Credit: Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo
Tokyo, Japan – Glass is such a common, everyday material that you probably don’t think about it much. It may surprise you to learn that researchers today still don’t understand how glass forms. Figuring this out is important for glass industries and many other surprising applications of glasses.
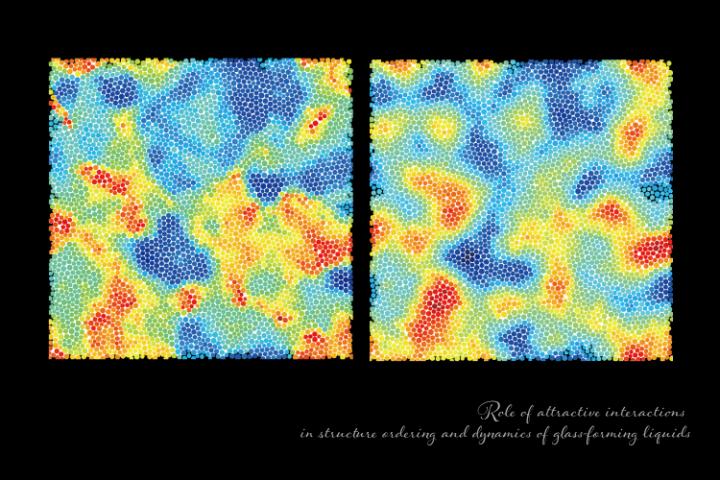
In a study published in Physical Review Letters, researchers from The University of Tokyo have revealed a structural origin of slow glassy dynamics that’s aimed at understanding how a liquid becomes more viscous on cooling and can form a glass. The researchers found the correlation between the structure and motion of particles within simulated glass-forming liquids, on the level of individual particles and larger-scale particle assemblies.
A central puzzle in glass physics is why a glass-forming liquid becomes so viscous before forming a glass. Whether this unusually slow motion in a liquid is mainly attributable to changes in spatial structure remains unknown. A physical model that reproduces how glass forms would help resolve this debate.
“We used the concept of mutual information to understand the interrelationship between local particle arrangement and dynamics in glass-forming liquids,” explains lead author of the study Hua Tong, who is now Assistant Professor in Shanghai Jiao Tong University. “Our results suggest that spatial structure controls the unique cooperative particle motion seen in glass-forming liquids.”
The researchers based their simulations on a structural order parameter that quantifies how closely the particles can pack together. The simulations focused on particle motions attributable to the original state of the particles, i.e., on the spatial structure. With the concept of mutual information, the simulations showed that particles structurally organize into assemblies that move more slowly than the rest of the particles, as seen in a real glass.
“We found no clear relationship between particle-level potential energy and relaxation time,” says Hajime Tanaka, senior author. “This suggests that slow glassy dynamics is fundamentally controlled by structural order formed by interparticle interactions, including both the repulsive and attractive parts.”
This liquid-to-glass research has many applications, including window glasses, optical fibers, and improved smart touch screens. Ultrahigh viscosity of a glass-forming material is very useful to deform it to arbitrary shape. By understanding what controls the viscosity of glass-forming liquids, the shape processability may be much improved.
###
The article, “Role of attractive interactions in structure ordering and dynamics of glass-forming liquids,” was published in Physical Review Letters.
About Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), the University of Tokyo
Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), the University of Tokyo is one of the largest university-attached research institutes in Japan.
More than 120 research laboratories, each headed by a faculty member, comprise IIS, with more than 1,000 members including approximately 300 staff and 700 students actively engaged in education and research. Our activities cover almost all the areas of engineering disciplines. Since its foundation in 1949, IIS has worked to bridge the huge gaps that exist between academic disciplines and real-world applications.
Media Contact
Hajime Tanaka
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




