Scientists conducted a sweeping review of nature’s contributions to humans in order to present a clear breakdown of global trends since 1970. Not surprisingly, the results are grim
Credit: Brauman et al. (2020)
It is no secret that over the last few decades, humans have changed nature at an ever-increasing rate. A growing collection of research covers the many ways this is impacting our quality of life, from air quality to nutrition and income. To better understand how which areas are most at risk, scientists have combed through volumes of literature to present global trends in the relationship between human wellbeing and environmental degradation.
Their work, which included Fabrice DeClerck from the Alliance of Bioversity International and CIAT, was summarized in “Global trends in nature’s contributions to people”, which was recently published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
This systematic review builds on the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) Global Assessment Report, which in 2019 provided the most comprehensive assessment yet of nature’s decline and biodiversity loss, when it emphasized that 1 million plant and animal species face extinction.
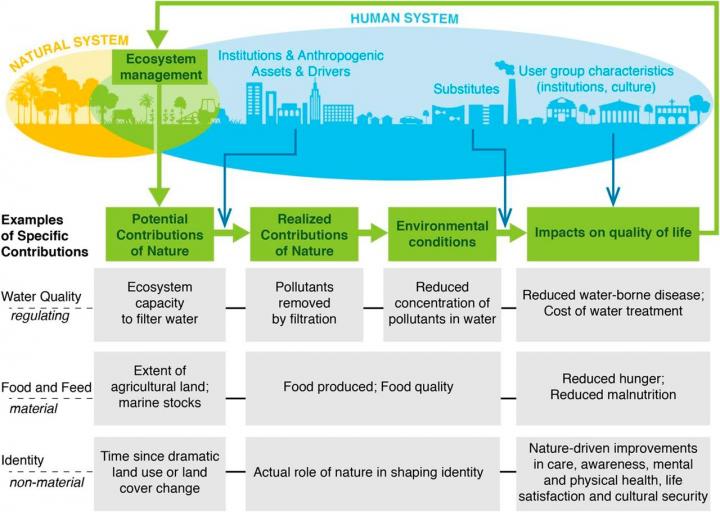
The PNAS review evaluates how biodiversity loss affects human wellbeing. It differentiates between nature’s potential contributions, realized contributions, environmental conditions, and impact on quality of life. Material and non-material indicators, including greenhouse gas concentration, pest control and cultural knowledge were used to assess whether trends were worsening, about the same, or improving since 1970. Unsurprisingly, many were shown to be in sharp decline. Particularly in the context of agriculture, the review underscores that we face interrelated risks such as declining crop yields, declining pollinator populations, and reduced soil productivity.
Even increases in areas such as volume of crop commodity production hold a warning, as trends on human health from food diverge depending on variables such as region and socioeconomic context.
This paper represents one step in documenting the importance of nature’s contributions to people, which the scientists hope can improve our ability to manage earth systems effectively, equitably, and sustainably.
“Nature contributes to our health and well-being in many ways, and our actions put these benefits at risk,” said author Kate Brauman of the University of Minnesota.
###
Media Contact
Eliot Gee
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




