Credit: University of Warwick
Flash sintering is a ceramic processing technique which uses electric current to intensively heat the ceramic sample internally rather than using only external furnace heating. The process can lower ceramic processing temperatures and durations significantly, enabling ceramics to be co-processed with metals or other materials, and reducing energy use.
- However, the process can result in low quality ceramics due to weaknesses caused by inhomogeneities in the microstructure.
- The origins of these inhomogeneities caused by thermal gradients in the material during flash sintering have been studied by researchers based at WMG, University of Warwick and academic and industrial collaborators, and routes to mitigate the effects of these gradients are outlined.
- Adopting these modified flash sintering routes will enable the wider use of flash sintering in ceramic processing, enabling lower energy production of many useful ceramic products including solid-state batteries.
Densifying ceramics using flash sintering reduces energy use and may be used to improve the viability of manufacturing complex ceramic structures such as those required for solid state batteries by lowering the temperatures and shortening the duration of the heat treatment.
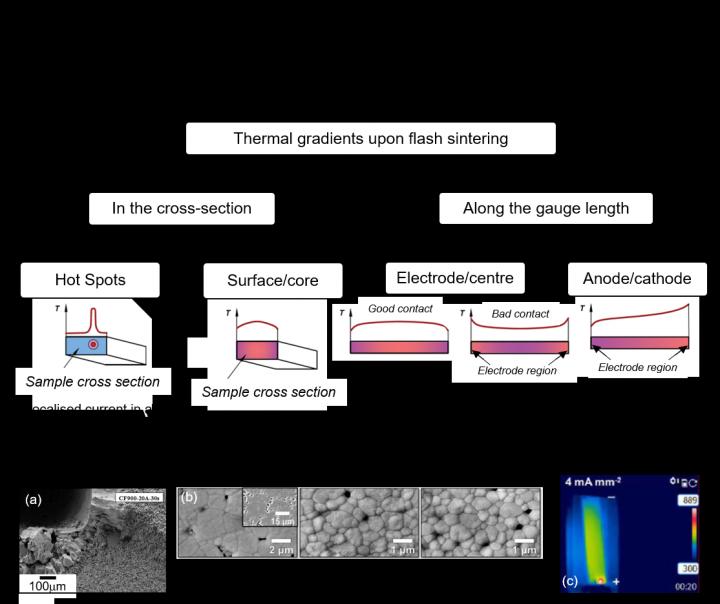
Caption: Causes and Effects of thermal and microstructural gradients in flash sintered ceramics. Credit: WMG, University of Warwick
Working in collaboration with academic and industrial partners, researchers from WMG, University of Warwick have published a review of the state of the art of flash sintering focusing on the formation of inhomogeneous regions within the ceramics which currently limit the scale-up potential of flash sintering. The review finds that thermal gradients are responsible for microstructural inhomogeneities and suggests of routes to eliminate or reduce these effects.
The reduction of energy use in the ceramic manufacturing industry is a key step in meeting global emissions reduction targets, as conventional processes require long firing treatments at very high temperatures. Several low-energy processes have been developed over the past decade, with flash sintering emerging as a particularly promising route for densification of materials for use in applications including solid state batteries, thermal barrier coatings, and ceramic joints.
In the paper, ‘Promoting microstructural homogeneity during flash sintering of ceramics through thermal management’ published as part of a special issue of the MRS Bulletin, Gareth Jones and Dr Claire Dancer from WMG, University of Warwick worked with collaborators from the University of Trento, Wuhan University of Technology, Normandie Université, and Lucideon Ltd to review the origins of microstructural variations in different regions of ceramic materials undergoing flash sintering.
Caption: Microstructural development changes with different sintering approaches. Flash sintering produces fine microstructures with very high density with lower energy use than conventional approaches. Credit: WMG, University of Warwick
Differences in microstructural development originate from thermal gradients within the material during processing, and these can be reduced by careful thermal management during the flash sintering process. These include:
- Altering the method for applying electrodes
- Improving thermal homogeneity through insulation
- Tailoring the frequency of the AC current
- Developing contactless methods for applying the electric current – which are currently limited to consolidation of thermal barrier coatings.Caption: Simulation of heat distribution during flash sintering. Credit: WMG, University of Warwick
The findings of this review provide a roadmap for further research on thermal management in flash sintering, which will accelerate the development of the process for industrial implementation.
Dr Claire Dancer, leader of the Ceramics Group within the Materials and Sustainability Directorate at WMG, University of Warwick comments:
“Lowering ceramic processing temperatures by using techniques such as flash sintering is an essential step for manufacturing complex multi-material structures such as those needed for solid-state batteries, and for lowering overall energy use in the ceramic industry.
“However, the process must produce robust homogenous ceramic materials to be of widespread use. Our paper explains why flash sintering can result in inhomogeneous properties in ceramics and suggests a number of routes to mitigate these effects.”
###
Media Contact
Alice Scott
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




