Mainz University Medical Center uncovers new insights into the effects of food nanoparticles on the intestinal flora
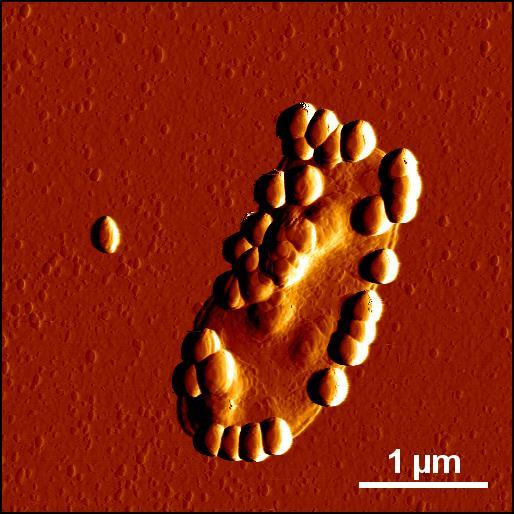
Credit: source: Stauber Group, Mainz University Medical Center
The intestinal microbiome is not only key for food processing but an accepted codeterminant for various diseases. Researchers led by the University Medical Center of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) identified effects of nanoparticles on intestinal microorganisms. The ultra-small particles adhere to intestinal microorganisms, thereby affecting their life cycle as well as cross talk with the host. One of the researchers’ observations was that nanoparticles’ binding inhibits the infection with Helicobacter pylori, a pathogen implicated in gastric cancer. The findings will stimulate further epidemiological studies and pave the way for the development of potential ‘probiotic’ nanoparticles for food. The discoveries were published in Science of Food.
Due to their minute size, nanoparticles have unique characteristics and capabilities, such as adhering to microstructures. Nanotechnology is as an important driver of innovation for both consumer industry and medicine. In medicine, the focus is on improving diagnostics and therapeutics, while industry addresses mainly product optimization. Hence, synthetic nanoparticles are already used as additives to improve the characteristics of food. But how can we use nanotechnology more efficiently and safely in food? And are there unknown effects of nanoparticles, which need to be further exploited?
Nutrition strongly influences the diversity and composition of our microbiome. ‘Microbiome’ describes all colonizing microorganisms present in a human being, in particular, all the bacteria in the gut. In other words, your microbiome includes your intestinal flora as well as the microorganisms that colonize your skin, mouth, and nasal cavity.
Scientists and clinicians are interested in microbiomes because of their positive or negative effects on the host. These include modulation of our immune system, metabolism, vascular aging, cerebral functioning, and our hormonal system. The composition of the microbiome seems to play an important role for the development of various disorders, such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer, allergies, obesity, and even mental disorders. “Hence, nutrition and its containing nanoparticulates may affect the microbiome-host balance, finally influencing human health. In order to reduce potential risks and, ideally, promote health, the impact of dietary nanoparticles needs to be understood,” emphasized Professor David J. McClements from the Department of Food Science at the University of Massachusetts in Amherst, USA.
“Prior to our studies, nobody really looked whether and how nano-additives directly influence the gastrointestinal flora,” commented Professor Roland Stauber of the Department of Otolaryngology, Head, and Neck Surgery at the Mainz University Medical Center. “Hence, we studied at a wide range of technical nanoparticles with clearly defined properties in order to mimic what happens to currently used or potential future nanosized food additives. By simulating the journey of particles through the different environments of the digestive tract in the laboratory, we found that the all tested nanomaterials were indeed able to bind to bacteria.” explained Stauber.
The scientists discovered that these binding processes can have different outcomes. On the one hand, nanoparticle-bound microorganisms were less efficiently recognized by the immune system, which may lead to increased inflammatory responses. On the other hand, ‘nano-food’ showed beneficial effects. In cell culture models, silica nanoparticles inhibited the infectivity of Helicobacter pylori, which is considered to be one of the main agents involved in gastric cancer.
‘It was puzzling that we were able to also isolate naturally occurring nanoparticles from food, like beer, which showed similar effects. Nanoparticles in our daily food are not just those added deliberately but can also be generated naturally during preparation. Nanoparticulates are already omnipresent,” concluded Stauber.
The insights of the study will allow to derive strategies for developing and utilizing synthetic or natural nanoparticles to modulate the microbiome as beneficial ingredients in functional foods. “The challenge is to identify nanoparticles that fit the desired purpose, perhaps even as probiotic food supplements in the future. Challenge accepted,” emphasized Stauber and his team.
###
Media Contact
Dr. Roland H. Stauber
[email protected]
49-613-117-6030
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




