A paper saw light in Behavioural Brain Research.
Homocysteine (HCY) is a sulfur-containing aminoacid, which attract more and more attention as the increase of homocysteine level associates with a number of pathological conditions. Hyperhomocysteinemia (hHCY) is an elevation of HCY level in plasma and develops due to genetic mutations of enzymes involved in regulation of HCY metabolism, nutritional deficiencies of vitamins B12, B6 and folate; chronic renal failure; alcoholism, smoking, excess coffee consumption, hypothyroidism; taking a number of medications like antiepileptic drugs and LDOPA; and aging. hHcy is a well-known independent risk factor for cardio-vascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and associated with common pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia, and adverse pregnancy outcomes. High level of oxidative stress was shown in brain tissues of rodents in the model of hHCY.
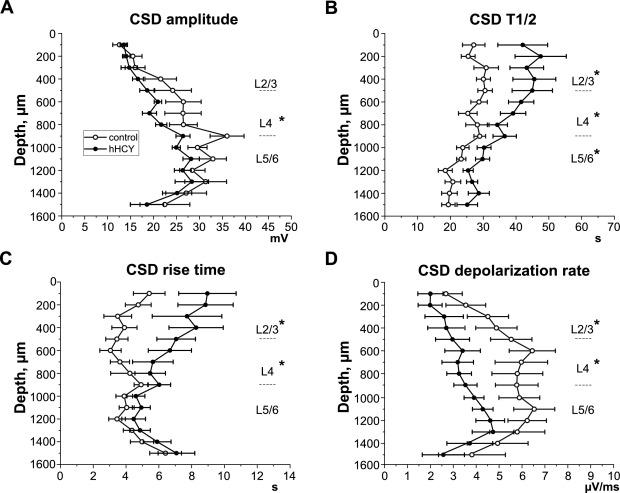
Population studies suggested a link between migraine and HCY level, especially migraine with aura; however, there is no evidence of this link in animal studies. Migraine is a disabling neurovascular disorder, characterized mainly by unilateral pulsating headache and several neurological symptoms, including hypersensitivity to light known as photophobia, which is one of the leading symptoms of migraine. Moreover, migraine sufferers often acquire various autonomic, cognitive and emotional dysfunctions, including depression and anxiety. About a third of migraine patients complain of transient aura symptoms starting from minutes to hours before the headache or during the headache phase. Cortical spreading depression is a slowly propagating wave of transient neuronal and glial depolarization – an electrical phenomenon of the brain underlies the migraine with aura. In this study, the team used the model of prenatal hHCY to evaluate the sensitivity of rats to cortical spreading depression and behavioral features of migraine. Electrophysiological data indicated that rats with an elevated plasma level of HCY have a higher susceptibility to the development of the cortical spreading depression. Moreover, in the behavioral tests, the authors revealed typical migraine related symptoms in rats with hHCY, such as mechanical allodynia, photophobia and higher anxiety. Taken together, the findings support a link between HCY and migraine with aura; this suggests that timely correction of the elevated HCY level in persons from higher risk groups may be beneficial for treatment.
The study is part of a project related to the investigation of the etiology of migraine. Using experimental animal models, one can reveal mechanisms underlying the excitability of the brain cortex and peripheral afferents innervating the meninges, which triggers migraine attacks. Moreover, the search for endogenous factors provoking migraines will help to develop strategies for the correction of pathological conditions.
The researchers plan to analyze sensitivity of rats with hHCY in nitroglycerine-induced hyperalgesia, photophobia and anxiety, which is widely used to imitate migraine symptoms in rodents. To reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying the higher susceptibility of rats with hHCY to migraine-like symptoms, they will assess the excitability of the peripheral part of the trigeminal system, including recordings of the electrical activity of trigeminal nerve and the membrane properties of isolated trigeminal neurons. Finally, the authors will develop and test strategies for correcting high homocysteine levels, such as administrating vitamins of the B group or antioxidants.
###
Media Contact
Yury Nurmeev
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.