Credit: IRB Barcelona
In cancer, personalised medicine takes advantage of the unique genetic changes in an individual tumour to find its vulnerabilities and fight it. Many tumours have a higher number of mutations due to a antiviral defence mechanism, the APOBEC system, which can accidentally damage DNA and cause mutations.
Researchers at IRB Barcelona led by Dr. Travis Stracker and Dr. Fran Supek have found the HMCES enzyme to be the Achilles heel of some lung tumours, specifically those with a higher number of mutations caused by the APOBEC system.
“We have discovered that blocking HMCES is very damaging to cells with an activated APOBEC system (which are many lung cancer cells), but much less so for those in which it is not activated (as is often the case in healthy cells),” explains Dr. Supek, ICREA researcher and head of the Genome Data Science lab at IRB Barcelona.
“Besides showing specificity to cancer cells, HMCES is potentially targetable by drugs, which makes it a great candidate for future lung cancer treatments,” adds Dr. Stracker, former group leader at IRB Barcelona, now working at the National Cancer Institute (NIH/NCI) in the USA.
A multidisciplinary approach to double-check the best strategy
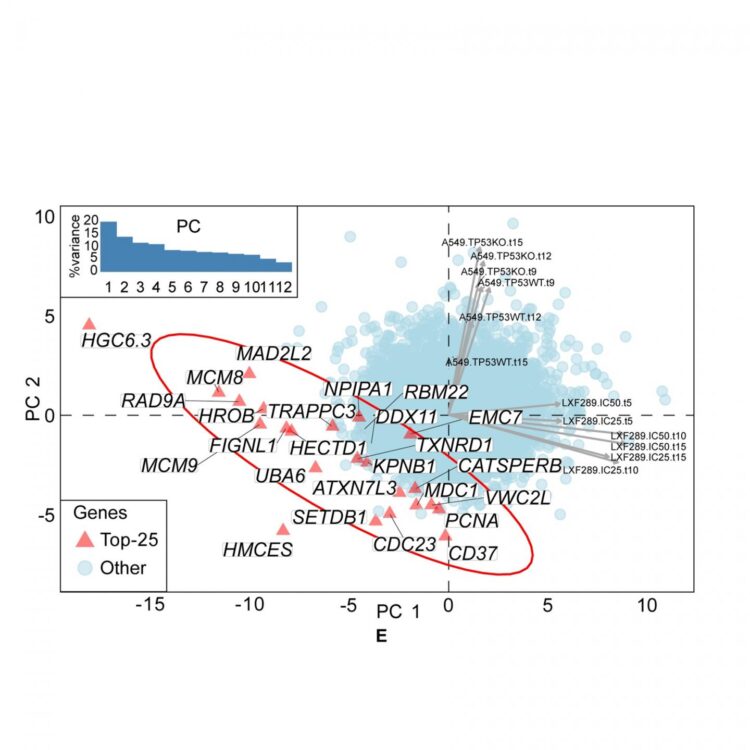
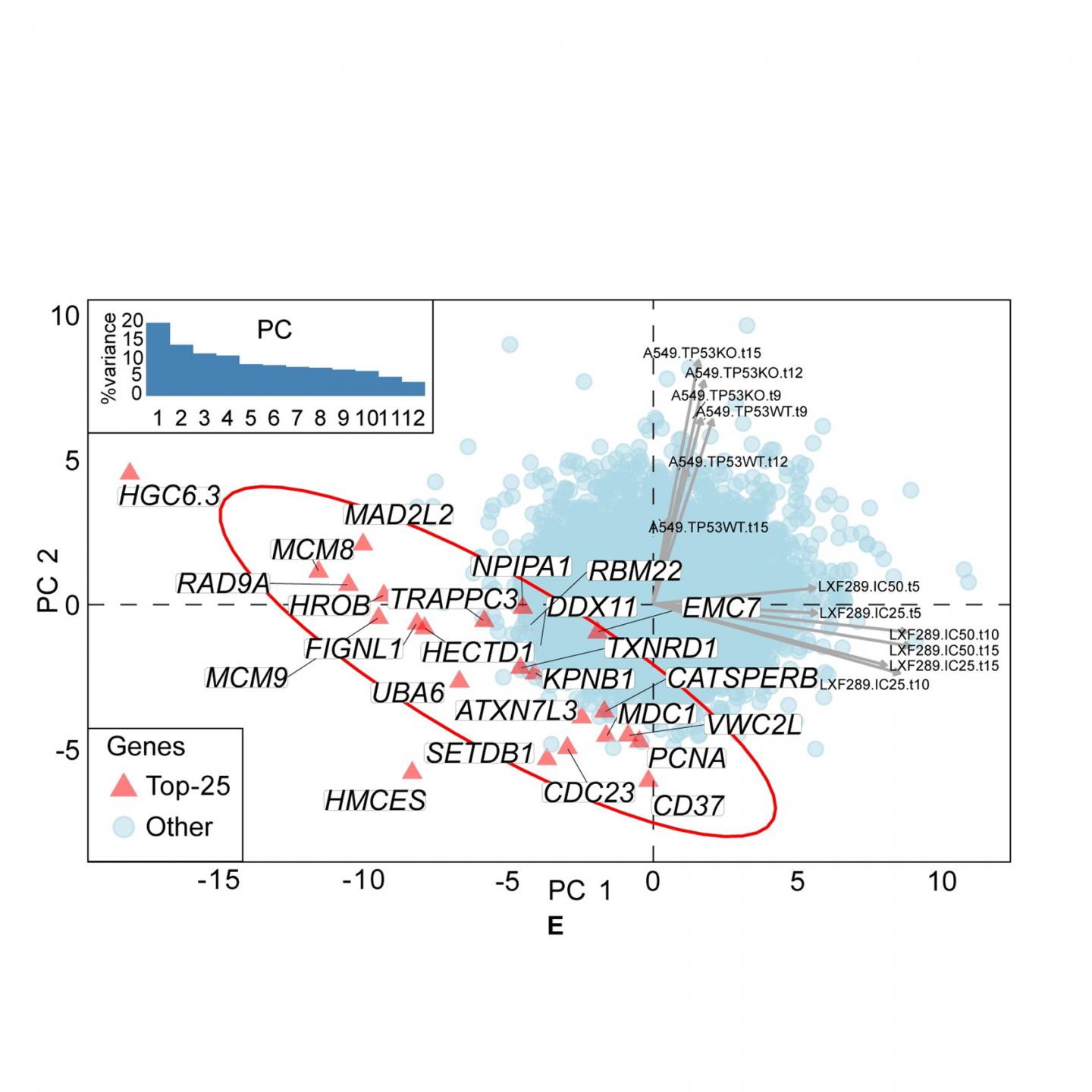
Involving collaboration between two research groups working on different disciplines, the study comprised both a computational and experimental approach. Genetic screening experiments were performed using CRISPR/Cas9 on several types of human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. “These experiments can interrogate the effects of removing each gene individually from the cancer cells and they allow us to see whether the cancer can tolerate this change,” say Josep Biayna and Isabel Garcia, IRB Barcelona researchers and first and second authors of the article. Previous data from CRISPR genetic screens performed by other labs were also statistically analysed and confirmed the experimental results.
A mutation fog caused by a defence system
When cells sense a mismatch in their DNA, they undergo a DNA repair reaction to preserve genetic information. Remarkably, this reaction can become coupled to the APOBEC enzymes, typically used by human cells to defend against viruses and having an important role in fighting hepatitis and HIV. This mechanism was previously described by the Genome Data Science lab and indicates that, in some cases, when the APOBEC enzymes and the DNA repair process are simultaneously active, APOBEC hijacks DNA repair, thus generating the mutation fog.
Outsmarting cancer evolution
Late-stage cancers can accumulate a high number of mutations in their DNA, which can cause the cancer to become more aggressive or to resist drugs better. Many of these mutations may be caused by APOBEC which accelerates tumor evolution. Therefore, killing cancer cells that activate APOBEC should slow down tumor evolution and prevent it from gaining new dangerous mutations.
###
This work was funded by the ERC Starting Grant “HYPER-INSIGHT”, awarded to Dr. Fran Supek, ICREA researcher and EMBO Young Investigator, the Severo Ochoa grant awarded to IRB Barcelona by the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities, and the NIH/NCI.
Media Contact
Nahia Barberia
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.