NIH scientists discover that the resting brain repeatedly replays compressed memories of what was just practiced
In a study of healthy volunteers, National Institutes of Health researchers have mapped out the brain activity that flows when we learn a new skill, such as playing a new song on the piano, and discovered why taking short breaks from practice is a key to learning. The researchers found that during rest the volunteers’ brains rapidly and repeatedly replayed faster versions of the activity seen while they practiced typing a code. The more a volunteer replayed the activity the better they performed during subsequent practice sessions, suggesting rest strengthened memories.
“Our results support the idea that wakeful rest plays just as important a role as practice in learning a new skill. It appears to be the period when our brains compress and consolidate memories of what we just practiced,” said Leonardo G. Cohen, M.D., senior investigator at the NIH’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) and the senior author of the study published in Cell Reports. “Understanding this role of neural replay may not only help shape how we learn new skills but also how we help patients recover skills lost after neurological injury like stroke.”
The study was conducted at the NIH Clinical Center. Dr. Cohen’s team used a highly sensitive scanning technique, called magnetoencephalography, to record the brain waves of 33 healthy, right-handed volunteers as they learned to type a five-digit test code with their left hands. The subjects sat in a chair and under the scanner’s long, cone-shaped cap. An experiment began when a subject was shown the code “41234” on a screen and asked to type it out as many times as possible for 10 seconds and then take a 10 second break. Subjects were asked to repeat this cycle of alternating practice and rest sessions a total of 35 times.
During the first few trials, the speed at which subjects correctly typed the code improved dramatically and then leveled off around the 11th cycle. In a previous study, led by former NIH postdoctoral fellow Marlene Bönstrup, M.D., Dr. Cohen’s team showed that most of these gains happened during short rests, and not when the subjects were typing. Moreover, the gains were greater than those made after a night’s sleep and were correlated with a decrease in the size of brain waves, called beta rhythms. In this new report, the researchers searched for something different in the subjects’ brain waves.
“We wanted to explore the mechanisms behind memory strengthening seen during wakeful rest. Several forms of memory appear to rely on the replaying of neural activity, so we decided to test this idea out for procedural skill learning,” said Ethan R. Buch, Ph.D., a staff scientist on Dr. Cohen’s team and leader of the study.
To do this, Leonardo Claudino, Ph.D., a former postdoctoral fellow in Dr. Cohen’s lab, helped Dr. Buch develop a computer program which allowed the team to decipher the brain wave activity associated with typing each number in the test code.
The program helped them discover that a much faster version – about 20 times faster – of the brain activity seen during typing was replayed during the rest periods. Over the course of the first eleven practice trials, these compressed versions of the activity were replayed many times – about 25 times – per rest period. This was two to three times more often than the activity seen during later rest periods or after the experiments had ended.
Interestingly, they found that the frequency of replay during rest predicted memory strengthening. In other words, the subjects whose brains replayed the typing activity more often showed greater jumps in performance after each trial than those who replayed it less often.
“During the early part of the learning curve we saw that wakeful rest replay was compressed in time, frequent, and a good predictor of variability in learning a new skill across individuals,” said Dr. Buch. “This suggests that during wakeful rest the brain binds together the memories required to learn a new skill.”
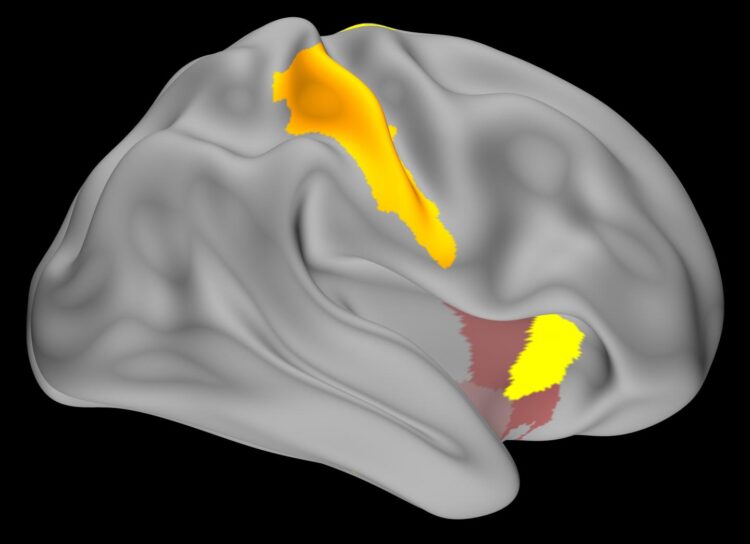
As expected, the team discovered that the replay activity often happened in the sensorimotor regions of the brain, which are responsible for controlling movements. However, they also saw activity in other brain regions, namely the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex.
“We were a bit surprised by these last results. Traditionally, it was thought that the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex may not play such a substantive role in procedural memory. In contrast, our results suggest that these regions are rapidly chattering with the sensorimotor cortex when learning these types of skills,” said Dr. Cohen. “Overall, our results support the idea that manipulating replay activity during waking rest may be a powerful tool that researchers can use to help individuals learn new skills faster and possibly facilitate rehabilitation from stroke.”
###
Article:
Buch et al., Consolidation of human skill linked to waking hippocampo-neocortical replay, Cell Reports, June 8, 2021, DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109193
This study was supported by the NIH Intramural Research Program at the NINDS.
For more information:
http://www.
http://www.
http://www.
irp.nih.gov/
clinicalcenter.nih.gov/
neuroscience.nih.gov/ninds/Home.aspx
dir.ninds.nih.gov/ninds/Home.html
NINDS is the nation’s leading funder of research on the brain and nervous system. The mission of NINDS is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.
Media Contact
Christopher Thomas
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.