Your new apartment is just a couple of blocks down the street from the bus stop but today you are late and you see the bus roll past you. You break into a full sprint. Your goal is to get to the bus as fast as possible and then to stop exactly in front of the doors (which are never in exactly the same place along the curb) to enter before they close. To stop quickly and precisely enough, a new MIT study in mice finds, the mammalian brain is niftily wired to implement principles of calculus.
Credit: Elie Adam/MIT Picower Institute
Your new apartment is just a couple of blocks down the street from the bus stop but today you are late and you see the bus roll past you. You break into a full sprint. Your goal is to get to the bus as fast as possible and then to stop exactly in front of the doors (which are never in exactly the same place along the curb) to enter before they close. To stop quickly and precisely enough, a new MIT study in mice finds, the mammalian brain is niftily wired to implement principles of calculus.
One might think that coming to a screeching halt at a target after a flat out run would be as simple as a reflex, but catching a bus or running right up to a visually indicated landmark to earn a water reward (as the mice did), is a learned, visually guided, goal-directed feat. In such tasks, which are a major interest in the lab of senior author Mriganka Sur, Newton Professor of Neuroscience in The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT, the crucial decision to switch from one behavior (running) to another (stopping) comes from the brain’s cortex, where the brain integrates the learned rules of life with sensory information to guide plans and actions.
“The goal is where the cortex comes in,” said Sur, a faculty member of MIT’s Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences. “Where am I supposed to stop to achieve this goal of getting on the bus.”
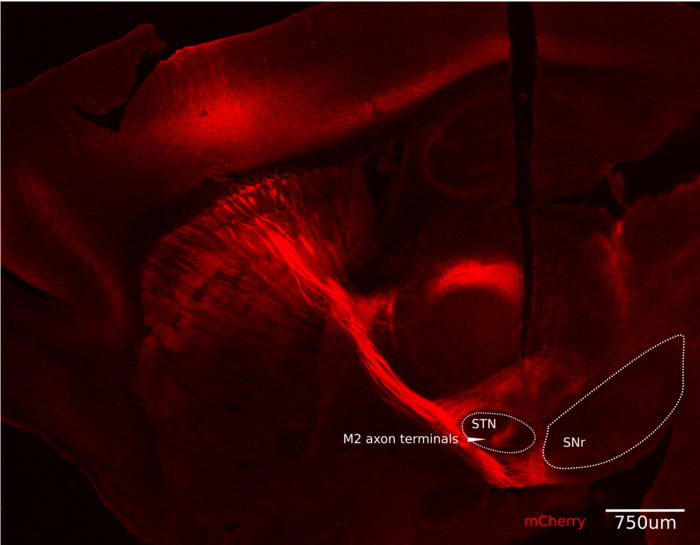
And that’s also where it gets complicated. The mathematical models of the behavior that postdoc and study lead author Elie Adam developed predicted that a “stop” signal going directly from the M2 region of the cortex to regions in the brainstem, which actually control the legs, would be processed too slowly.
“You have M2 that is sending a stop signal, but when you model it and go through the mathematics, you find that this signal, by itself, would not be fast enough to make the animal stop in time,” said Adam, whose work appears in the journal Cell Reports.
So how does the brain speed up the process? What Adam, Sur and co-author Taylor Johns found was that M2 sends the signal to an intermediary region called the subthalamic nucleus (STN), which then sends out two signals down two separate paths that re-converge in the brainstem. Why? Because the difference made by those two signals, one inhibitory and one excitatory, arriving one right after the other turns the problem from one of integration, which is a relatively slow adding up of inputs, to differentiation, which is a direct recognition of change. The shift in calculus implements the stop signal much more quickly.
Adam’s model employing systems and control theory from engineering—accurately—predicted the speed needed for a proper stop and that differentiation would be necessary to achieve it, but it took a series of anatomical investigations and experimental manipulations to confirm the model’s predictions.
First, Adam confirmed that indeed M2 was producing a surge in neural activity only when the mice needed to achieve their trained goal of stopping at the landmark. He also showed it was sending the resulting signals to the STN. Other stops for other reasons did not employ that pathway. Moreover, artificially activating the M2-STN pathway compelled the mice to stop and artificially inhibiting it caused mice overrun the landmark somewhat more often.
The STN certainly then needed to signal the brainstem—specifically the pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN) in the mesenecephalic locomotor region. But when the scientists looked at neural activity starting in the M2 and then quickly resulting in the PPN, they saw that different types of cells in the PPN responded with different timing. Particularly, before the stop, excitatory cells were active and their activity reflected the speed of the animal during stops. Then, looking at the STN, they saw two kinds of surges of activity around stops—one slightly slower than the other—that were conveyed either directly to PPN through excitation or indirectly via the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr) through inhibition. The net result of the interplay of these signals in the PPN was an inhibition sharpened by excitation. That sudden change could be quickly found by differentiation to implement stopping.
“An inhibitory surge followed by excitation can create a sharp [change of] signal,” Sur said.
The study dovetails with other recent papers. Working with Picower Institute investigator Emery N. Brown, Adam recently produced a new model of how deep brain stimulation in the STN quickly corrects motor problems that result from Parkinson’s disease. And last year members of Sur’s lab, including Adam, published a study showing how the cortex overrides the brain’s more deeply ingrained reflexes in visually guided motor tasks. Together such studies contribute to understanding how the cortex can consciously control instinctually wired motor behaviors but also how important deeper regions, such as the STN, are to quickly implementing goal-directed behavior. A recent review from the lab expounds on this.
Adam speculated that the “hyperdirect pathway” of cortex-to-STN communications may have a role broader than quickly stopping action, potentially expanding beyond motor control to other brain functions such as interruptions and switches in thinking or mood.
The JPB Foundation, the National Institutes of Health and the Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative funded the study.
Journal
Cell Reports
DOI
10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111139
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Dynamic control of visually-guided locomotion through cortico-subthalamic projections
Article Publication Date
26-Jul-2022




