Credit: ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces
Virtually all digital devices that perform any sort of processing of information require not only a processing unit, but also a quick memory that can temporarily hold the inputs, partial results, and outputs of the operations performed. In computers, this memory is referred to as dynamic random-access memory, or DRAM. The speed of DRAM is very important and can have a significant impact in the overall speed of the system. In addition, lowering the energy consumption of memory devices has recently become a hot topic to achieve highly energy-efficient computing. Therefore, many studies have focused on testing out new memory technologies to surpass the performance of conventional DRAM.
The most basic unit in a memory chip are its memory cells. Each cell typically stores a single bit by adopting and holding one of two possible voltage values, which correspond to a stored value of either “0” or “1”. The characteristics of the individual cell largely determine the performance of the overall memory chip. Simpler and smaller cells with high speed and low energy consumption would be ideal to take highly efficient computing to the next level.
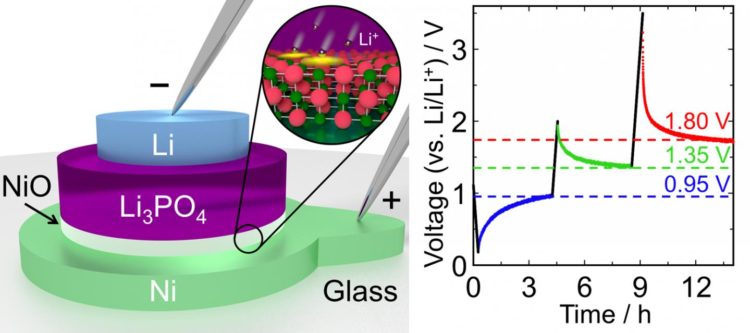
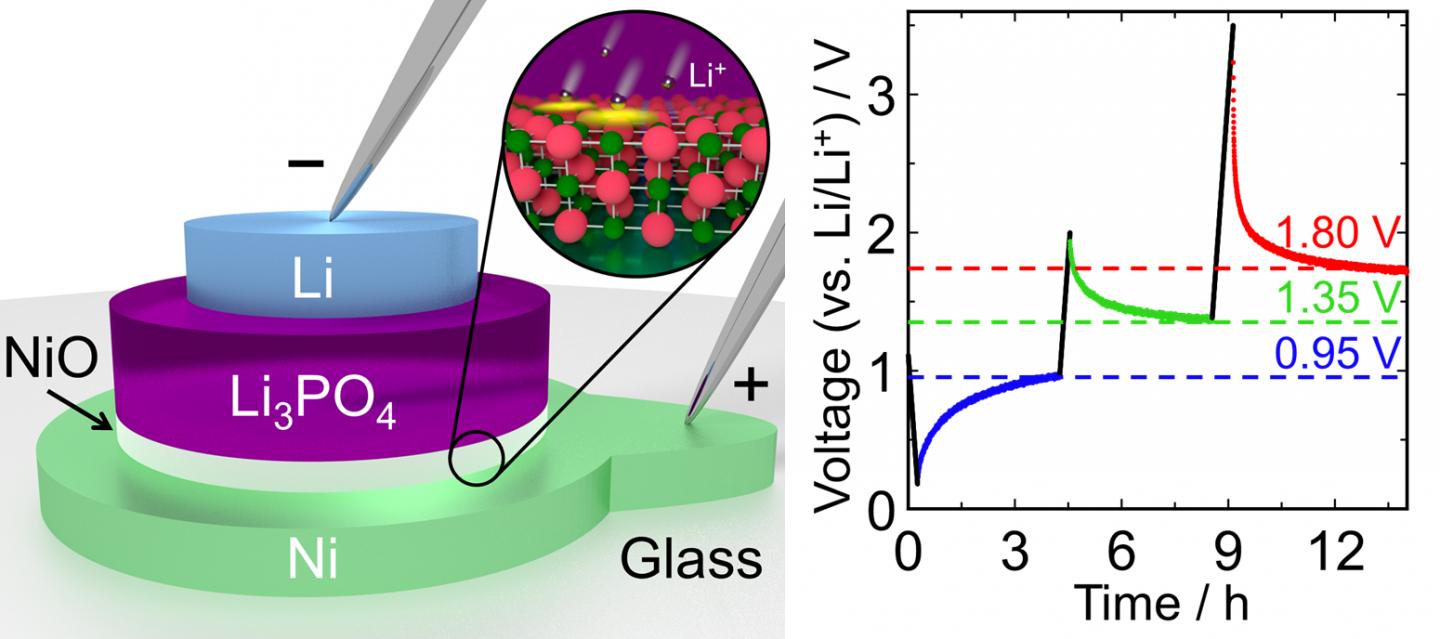
A research team from Tokyo Tech led by Prof. Taro Hitosugi and student Yuki Watanabe recently reached a new milestone in this area. These researchers had previously developed a novel memory device inspired by the design of solid lithium-ion batteries. It consisted of a stack of three solid layers made of lithium, lithium phosphate, and gold. This stack is essentially a miniature low-capacity battery that functions as a memory cell; it can be quickly switched between charged and discharged states that represent the two possible values of a bit. However, gold combines with lithium to form a thick alloy layer, which increases the amount of energy required to switch from one state to the other.
In their latest study, the researchers created a similar three-layer memory cell using nickel instead of gold. They expected better results using nickel because it does not easily form alloys with lithium, which would lead to lower energy consumption when switching. The memory device they produced was much better than the previous one; it could actually hold three different voltage states instead of two, meaning that it is a three-valued memory device. “This system can be viewed as an extremely low-capacity thin-film lithium battery with three charged states,” explains Prof. Hitosugi. This is a very interesting feature that has potential advantages for three-valued memory implementations, which may be more area efficient.
The researchers also found that nickel forms a very thin nickel oxide layer between the Ni and the lithium phosphate layers (see Fig. 1), and this oxide layer is essential for the low-energy switching of the device. The oxide layer is much thinner than that of the gold-lithium alloys that formed in their previous device, which means that this new “mini-battery” cell has a very low capacity and is therefore quickly and easily switched between states by applying minuscule currents. “The potential for extremely low energy consumption is the most noteworthy advantage of this device,” remarks Prof. Hitosugi.
Increased speed, lower energy consumption, and smaller size are all highly demanded features in future memory devices. The memory cell developed by this research team is a very promising stepping stone toward much more energy-efficient and faster computing.
###
Media Contact
Kazuhide Hasegawa
[email protected]
81-357-342-975
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.