Protection against electromagnetic interference
Credit: Empa
Electric motors and electronic devices generate electromagnetic fields that sometimes have to be shielded in order not to affect neighboring electronic components or the transmission of signals. High-frequency electromagnetic fields can only be shielded with conductive shells that are closed on all sides. Often thin metal sheets or metallized foils are used for this purpose. However, for many applications such a shield is too heavy or too poorly adaptable to the given geometry. The ideal solution would be a light, flexible and durable material with extremely high shielding effectiveness.
Aerogels against electromagnetic radiation
A breakthrough in this area has now been achieved by a research team led by Zhihui Zeng and Gustav Nyström. The researchers are using nanofibers of cellulose as the basis for an aerogel, which is a light, highly porous material. Cellulose fibres are obtained from wood and, due to their chemical structure, enable a wide range of chemical modifications. They are therefore a highly popular research object. The crucial factor in the processing and modification of these cellulose nanofibres is to be able to produce certain microstructures in a defined way and to interpret the effects achieved. These relationships between structure and properties are the very field of research of Nyström’s team at Empa.
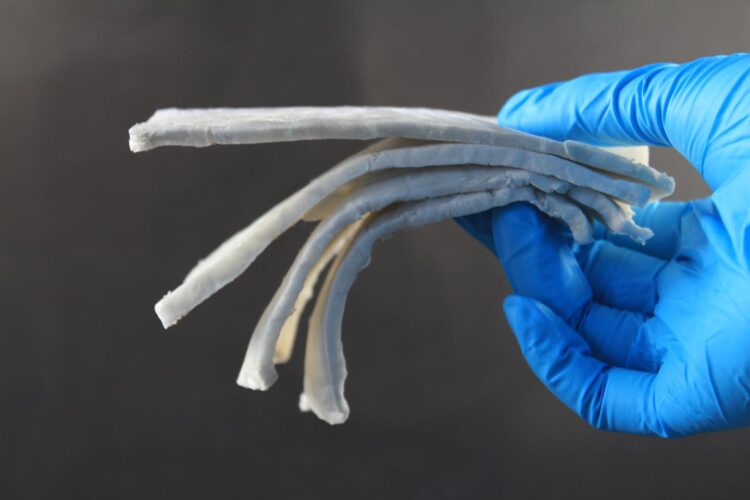
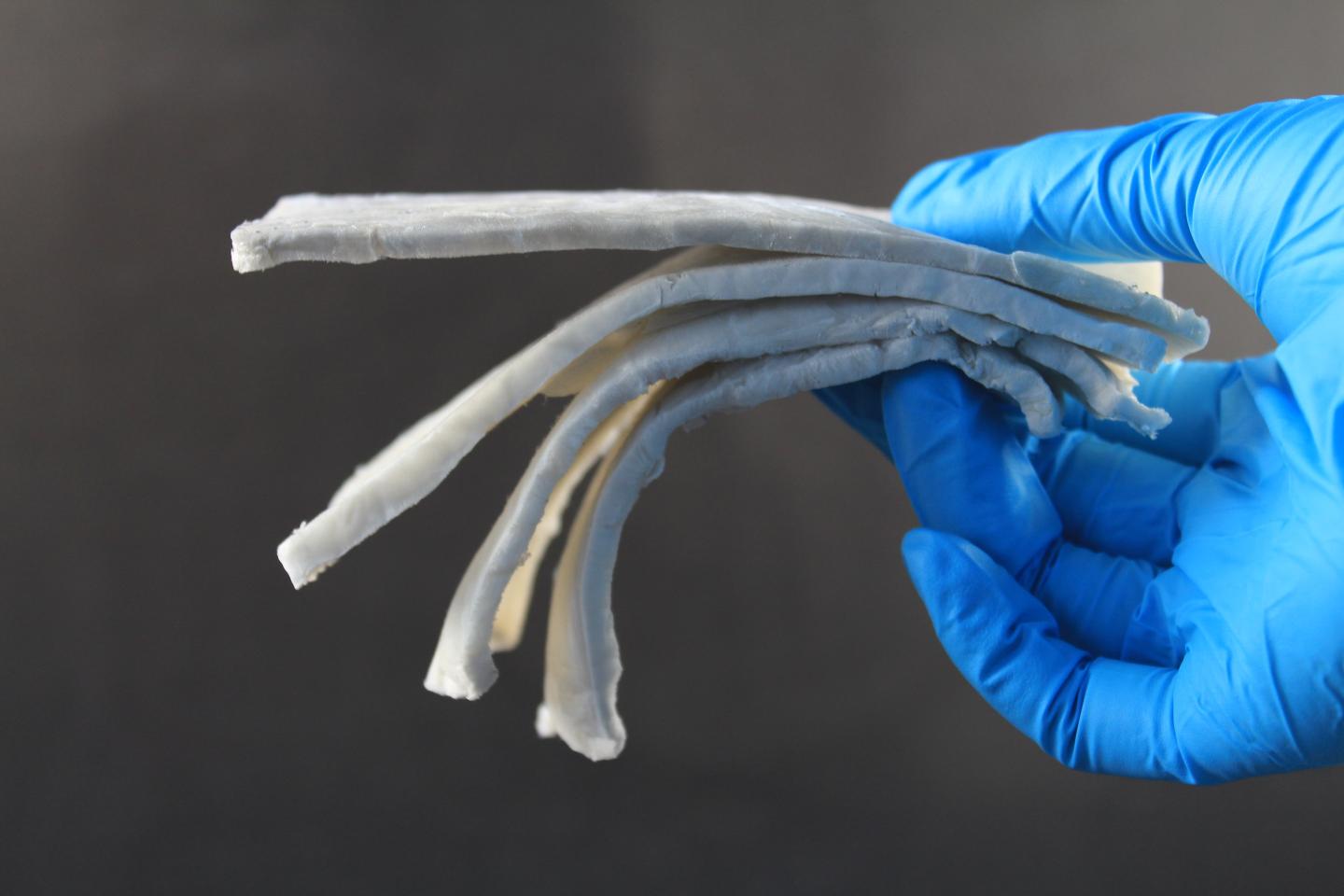
The researchers have succeeded in producing a composite of cellulose nanofibers and silver nanowires, and thereby created ultra-light fine structures which provide excellent shielding against electromagnetic radiation. The effect of the material is impressive: with a density of only 1.7 milligrams per cubic centimeter, the silver-reinforced cellulose aerogel achieves more than 40 dB shielding in the frequency range of high-resolution radar radiation (8 to 12 GHz) – in other words: Virtually all radiation in this frequency range is intercepted by the material.
Ice crystals control the shape
Not only the correct composition of cellulose and silver wires is decisive for the shielding effect, but also the pore structure of the material. Within the pores, the electromagnetic fields are reflected back and forth and additionally trigger electromagnetic fields in the composite material, which counteract the incident field. To create pores of optimum size and shape, the researchers pour the material into pre-cooled moulds and allow it to freeze out slowly. The growth of the ice crystals creates the optimum pore structure for damping the fields.
With this production method, the damping effect can even be specified in different spatial directions: If the material freezes out in the mould from bottom to top, the electromagnetic damping effect is weaker in the vertical direction. In the horizontal direction – i.e. perpendicular to the freezing direction – the damping effect is optimized. Shielding structures cast in this way are highly flexible: even after being bent back and forth a thousand times, the damping effect is practically the same as with the original material. The desired absorption can even be easily adjusted by adding more or less silver nanowires to the composite, as well as by the porosity of the cast aerogel and the thickness of the cast layer.
The lightest electromagnetic shield in the world
In another experiment, the researchers removed the silver nanowires from the composite material and connected their cellulose nanofibres with two-dimensional nanoplates of titanium carbide, which were produced using a special etching process. The nanoplates act like hard “bricks” that are joined together with flexible “mortar” made of cellulose fibers. This formulation was also frozen in cooled forms in a targeted manner. In relation to the weight of the material, no other material can achieve such shielding. This ranks the titanium carbide nanocellulose aerogel as by far the lightest electromagnetic shielding material in the world.
###
Media Contact
Gustav Nyström
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.