Credit: Skoltech
Scientists from Russia and Germany studied the molecular composition of carbonaceous chondrites – the insoluble organic matter of the Murchison and Allende meteorites – in an attempt to identify their origin. Ultra-high resolution mass spectrometry revealed a wide diversity of chemical compositions and unexpected similarities between meteorites from different groups. The research was published in the Scientific Reports.
Carbonaceous chondrites contain nearly the entire spectrum of organic molecules encountered on Earth, including nucleic acids which might have played a pivotal role in the origin of life. Since the majority of modern meteorites are of nearly the same age as the Earth, their composition should be similar to that of meteorites that bombarded the Earth’s surface in ancient times. Just like comets, they can be considered a source of organic compounds which most likely formed the core of the Earth’s biosphere.
According to Skoltech Senior Research Scientist Alexander Zherebker, “the geological history of the Earth is a continuous process that involves division and transformation (biological or otherwise) of the Solar System’s primary matter. What remains of that matter ends up on Earth in the form of chondrites. However, two centuries of research on the organic matter of meteorites fall short of a full picture of its molecular composition: for instance, there is no systematic data on insoluble organic matter of meteorites which may account for up to 70% of all organic carbon in the samples. Presumably, these substances have much higher molecular complexity than suggested by research focusing on particular classes of organic compounds.”
Scientists from Skoltech, Moscow State University, Vernadsky Institute of Geochemistry and Analytical Chemistry of RAS, and the Rostock Institute (Germany) applied ultra-high resolution mass spectrometry methods to study the composition of meteorites. The Skoltech team included researchers from the Mass Spectrometry Laboratory at the Skoltech Center for Computational and Data-Intensive Science and Engineering (CDISE): Alexander Zherebker, Yury Kostyukevich, Alexey Kononikhin, and Oleg Kharybin. The research was led by Skoltech Professor Evgeny Nikolaev, Corresponding Member of RAS, Doctor of Physics and Mathematics, Head of the Mass Spectrometry Laboratory.
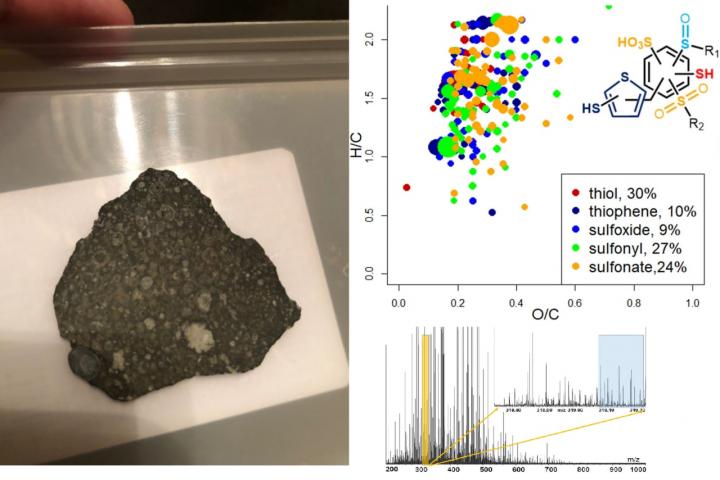
The team discovered an amazing molecular diversity in the insoluble organic matter of carbonaceous chondrites. “Considering that meteorites and the Earth are of similar age, we can argue that the organic matter of carbonaceous chondrites could have been the source of chemical compounds which served as building blocks for biological molecules and life on Earth. However, meteorite composition has nothing to do with living matter, which is evidenced, for example, by totally different oxidative profiles of extraterrestrial organic matter and a similar fraction of coal of biological origin. That is to say, meteorites showed no signs of “selection” of compounds,” Alexander Zherebker comments.
The analysis of carbonaceous chondrite extracts by isotopic exchange mass spectrometry revealed the presence of sulfur-containing compounds with all possible oxidation states from -2 to +6, which was in no way related to the sample’s thermal history, as previously thought. The relative content of these compounds was the only difference, as confirmed by the Murchison and Allende samples.
The team’s findings suggest that the precursors which created different celestial bodies produced similar organic matter which later transformed in various ways, depending on the environment and its various effects.
###
Skoltech is a private international university located in Russia. Established in 2011 in collaboration with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Skoltech is cultivating a new generation of leaders in the fields of science, technology, and business is conducting research in breakthrough fields and is promoting technological innovation with the goal of solving critical problems that face Russia and the world. Skoltech is focusing on six priority areas: data science and artificial intelligence, life sciences, advanced materials and modern design methods, energy efficiency, photonics, and quantum technologies, and advanced research. Web: https:/
Media Contact
Ilyana Zolotareva
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




