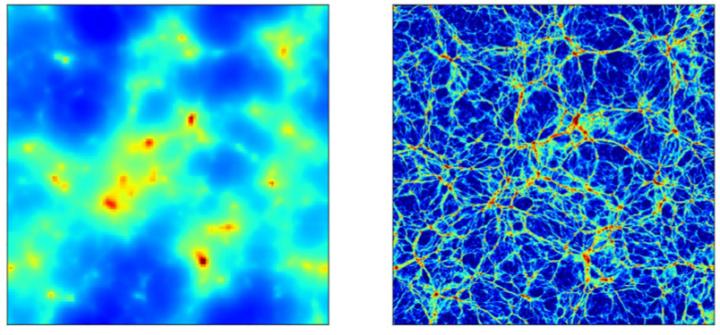
Credit: Kavli IPMU
The effect that nearly massless, subatomic particles called neutrinos have on the formation of galaxies has long been a cosmological mystery–one that physicists have sought to measure since discovering the particles in 1956.
But an international research team including the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU) Principal Investigator Naoki Yoshida, who is also a professor in the department of physics at the University of Tokyo, has created cosmological simulations that accurately depict the role of neutrinos in the evolution of the universe. Their study was recently published in The Astrophysical Journal.
Missouri University of Science and Technology (Missouri S&T) cosmologist Dr. Shun Saito, an assistant professor of physics and a researcher on the team, says the work is a milestone in the process of simulating the formation of the structure of the universe. Saito is also a visiting associate scientist at the Kavli IPMU.
The team used a system of differential equations known as the Vlasov-Poisson equations to explain how neutrinos move through the universe with different values assigned to their mass.
The technique accurately represented the velocity distribution function of the neutrinos and followed its evolution over time. The researchers then examined the effects of neutrinos on galaxy formation and evolution.
Their results showed that neutrinos suppress the clustering of dark matter–the undefined mass in the universe–and, in turn, galaxies. They found that neutrino-rich regions are strongly correlated with massive galaxy clusters, and that the effective temperature of the neutrinos varies substantially depending on the mass of the neutrino.
The researchers say that the most stringent experiments used to estimate neutrino mass are cosmological observations, but those can only be relied upon if simulation predictions are accurate.
“Overall, our findings are consistent with both theoretical predictions and the results of previous simulations,” says Dr. Kohji Yoshikawa from the Center for Computational Sciences at the University of Tsukuba and lead author of the study. “It is reassuring that the results from entirely different simulation approaches agree with each other.”
“Our simulations are important because they set constraints on the unknown quantity of the neutrino mass,” says Saito from Missouri S&T. “Neutrinos are the lightest particles we know of. We only recently learned neutrinos have mass from the discovery featured in the 2015 Nobel Prize in physics.”
That prize awarded two scientists, including Kavli IPMU Principal Investigator Takaaki Kajita, who is also the Director at the Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, University of Tokyo, for their separate discoveries that one kind of neutrino can change into another, which showed that neutrinos have mass.
“Our work might ultimately lead to a robust determination of the neutrino mass,” Saito says.
###
Dr. Satoshi Tanaka, a postdoctoral fellow at the Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics at Kyoto University, was the fourth member of the study, titled “Cosmological Vlasov-Poisson Simulations of Structure Formation with Relic Neutrinos: Nonlinear Clustering and the Neutrino Mass.”
Authors: Kohji Yoshikawa (1), Satoshi Tanaka (2), Naoki Yoshida (3, 4, 5), Shun Saito (6, 4)
Author affiliation:
- 1. Center for Computational Sciences, University of Tsukuba, 1-1-1 Tennodai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8577, Japan
2. Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University, Kitashirakawa Oiwake-Cho, Sakyo-Ku, Kyoto 606-8502, Japan
3. Department of Physics, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan
4. Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe, The University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8583, Japan
5. Research Center for the Early Universe, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan
6. Institute for Multi-messenger Astrophysics and Cosmology, Department of Physics, Missouri University of Science and Technology, 1315 N Pine St, Rolla, MO 65409
Abstract of the paper: https:/
Preprint (arXiv.org)
Research contact:
Naoki Yoshida
Principal Investigator
Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe, The University of Tokyo
Professor
Department of Physics, the University of Tokyo
E-mail: [email protected]
Media Contact
John Amari
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




