Researchers working at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have captured the first X-ray portraits of living bacteria.
This milestone, reported in the Feb. 11 issue of Nature Communications, is a first step toward possible X-ray explorations of the molecular machinery at work in viral infections, cell division, photosynthesis and other processes that are important to biology, human health and our environment. The experiment took place at SLAC’s Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) X-ray laser, a DOE Office of Science User Facility.
“We have developed a unique way to rapidly explore, sort and analyze samples, with the possibility of reaching higher resolutions than other study methods,” said Janos Hajdu, a professor of biophysics at Uppsala University in Sweden, which led the research. “This could eventually be a complete game-changer.”
Photo Albums on the Fly
The experiment focused on cyanobacteria, or blue-green algae, an abundant form of bacteria that transformed Earth’s atmosphere 2.5 billion years ago by releasing breathable oxygen, making possible new forms of life that are dominant today. Cyanobacteria play a key role in the planet’s oxygen, carbon and nitrogen cycles.
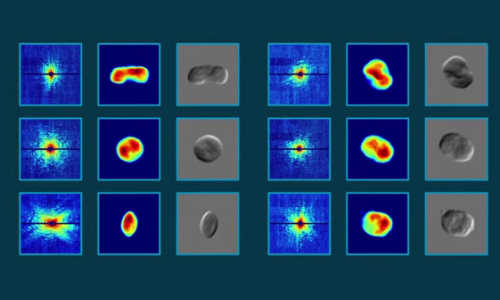
Researchers sprayed living cyanobacteria in a thin stream of humid gas through a gun-like device. The cyanobacteria were alive and intact when they flew into the ultrabright, rapid-fire LCLS X-ray pulses, producing diffraction patterns recorded by detectors.
The diffraction patterns preserved details of the living cyanobacteria that were compiled to reconstruct 2-D images. Researchers said it should be possible to produce 3-D images of some samples using the same technique.
The technique works with live bacteria and requires no special treatment of the samples before imaging. Other high-resolution imaging methods may require special dyes to increase the contrast in images, or work only on dead or frozen samples.
Biology Meets Big Data
The technique can capture about 100 images per second, amassing many millions of high-resolution X-ray images in a single day. This speed allows sorting and analysis of the inner structure and activity of biological particles on a massive scale, which could be arranged to show the chronological steps of a range of cellular activities.
In this way, the technique merges biology and big data, said Tomas Ekeberg, a biophysicist at Uppsala University. “You can study the full cycle of cellular processes, with each X-ray pulse providing a snapshot of the process you want to study,” he said.
Hajdu added, “One can start to analyze differences and similarities between groups of cellular structures and show how these structures interact: What is in the cell? How is it organized? Who is talking to whom?”
While optical microscopes and X-ray tomography can also produce high-resolution 3-D images of living cells, LCLS, researchers say, could eventually achieve much better resolution – down to fractions of a nanometer, or billionths of a meter, where molecules and perhaps even atoms can be resolved.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory.