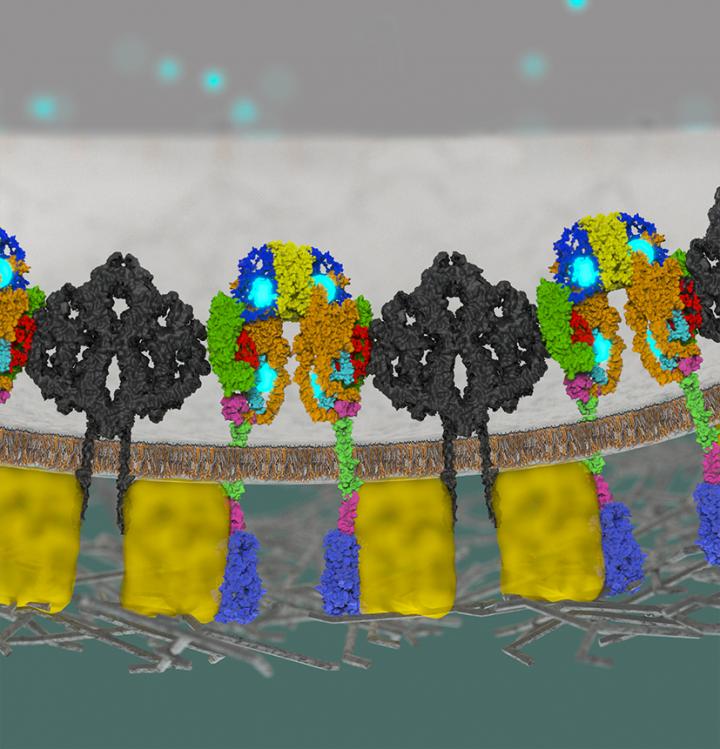
Credit: Helmholtz Zentrum München
Researchers have discovered a novel and druggable insulin inhibitory receptor, named inceptor. The latest study from Helmholtz Zentrum Muenchen, the Technical University of Munich and the German Center for Diabetes Research is a significant milestone for diabetes research as the scientific community celebrates 100 years of insulin and 50 years of insulin receptor discovery. The blocking of inceptor function leads to an increased sensitisation of the insulin signaling pathway in pancreatic beta cells. This might allow protection and regeneration of beta cells for diabetes remission.
Diabetes mellitus is a complex disease characterized by the loss or dysfunction of insulin-producing beta cells in the islets of Langerhans, a specialist “micro-organ” in the pancreas that controls systemic blood sugar levels. Diabetes complications, such as chronic high blood sugar, systemic metabolic failure and, in the long-term, multi-organ damage, create enormous medical and social burdens and leads to premature death. Currently no pharmacological treatment can stop or reverse disease progression. Previous studies have demonstrated that intensive insulin therapy has the potential for improved blood sugar control and diabetes remission but also leads to unintended weight gain and even more severe side effects, such as an increased risk of deep drop in blood sugar causing unawareness.
Heiko Lickert’s* research focuses on the development of regenerative approaches to treat diabetes complementary and alternative to the classical immunological and metabolic therapies. “Insulin resistance in pancreatic beta cells causes diabetes. Therapies that sensitize those cells to insulin may protect patients with diabetes against beta cell loss and failure”, says Lickert. With the discovery of the insulin inhibitory receptor, his research group has found a promising molecular target for beta cell protection and regeneration therapy that does not carry the unintended side effects of intensive insulin therapy.
In experiments with mice, the researchers showed that the function of inceptor is to shield the insulin-producing beta cells from constitutive insulin pathway activation. Remarkably, inceptor is upregulated in diabetes and by blocking insulin signaling it might contribute to insulin resistance.
What happens if the function of inceptor is inhibited genetically or pharmacologically? The group explored this question by knocking out inceptor in beta cells and by blocking its function using monoclonal antibodies. “The result was exactly what we were hoping for: Insulin signaling and the functional beta cell mass was increased. This makes inceptor a very promising target to treat the root cause of diabetes, the loss and dysfunction of beta cells,” says Ansarullah, one of the first-authors of the study published in Nature and diabetes researcher at Helmholtz Zentrum München.
“Frederick Banting noted already in his Nobel Prize lecture for the discovery of the life-saving drug insulin a hundred years ago that ‘Insulin is not a cure for diabetes, but a treatment of the symptoms’. This has not changed in the last century. Our goal for future research is to leverage on the discovery of inceptor and develop drugs for beta cell regeneration. This could be beneficial for patients with type 1 and 2 diabetes and ultimately lead to diabetes remission”, states Lickert.
“A hundred years ago, the discovery of insulin has transformed a deadly illness into a manageable disease. Our discovery of the insulin inhibitory receptor now is another important step to finally get rid of the disease,” says Matthias Tschöp, CEO at Helmholtz Zentrum München. “While the COVID-19 pandemic represents an immediate threat we will overcome, we must not forget that diabetes remains one of the biggest and fastest growing killers on our planet. With a series of recent breakthroughs, now including the discovery of inceptor, our Helmholtz Diabetes Center is doubling down on its mission that is a world without diabetes.”
###
*Heiko Lickert is Director of the Institute of Diabetes and Regeneration Research at Helmholtz Zentrum Muenchen, Professor and Chair of Beta Cell Biology at the Technical University of Munich and member of the German Center for Diabetes Research.
Original publication
Ansarullah et al., 2021: Inceptor counteracts insulin signalling in β-cells to control glycaemia. Nature, DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03225-8
Helmholtz Zentrum Muenchen
Helmholtz Zentrum Muenchen is a research center with the mission to discover personalized medical solutions for the prevention and therapy of environmentally-induced diseases and promote a healthier society in a rapidly changing world. It investigates important common diseases which develop from the interaction of lifestyle, environmental factors and personal genetic background, focusing particularly on diabetes mellitus, allergies and chronic lung diseases. Helmholtz Zentrum Muenchen is headquartered in Neuherberg in the north of Munich and has about 2,500 staff members. It is a member of the Helmholtz Association, the largest scientific organization in Germany with more than 40,000 employees at 19 research centers.
Media Contact
Verena Schulz
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




