Tasmanian tigers start to look like dogs in the pouch
Credit: The Pask Lab
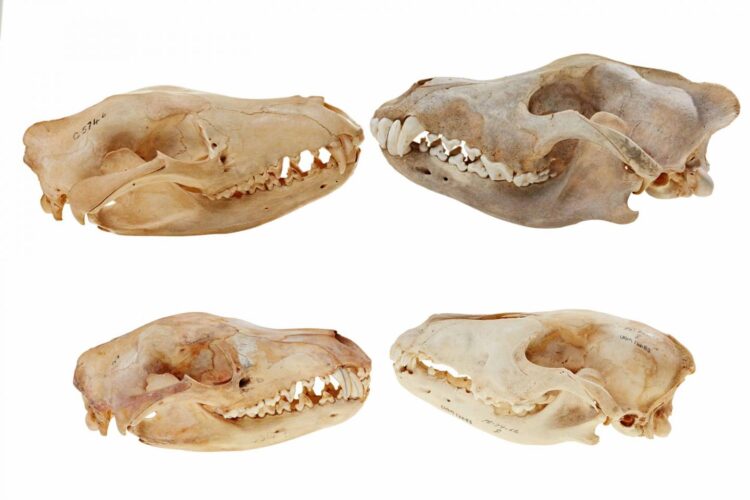
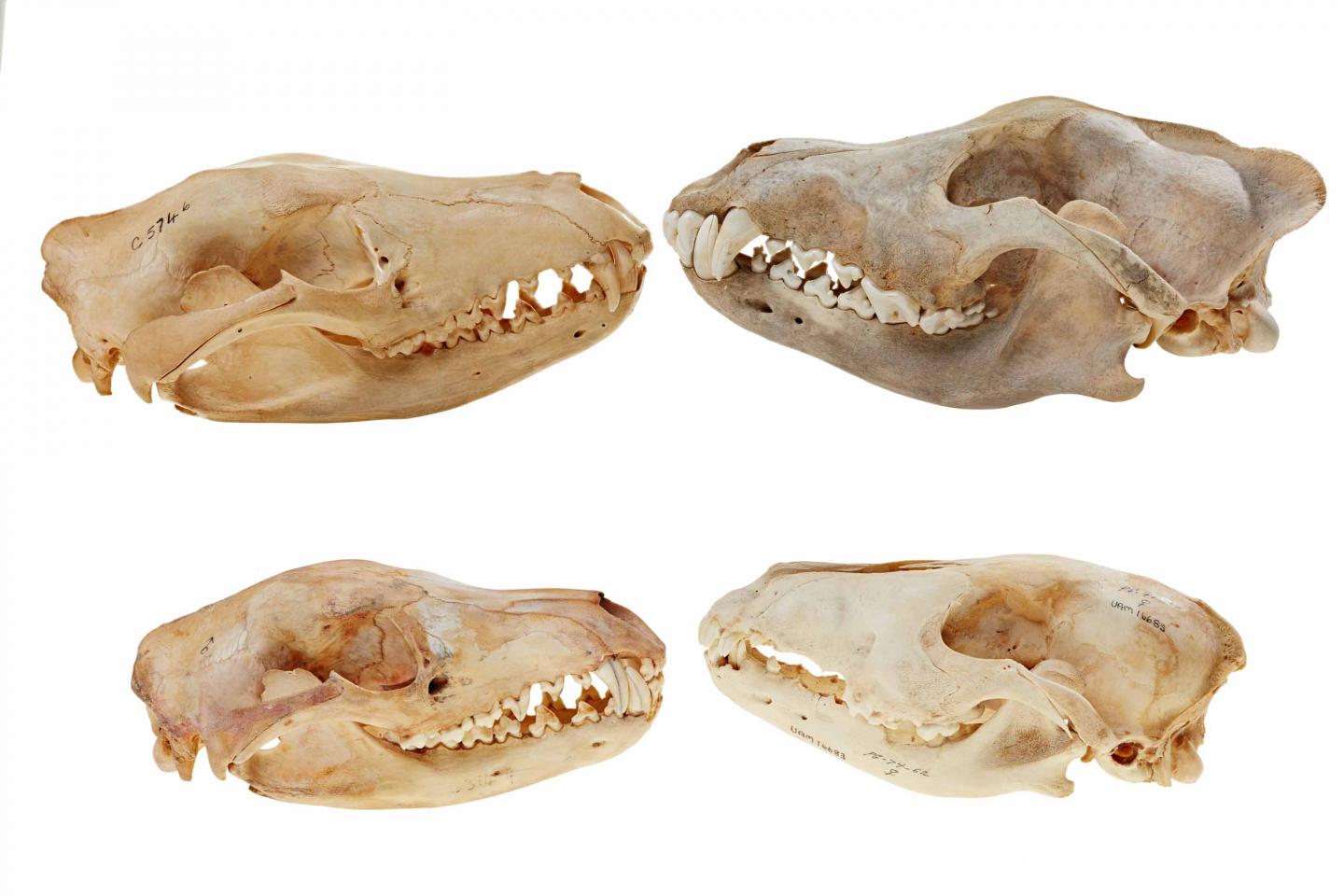
Micro-CT scanning and digital reconstructions have been used to compare the skulls of the Tasmanian tiger (thylacine) and wolf across their early development and into adulthood, establishing that not only did the thylacine resemble the wolf as adults, but also as newborns and juveniles.
“Remarkably, the Tasmanian tiger pups were more similar to wolf pups than to other closely related marsupials,” Professor Andrew Pask from the University of Melbourne said.
The collaborative study with Flinders University and Museums Victoria complement earlier findings that thylacine and wolf have evolved similar instructions in their genome, which influence cranial stem cells during development.
While scientists have worked out that different animals evolve to look the same because they occupy similar places in the ecosystem, they have yet to explain how animals evolve to become convergent, particularly the forces driving their early development. The study provides significant new insights into how animals develop to look a certain way and then when in development these things happen.
Through collaborations with Australian museums and the Museum of the North in Alaska, USA, the team loaned thylacine and wolf skulls of different ages, stages and sizes, from newborns through to fully grown adults. They then applied micro-CT scanning to the skulls to generate digital models which could be compared to determine when during development similarities arose between the thylacine and wolf.
After reconstructing the early pouch development of the thylacine, lead author Dr Axel Newton focused on the question of when during development the Tasmanian tiger establish its dog-like skull shape.
“We know that the thylacine and wolf look similar as adults, but we don’t know when they started to exhibit their remarkable similarities during development,” he said.
Micro-CT scanning is a technique similar to a medical CAT scan, allowing researchers to generate high-resolution, digital reconstructions of complex shapes such as skulls and bones. From here they were able to establish that not only did the Tasmanian tiger resemble the wolf as adults but were very similar as newborns and juveniles.
Dr Vera Weisbecker, from Flinders University, said all marsupials – including the thylacine – are born with unusually well-developed jaws relative to the rest of the head.
“Scientists think that this reduces the potential of marsupials to evolve some extreme skull shapes. However, it clearly did not prevent the evolution of the thylacine’s unusual wolf-like skull!”
The University of Melbourne’s Dr Christy Hipsley, who specialises in CT, said the research shows how 3D imaging can reveal hidden diversity in nature.
“By comparing entire growth series from newborns to adults, we were able to visualise tiny differences in development that pinpoint when and where in the skull adaptations to carnivory arise on a cellular level. That is only made possible through museum loans of preserved specimens, in this case from as far away as Alaska.”
###
Media Contact
Lito Vilisoni Wilson
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.