A routine check revealed a previously undocumented behavior in the intestinal parasite
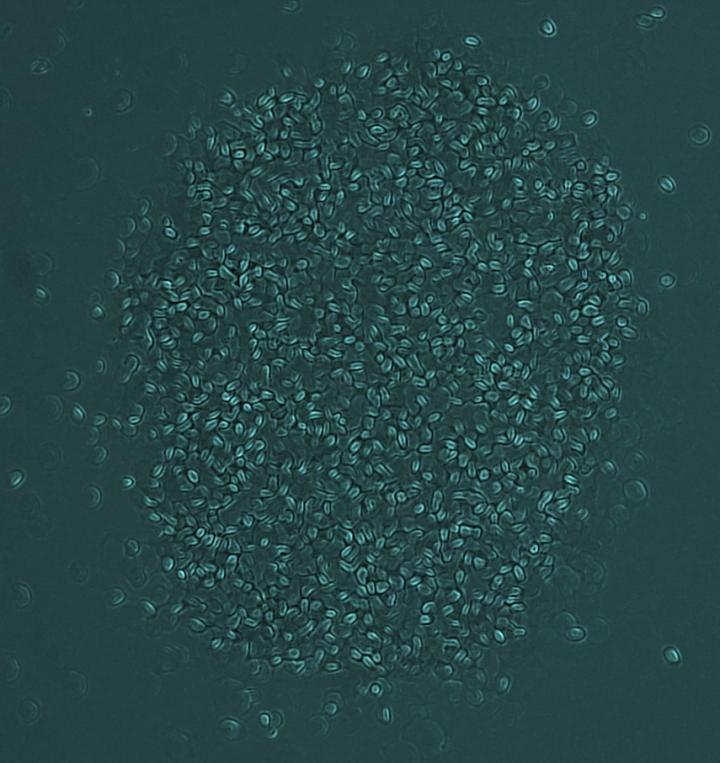
Credit: Sarah Poynton, Johns Hopkins Medicine
Johns Hopkins researchers have observed a previously unrecognized behavior in a single-celled parasite called Spironucleus vortens, which infects ornamental fish such as angelfish: The protozoans swarm.
Different species of Spironucleus infect other species of fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals, though this parasite family is not a threat to human health. One notorious member of the group is Spironucleus salmonicida, literally “salmon killer,” which can infect farmed salmon and turn their normally firm and tasty muscle to an unpalatable mush.
In a report published Nov. 23 in Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, the investigators suggest swarming behavior in Spironucleus vortens may have implications for better understanding the life cycle of the parasite, offer new avenues for control of infections, and may lead to the adoption of Spironucleus as a new laboratory model to study behavior in organisms that also use flagella — a microscopic, whiplike appendage — to swim. The movement of microswimmers, such as flagellated bacteria (one species of which causes urinary tract infections in humans) and flagellated protozoa, is currently of great interest to a variety of scientists.
Typically, the pear-shaped Spironucleus vortens parasites swim rapidly and individually in the lab, where researchers study them in drug development. However, when triggered to swarm, the flagellates accelerate and condense into a swarm measuring 200 to 900 micrometers across — or varying in size from half to twice the size of the period at the end of this sentence. The writhing spherical mass of organisms moves in a highly coordinated fashion. The swarms form and disperse spontaneously and unpredictably.
“The traveling swarm looks similar to a tumbleweed’s motion, moving in a single direction,” says Poynton. “And the individuals in the swarm remain in the group until the swarm disperses.”
The cohesive movement of the group indicates that there are interactions between the flagellates. Such behavior requires that organisms sense their surrounding conditions, interact with their neighbors and respond as a group — all behaviors that are akin to the swarming of insects, schooling of fish and flocking of birds.
“I have studied Spironucleus species for 20 years and have not seen this behavior described before,” says Sarah Poynton, Ph.D., associate professor of molecular and comparative pathobiology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, and lead author of the study.
The swarming, Poynton notes, is an intriguing behavior for these tiny flagellates because it may be a previously unappreciated contributing factor to the parasite’s life cycle and perhaps could be exploited for novel treatments to control the spread of this and similar infections.
###
VIDEO: Molecular and Comparative Pathobiology
Other researchers involved in the study include Lauren Ostrenga and Kenneth W. Witwer of the Department of Molecular and Comparative Pathobiology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
Media Contact
Rachel Butch
[email protected]
410-955-8665
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




