Experimental drug found to disrupt genes activated by worm parasite that causes lymphatic filariasis (elephantiasis)
Credit: University of Maryland School of Medicine
Using innovative RNA sequencing techniques, researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) Institute for Genome Sciences identified a promising novel treatment for lymphatic filariasis, a disabling parasitic disease that is difficult to treat. The potential new therapy is an experimental cancer drug called JQ1 and targets proteins found prominently in the worm’s genome; it appears to effectively kill the adult worms in a laboratory setting, according to the study which was published today in the journal mSystems.
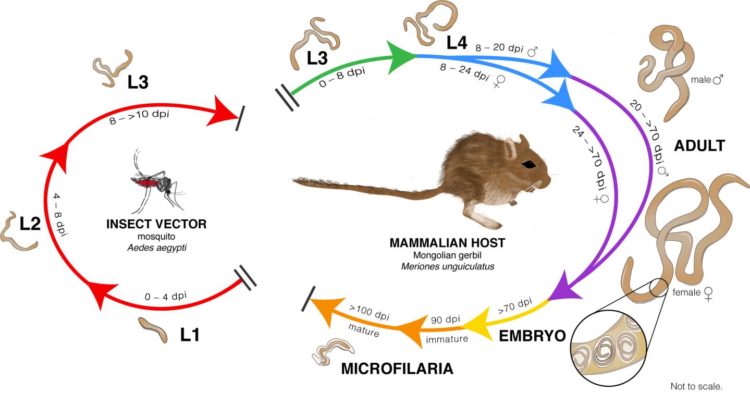
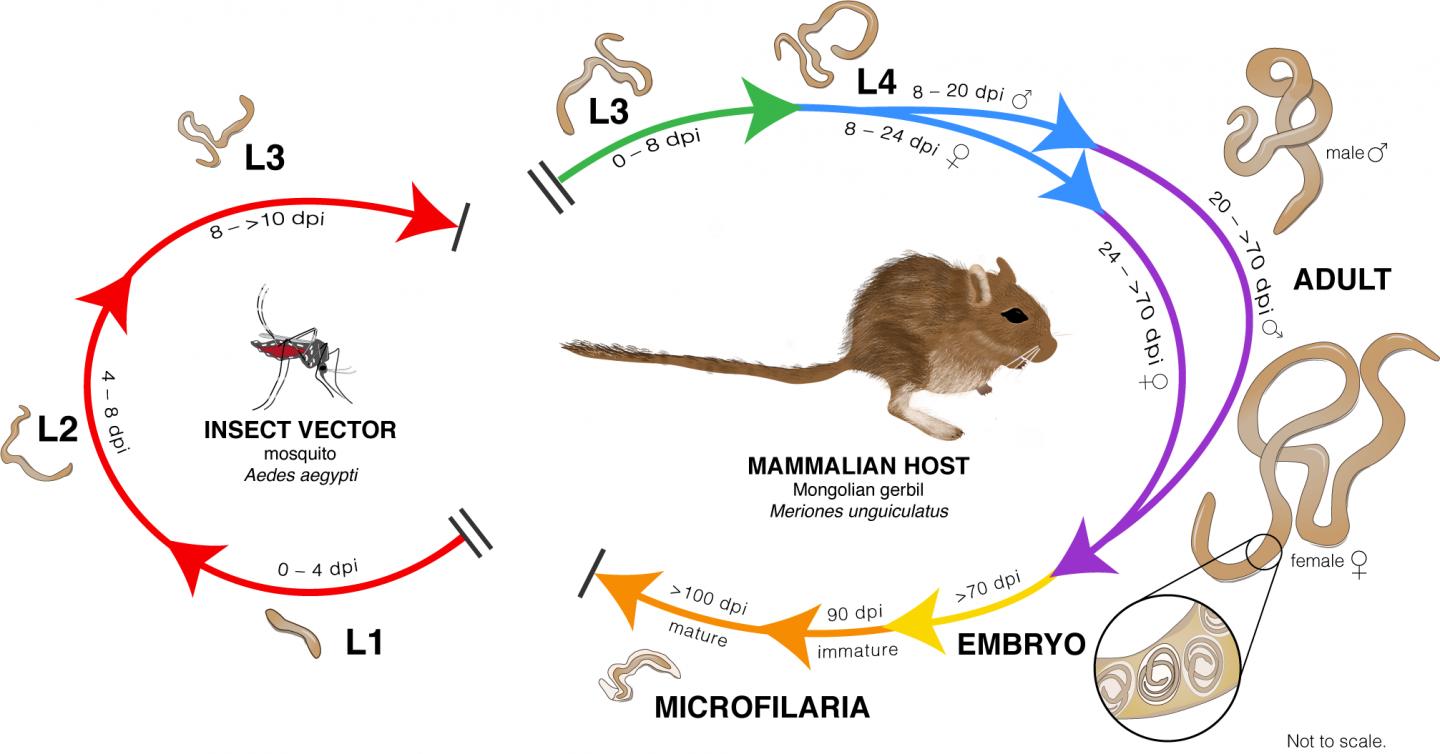
Lymphatic filariasis affects over 120 million people worldwide, mostly in the tropics of Asia, Western Pacific and Africa and parts of the Caribbean and South America. Those in the U.S. who have the disease, which is spread by mosquitoes that carry the baby worms, were infected while traveling abroad. The disease leads to dysfunction of the lymph system, causing swelling in the limbs (lymphedema) and hardening of the arms and legs (elephantiasis) or swelling of the scrotum in men (hydrocele). Lymphatic filariasis is a leading cause of permanent disability worldwide, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
While current treatments can reduce the risk of the disease being transmitted to other people, the CDC says it does not do much to alleviate symptoms. Studies suggest the antibiotic doxycycline can help manage mild to moderate lymphedema by killing the adult worms, but it must be given for four to six weeks in order to have any effectiveness.
“The drug JQ1 works by inhibiting bromodomain-containing proteins that are necessary for the adult worms to live,” said study author Julie Dunning Hotopp, PhD, Professor of Microbiology and Immunology at the Institute of Genome Sciences at the University of Maryland School of Medicine. “Based on our observations in the lab, we believe that this drug could be more effective than standard treatments at killing adult worms and may need to be administered only once.”
Working alongside Matthew Chung, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow in the Institute for Genome Sciences and co-author of the study, Dr. Dunning Hotopp used an RNA sequencing technique to identify genes in the parasitic worms that cause lymphatic filariasis. They identified an overrepresentation of genes that encode for bromodomain proteins. Based on those findings, they and their colleagues at the University of Wisconsin Oshkosh and at New England Biolabs decided to test JQ1, a bromodomain inhibitor, to see whether it would kill the adult worms, and they discovered that it was effective at killing them in the laboratory.
Their next step is to conduct preclinical studies to test JQ1 in rodents infected with the parasitic worms to see whether the drug can wipe out the infection. If successful, the drug could then be tested in human trials.
“While this research is still in its early stages, it highlights the ability of transcriptomics to identify potential new therapeutics,” said UMSOM Dean E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, University Executive Vice President for Medical Affairs and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor. “I am eager to see the results of future research studies on this since patients with this neglected tropical disease are in dire need of more effective treatments.”
###
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
Now in its third century, the University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 as the first public medical school in the United States. It continues today as one of the fastest growing, top-tier biomedical research enterprises in the world — with 43 academic departments, centers, institutes, and programs; and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians, scientists, and allied health professionals, including members of the National Academy of Medicine and the National Academy of Sciences, and a distinguished recipient of the Albert E. Lasker Award in Medical Research. With an operating budget of more than $1 billion, the School of Medicine works closely in partnership with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide research-intensive, academic and clinically based care for more than 1.2 million patients each year. The School has over 2,500 students, residents, and fellows, and more than $540 million in extramural funding, with most of its academic departments highly ranked among all medical schools in the nation in research funding. As one of the seven professional schools that make up the University of Maryland, Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine has a total workforce of nearly 7,000 individuals. The combined School and Medical System (“University of Maryland Medicine”) has an annual budget of nearly $6 billion and an economic impact more than $15 billion on the state and local community. The School of Medicine faculty, which ranks as the 8th highest among public medical schools in research productivity, is an innovator in translational medicine, with 600 active patents and 24 start-up companies. The School works locally, nationally, and globally, with research and treatment facilities in 36 countries around the world. Visit medschool.umaryland.edu
About the Institute for Genome Sciences
The Institute for Genome Sciences, founded in 2007, is an international research center within the University of Maryland School of Medicine. Comprised of an interdisciplinary, multidepartment team of investigators, the Institute uses the powerful tools of genomics and bioinformatics to understand genome function in health and disease, to study molecular and cellular networks in a variety of model systems, and to generate data and bioinformatics resources of value to the international scientific community.
igs.umaryland.edu
Media Contact
Deborah Kotz
[email protected]
410-706-4255
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.