Credit: Lianwei Li, Shengpei Zhang, Xinyu Liu, Rui Yu, Xinrui Li, Muxing Liu, Haifeng Zhang, Xiaobo Zheng, Ping Wang, and Zhengguang Zhang
Rice blast fungus (Magnaporthe oryzae) is a global food security threat due to its destruction of cultivated rice, the most widely consumed staple food in the world. Disease containment efforts using traditional breeding or chemical approaches have been unsuccessful as the fungus can rapidly adapt and mutate to develop resistance. Because of this, it is necessary to understand fungal infection-related development to formulate new, effective methods of blast control.
A group of scientists at Nanjing Agricultural University and Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center examined the fungal cell biology of rice blast fungus pathogenesis and recently published the first systematic and comprehensive report on the molecular mechanism of the actin-binding protein (MoAbp1) that plays a crucial role in the pathogenicity of the fungus.
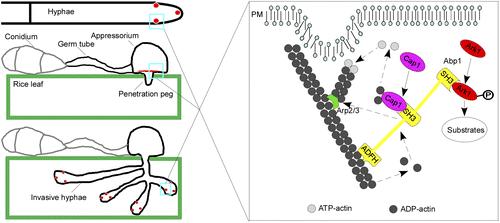
Through ongoing research, these scientists found that rice blast fungus forms a specialized infection structure that applies mechanical force to rupture the rice leaf cuticle. Once inside the host, the infection proliferates by living off the plant’s nutrients. These two processes are enabled by the actin-binding protein (MoABp1) that links an actin-regulating kinase (MoArk1) and a cyclase-associated protein (MoCap1) to an actin protein (MoAct1). These processes are necessary for the growth and perseverance of the fungus.
On a large scale, these findings shed a new light on the eukaryotic cell biology and virulence mechanisms of plant pathogenic fungi. On a smaller scale, these findings could reveal novel approaches or targets for anti-blast fungus management.
###
For additional details, read “Magnaporthe oryzae Abp1, a MoArk1 Kinase-Interacting Actin Binding Protein, Links Actin Cytoskeleton Regulation to Growth, Endocytosis, and Pathogenesis” published in Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions in April 2019.
About Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions (MPMI)
Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions® (MPMI) publishes fundamental and advanced applied research on the genetics, genomics, molecular biology, biochemistry, and biophysics of pathological, symbiotic, and associative interactions of microbes, insects, nematodes, or parasitic plants with plants.
Media Contact
Ashley Bergman Carlin
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




