Innovative method provides new insight into molecular processes involving RNA
Credit: Heidelberg University/Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is key to various fundamental biological processes. It transfers genetic information, translates it into proteins or supports gene regulation. To achieve a more detailed understanding of the precise functions it performs, researchers based at Heidelberg University and at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have devised a new fluorescence imaging method which enables live-cell RNA imaging with unprecedented resolution.
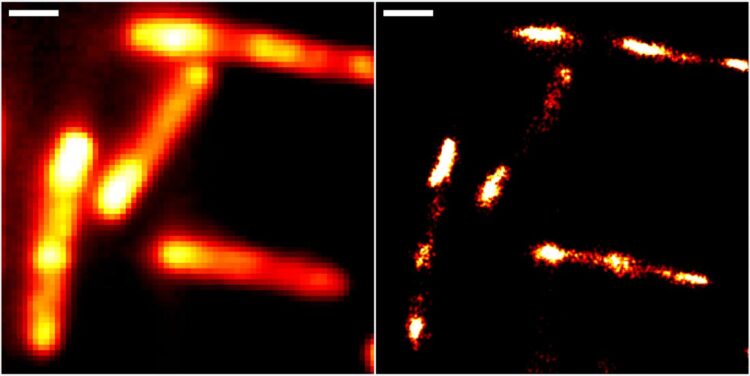
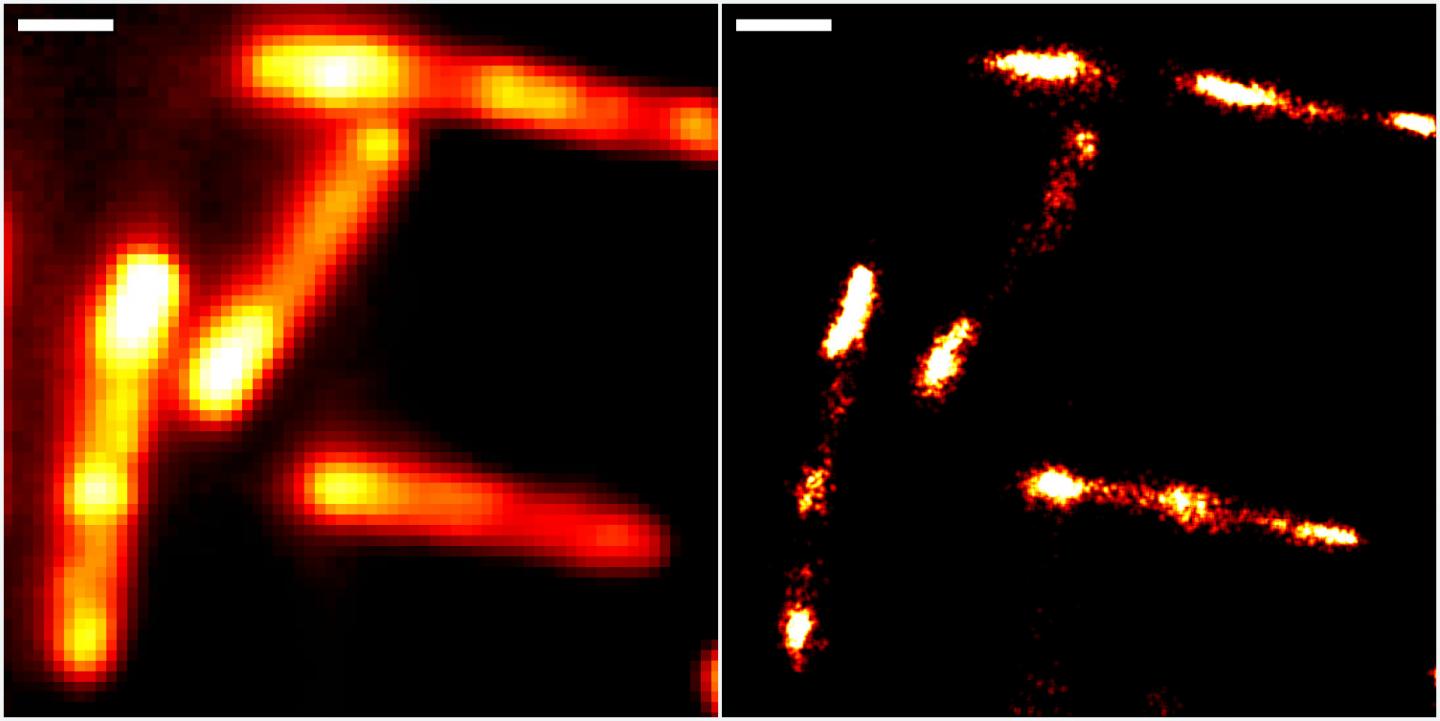
The method is based on a novel molecular marker called Rhodamine-Binding Aptamer for Super-Resolution Imaging Techniques (RhoBAST). This RNA-based fluorescence marker is used in combination with the dye rhodamine. Due to their distinctive properties, marker and dye interact in a very specific way, which makes individual RNA molecules glow. They can then be made visible using single-molecule localisation microscopy (SMLM), a super-resolution imaging technique. Due to a lack of suitable fluorescence markers, direct observation of RNA via optical fluorescence microscopy has been severely limited to date.
RhoBAST was developed by researchers from the Institute of Pharmacy and Molecular Biotechnology (IPMB) at Heidelberg University and the Institute of Applied Physics (APH) at KIT. The marker created by them is genetically encodable, which means that it can be fused to the gene of any RNA produced by a cell. RhoBAST itself is non-fluorescent, but lights up a cell-permeable rhodamine dye by binding to it in a very specific way. “This leads to a dramatic increase in fluorescence achieved by the RhoBAST-dye complex, which is a key requirement for obtaining excellent fluorescence images,” explains Dr Murat Sunbul from the IPMB, adding: “However, for super-resolution RNA imaging the marker needs additional properties.”
The researchers discovered that each rhodamine dye molecule remains bound to RhoBAST for approximately one second only before becoming detached again. Within seconds, this procedure repeats itself with a new dye molecule. “It is quite rare to find strong interactions – as between RhoBAST and rhodamine – combined with exceptionally fast exchange kinetics,” says Prof. Dr Gerd Ulrich Nienhaus from the APH. Since rhodamine only lights up after binding to RhoBAST, the constant string of newly emerging interactions between marker and dye results in incessant “blinking”. “This ‘on-off switching’ is exactly what we need for SMLM imaging,” continues Prof. Nienhaus.
At the same time, the RhoBAST system solves yet another important problem. Fluorescence images are collected under laser light irradiation, which destroys the dye molecules over time. The fast dye exchange ensures that photobleached dyes are replaced by fresh ones. This means that individual RNA molecules can be observed for longer periods of time, which can greatly improve image resolution, as Prof. Dr Andres Jaeschke, a scientist at the IPMB, explains.
The researchers from Heidelberg and Karlsruhe were able to demonstrate the superb properties of RhoBAST as an RNA marker by visualising RNA structures inside gut bacteria (Escherichia coli) and cultured human cells with excellent localisation precision. “We can reveal details of previously invisible subcellular structures and molecular interactions involving RNA using super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. This will enable a fundamentally new understanding of biological processes,” says Prof. Jaeschke.
###
The research carried out by Murat Sunbul and Andres Jaeschke in the context of the study was supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the work performed by Gerd Ulrich Nienhaus was supported by the DFG and the Helmholtz Association. The results were published in the journal Nature Biotechnology.
Media Contact
Andres Jaeschke
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.