Steady decline in acute cases reflects successful vaccination programmes
Credit: ECDC
In 2017, the majority (58%) of the almost 27 000 newly reported hepatitis B cases in the European Union and European Economic Area were classified as chronic infections. This follows a consistent upward trend in reported chronic hepatitis B cases since 2008.
There is evidence of on-going transmission of hepatitis B and continued importation of cases to many European countries according to the available surveillance data for countries of the European Union and the European Economic Area (EU/EEA) for 2017. Incomplete data as well as varying national surveillance systems and practices however impair more detailed epidemiological analysis of reported data.
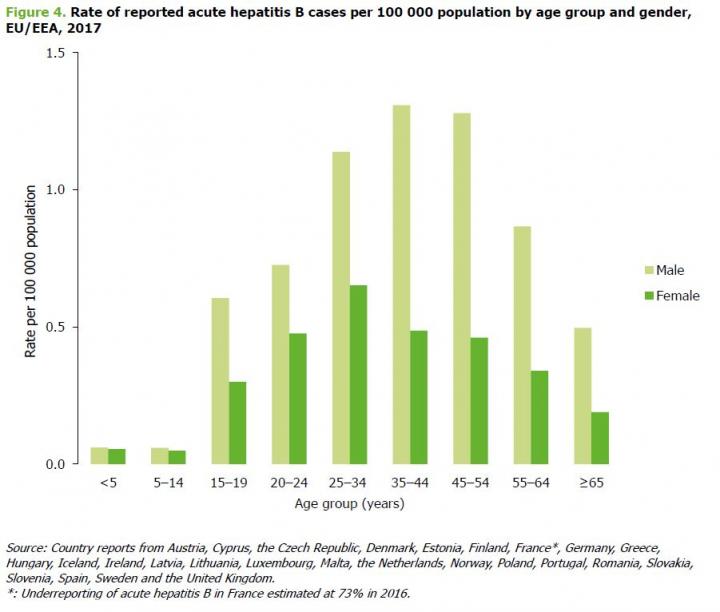
The majority of EU/EEA countries consistently reporting experienced a steady decline in newly reported acute hepatitis B infections from 1.1 per 100 000 population in 2008 to 0.6 in 2017. This reflects overall global trends and is most likely a result of successful national vaccination programmes: in these countries, the proportion of acute hepatitis B infections among people below 25 years of age declined from 20% in 2008 to 12% in 2017. The proportion of chronic cases under 25 declined from 21% in 2008 to 10% in 2017.
However, during the same time period notifications of chronic hepatitis B overall increased from 6.7 per 100 000 population to 10.2 in 2017 with the highest rates reported among the 25-34-year-olds. Overall, the reported data on chronic hepatitis B seems to mirror the intensity of local testing and screening policies – thus countries with comprehensive testing programmes in place appear to have the highest notification rates. The high number of chronic infections from northern Europe has a strong influence on trends with e.g. 62% of chronic hepatitis B cases in 2017 notified by the United Kingdom.
Incomplete data affects interpretation
Transmission data are key to understanding the epidemiology of hepatitis B. However, information on the transmission mode was only complete for roughly a third (29%) of the reported acute cases in 2017 and only 13% of the notified chronic cases. Hence, data are unlikely to be fully representative, and observed trends and differences between countries are hard to interpret.
For the 718 acute cases with complete information, heterosexual transmission was most commonly reported (27%), followed by nosocomial transmission (16%), sex between men (13%), non-occupational injuries (10%) and injecting drug use (10%). Italy, Poland and Romania accounted for 74% of the acute cases attributed to healthcare-associated hepatitis B infections in 2017.
Where this information was available, transmission from mother to child and in healthcare settings were the most commonly reported routes for chronic hepatitis B infection (41% and 28% respectively). Poland reported 90% of chronic cases related to nosocomial transmission.
Of the 12 018 cases (45%) with information on importation status, 3 778 (31%) were reported as imported. The influence of migration on hepatitis B epidemiology highlights the need for countries to develop evidence-based screening interventions that target the most affected migrant communities. It also highlights the importance of monitoring routine surveillance indicators of migration, such as importation status.
The relatively high number of 26 907 reported hepatitis B infections in 2017and especially chronic cases, in combination with the diversity in reported transmission routes across Europe suggest that countries need to maintain and strengthen local hepatitis prevention and control programmes.
The World Health Organization’s European Action plan for the health sector response to viral hepatitis outlines ways to do this. Based on the information from the ECDC prevalence database, authorities can identify the key population groups and areas of high hepatitis prevalence for targeted efforts.
###
Read the Annual Epidemiological report for 2017 – hepatitis C
http://bit.
ECDC hepatitis B Prevalence Database
https:/
ECDC Public health guidance on HIV, hepatitis B and C testing in the EU/EEA
http://bit.
ECDC-EMCDDA Guidance on prevention and control of blood-borne viruses in prison settings
http://bit.
Media Contact
ECDC press office
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




