Researchers from the University of Tsukuba find that sea urchin larvae use light to control digestion
Credit: University of Tsukuba
Tsukuba, Japan – Many life forms use light as an important biological signal, including animals with visual and non-visual systems. But now, researchers from Japan have found that neuronal cells may have initially evolved to regulate digestion according to light information.
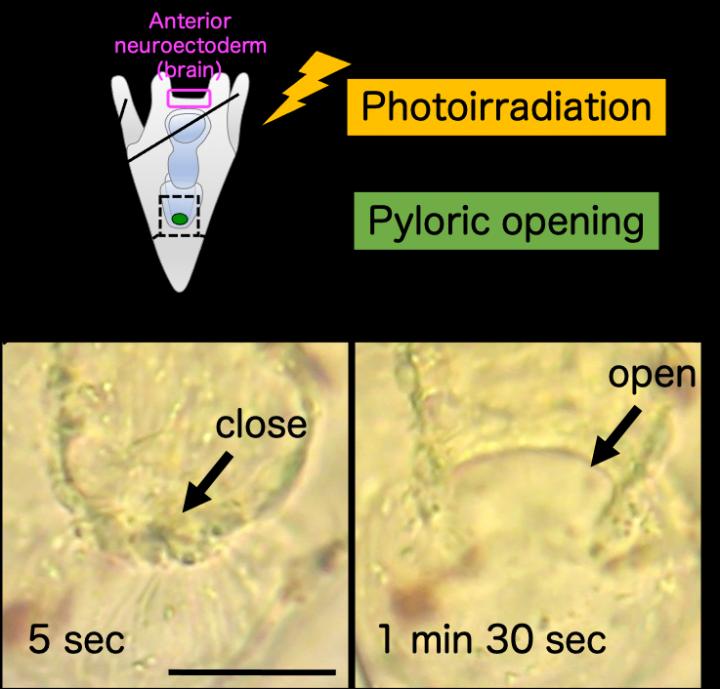
In a study published this month in BMC Biology, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have revealed that sea urchins use light to regulate the opening and closing of the pylorus, which is an important component of the digestive tract.
Light-dependent systems often rely on the activity of proteins in the Opsin family, and these are found across the animal kingdom, including in organisms with visual and non-visual systems. Understanding the function of Opsins in animals from different taxonomic groups may provide important clues regarding how visual/non-visual systems evolved in different creatures to use light as an external signal. The function of Opsins in the Ambulacraria groups of animals, which include sea urchins, has not been characterized, something the researchers aimed to address.
“The functions of eyes and visual systems have been well-characterized,” says senior author of the study Professor Shunsuke Yaguchi. “However, the way in which light dependent systems were acquired and diversified throughout evolution is unclear especially in deuterostomes because of the lack of data regarding the signaling pathway in the Ambulacraria group.”
To address this, the researchers tested whether light exposure caused changes in digestive tract activity in sea urchins. They then conducted micro-surgical and genetic knockdown experiments to test whether Opsin cells in the sea urchin digestive system mediated the effect of light.
“The results provided new information about the role of Opsins in sea urchins,” explains Professor Yaguchi. “Specifically, we found that stimulation of sea urchin larvae via light caused changes in digestive system function, even in the absence of food stimuli.”
Furthermore, the researchers identified brain serotonergic neurons near the Opsin-expressing cells that were essential for mediating the light-stimulated release of nitric oxide, which acts as a neurotransmitter.
“Our results have important implications for understanding the process of evolution, specifically, that of light-dependent systems controlled via neurotransmitters,” says Professor Yaguchi.
The data indicate that an early function of brain neurons may have been the regulation of the digestive tract in our evolutionary ancestors. Because food consumption and nutrient absorption are critical to survival, the development of a sophisticated brain-gut regulatory system may have been a major step in animal evolution.
###
The article, “Sea urchin larvae utilize light for regulating the pyloric opening” was published in BMC Biology at DOI:10.1186/s12915-021-00999-1
Media Contact
Naoko Yamashina
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




