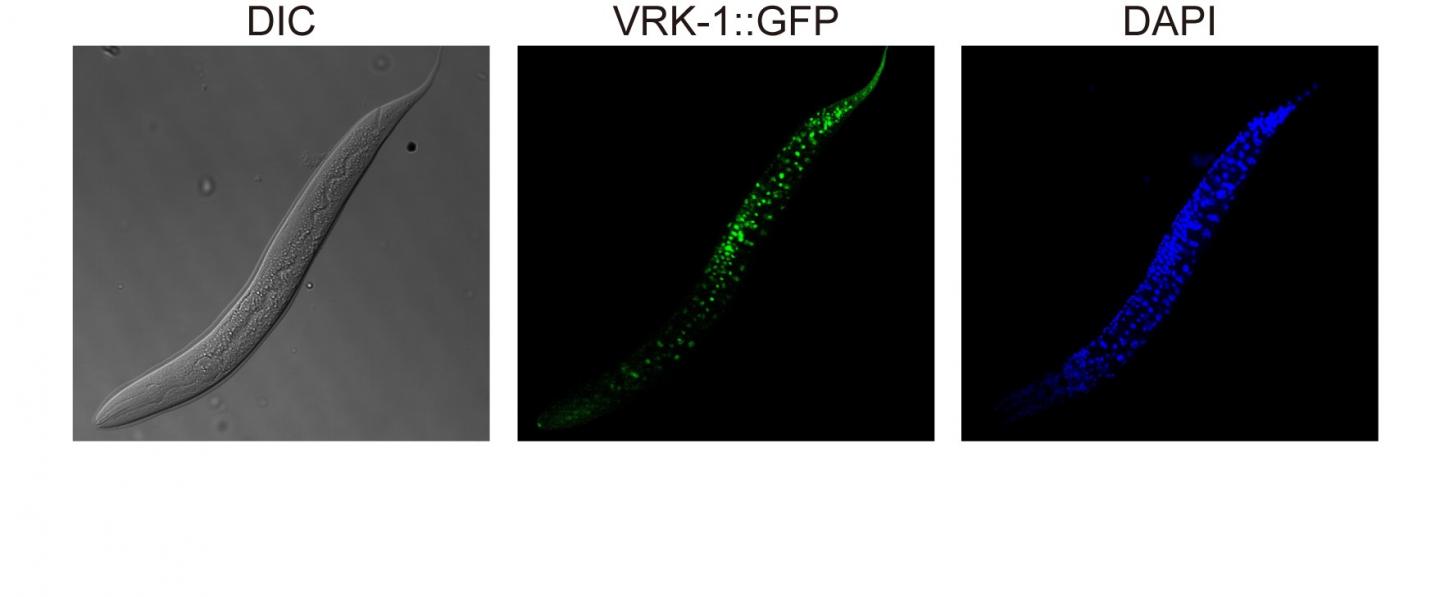
The somatic nuclear protein kinase VRK-1 increases the worm’s lifespan through AMPK activation, and this mechanism can be applied to promoting human longevity, the study reveals. –
Credit: Seung-Jae V. LEE, KAIST.
KAIST researchers have been able to dial up and down creatures’ lifespans by altering the activity of proteins found in roundworm cells that tell them to convert sugar into energy when their cellular energy is running low. Humans also have these proteins, offering up the intriguing possibilities for developing longevity-promoting drugs. These new findings were published on July 1 in Science Advances.
The roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), a millimeter-long nematode commonly used in lab testing, enjoyed a boost in its lifespan when researchers tinkered with a couple of proteins involved in monitoring the energy use by its cells.
The proteins VRK-1 and AMPK work in tandem in roundworm cells, with the former telling the latter to get to work by sticking a phosphate molecule, composed of one phosphorus and four oxygen atoms, on it. In turn, AMPK’s role is to monitor energy levels in cells, when cellular energy is running low. In essence, VRK-1 regulates AMPK, and AMPK regulates the cellular energy status.
Using a range of different biological research tools, including introducing foreign genes into the worm, a group of researchers led by Professor Seung-Jae V. Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST were able to dial up and down the activity of the gene that tells cells to produce the VRK-1 protein. This gene has remained pretty much unchanged throughout evolution. Most complex organisms have this same gene, including humans.
Lead author of the study Sangsoon Park and his colleagues confirmed that the overexpression, or increased production, of the VRK-1 protein boosted the lifespan of the C. elegans, which normally lives just two to three weeks, and the inhibition of VRK-1 production reduced its lifespan.
The research team found that the activity of the VRK-1-to-AMPK cellular-energy monitoring process is increased in low cellular energy status by reduced mitochondrial respiration, the set of metabolic chemical reactions that make use of the oxygen the worm breathes to convert macronutrients from food into the energy “currency” that cells spend to do everything they need to do.
It is already known that mitochondria, the energy-producing engine rooms in cells, play a crucial role in aging, and declines in the functioning of mitochondria are associated with age-related diseases. At the same time, the mild inhibition of mitochondrial respiration has been shown to promote longevity in a range of species, including flies and mammals.
When the research team performed similar tinkering with cultured human cells, they found they could also replicate this ramping up and down of the VRK-1-to-AMPK process that occurs in roundworms.
“This raises the intriguing possibility that VRK-1 also functions as a factor in governing human longevity, and so perhaps we can start developing longevity-promoting drugs that alter the activity of VRK-1,” explained Professor Lee.
At the very least, the research points us in an interesting direction for investigating new therapeutic strategies to combat metabolic disorders by targeting the modulation of VRK-1. Metabolic disorders involve the disruption of chemical reactions in the body, including diseases of the mitochondria.
But before metabolic disorder therapeutics or longevity drugs can be contemplated by scientists, further research still needs to be carried out to better understand how VRK-1 works to activate AMPK, as well as figure out the precise mechanics of how AMPK controls cellular energy.
###
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF), and the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of Korea.
Media Contact
Younghye Cho
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.