Research from the California Institute of Technology shows exactly how antibodies stick to and block the Zika virus, which will inform vaccine development
Credit: Image courtesy of Shannon Esswein.
ROCKVILLE, MD – The Zika outbreak of 2015 and 2016 is having lasting impacts on children whose mothers became infected with the virus while they were pregnant. Though the numbers of Zika virus infections have dropped, which scientists speculate may be due to herd immunity in some areas, there is still potential for future outbreaks. To prevent such outbreaks, scientists want to understand how the immune system recognizes Zika virus, in hopes of developing vaccines against it. Shannon Esswein, a graduate student, and Pamela Bjorkman, a professor, at the California Institute of Technology, have new insights on how the body’s antibodies attach to Zika virus. Esswein will present the work, which was published in PNAS, on Thursday, February 25 at the 65th Biophysical Society Annual Meeting.
Zika virus is a kind of flavivirus, and other flavivirus family members include dengue, West Nile, and yellow fever virus. To protect against these and other pathogens, “we have the ability to make a huge diversity of antibodies, and if we get infected or vaccinated, those antibodies recognize the pathogen,” Esswein said. But sometimes when the body mounts an immune response against a flavivirus, there is concern that this response could make the person sicker if they get infected a second time. Called antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE), this happens when the antibodies stick to the outside of the virus without blocking its ability to infect cells, which can inadvertently help the virus infect more cells by allowing it enter cells that the antibodies stick to.
In order to prevent ADE when creating a vaccine, it’s crucial for scientists to have a detailed understanding of how antibodies stick to a specific virus. This is especially important for flaviviruses, because antibodies that protect against one flavivirus may also stick to, but not protect against other flavivirus, increasing the risk of ADE. There is a concern that antibodies generated in response to a Zika virus vaccine could trigger ADE if someone were to be later infected with dengue or other flaviviruses.
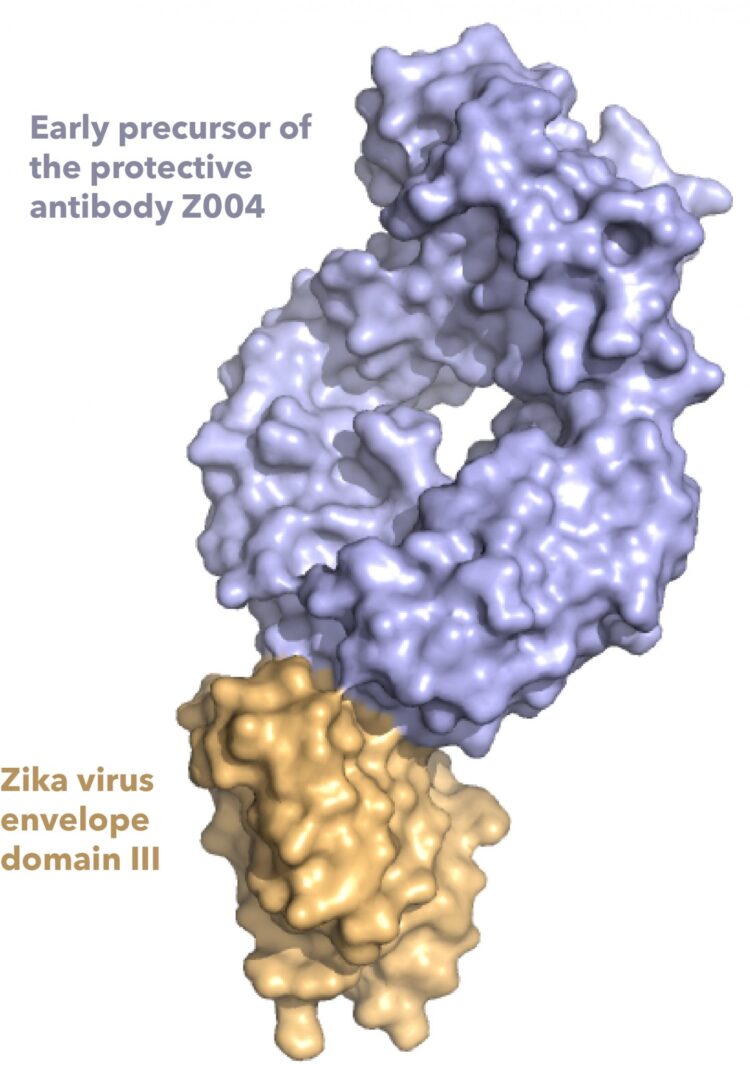
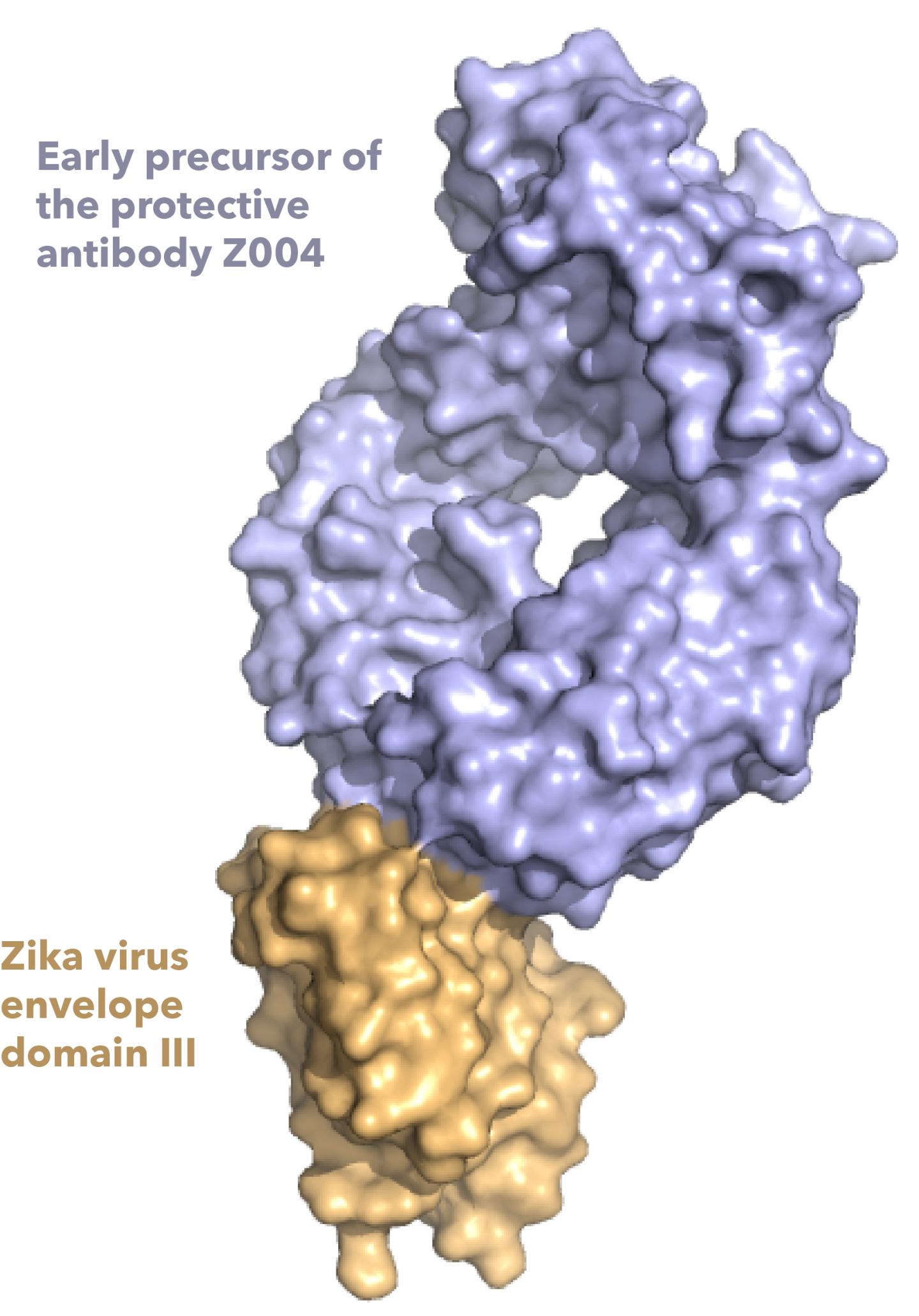
To study the antibody response to Zika and other flavivirus, Esswein and Bjorkman looked at several antibodies from the blood of patients from Mexico and Brazil. To find antibodies that recognize flaviviruses, they used a piece of the outside of the virus, called the envelope domain III protein. Previous studies have shown the envelope domain III is an important target of protective antibodies that fight flavivirus infections.
The researchers studied how those antibodies changed over time as they mature and become better able to stick to Zika virus, and also how the antibodies cross-react with other flaviviruses, including the four types of dengue viruses. They found that the Zika antibodies also tightly stick to and defend against dengue type 1, and weakly stick to West Nile and dengue types 2 and 4. “The weak cross-reactivity of these antibodies doesn’t seem to defend against those flaviviruses, but also doesn’t induce ADE,” Esswein said, suggesting envelope domain III may be useful to make a vaccine that is safe. They also determined structures showing how two antibodies recognize Zika and West Nile envelope domain III.
Together, the team’s experiments show how the body mounts “a potent immune response to Zika virus,” says Esswein. Their insights into the antibodies involved in this immune response will help inform vaccine design strategy.
###
Media Contact
Leann Fox
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/