Credit: S.Nersisyan et al.
HSE University researchers have become the first in the world to discover genetic predisposition to severe COVID-19. The results of the study were published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology.
T-cell immunity is one of the key mechanisms used by the human body to fight virus infections. The staging ground for cell immunity development is the presentation of virus peptides on the surface of infected cells. This is followed by activation of T lymphocytes, which start to kill the infected cells.
The ability to successfully present virus peptides is largely determined by genetics. In human cells, human leukocyte antigen class I (HLA-I) molecules are responsible for this presentation. The set of six such molecules is unique in every human and is inherited from an individual’s parents. In simple terms, if the set of alleles detects the virus well, then the immune cells will detect and destroy the infected cells fast; if a person has a set that is bad at such detection, a more severe case of disease is more likely to be observed.
Researchers from the HSE Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology – Maxim Shkurnikov, Stepan Nersisyan, Alexei Galatenko and Alexander Tonevitsky -together with colleagues from Pirogov Russian National Research Medical University and Filatov City Clinical Hospital (Tatjana Jankevic, Ivan Gordeev, Valery Vechorko) studied the interconnection between HLA-I genotype and the severity of COVID-19.
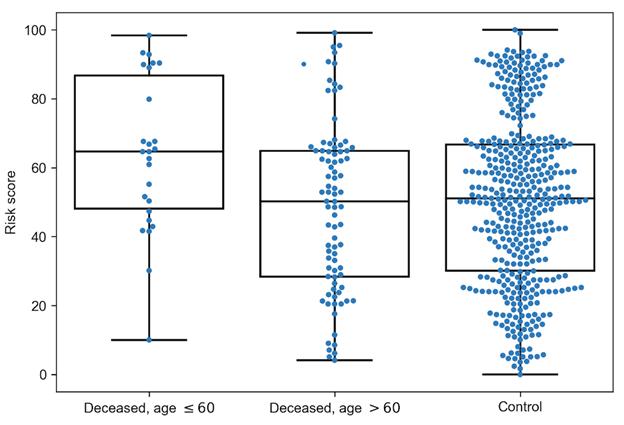
Using machine learning, they built a model that provides an integral assessment of the possible power of T-cell immune response to COVID-19: if the set of HLA-I alleles allows for effective presentation of the SARS-CoV-2 virus peptides, those individuals received low risk score, while people with lower presentation capability received higher risk scores (in the range from 0 to 100). To validate the model, genotypes of over 100 patients who had suffered from COVID-19 and over 400 healthy people (the control group) were analysed. It turned out that the modelled risk score is highly effective in predicting the severity of COVID-19.
In addition to analysing the Moscow population, the researchers used their model on a sample of patients from Madrid, Spain. The high precision of prediction was confirmed on this independent sample as well: the risk score of patients suffering severe COVID-19 was significantly higher than in patients with moderate and mild cases of the disease.
‘In addition to the discovered correlations between the genotype and COVID-19 severity, the suggested approach also helps to evaluate how a certain COVID-19 mutation can affect the development of T-cell immunity to the virus. For example, we will be able to detect groups of patients for whom infection with new strains of SARS-CoV-2 can lead to more severe forms of the disease,’ Alexander Tonevitsky said.
###
Once the paper is published, it will be available to view online at http://doi.
Media Contact
Liudmila Mezentseva
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




