Credit: YAO Zhonghua’s group
An international research team led by YAO Zhonghua from the Institute of Geology and Geophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGGCAS) has explained the cause of Jupiter’s X-ray aurorae, a mystery that has puzzled scientists for 40 years.
The findings were published in Science Advances on July 9.
It is the first time planetary researchers have described the entire causality chain for Jupiter’s X-ray auroral flares. The mechanism in producing X-ray auroral flares at Jupiter may have potential applications in X-ray astronomy.
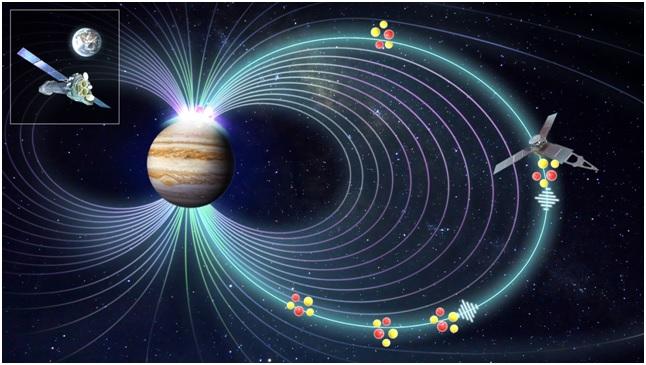
The X-ray auroral spectra tell us these aurorae are produced by heavy ions with energies in the mega electron volt range. But how they are formed and why these ions enter Jupiter’s atmosphere was previously unknown.
To understand the energetic processes associated with Jupiter’s polar emissions, researchers organized, over the last four years, a series of paradigm-shifting observation campaigns from Earth in tandem with in situ measurements by ESA’s flagship X-ray observatory, XMM-Newton, and NASA’s Juno spacecraft. These efforts included the most extensive X-ray campaign and the most extensive Hubble Space Telescope campaign ever conducted for Jupiter.
Using these tools, the researchers were able to probe the physics behind the phenomenon and reveal the processes that lead planets to produce X-ray aurorae.
“These are strikingly similar to the processes of producing ion aurorae on Earth, suggesting that ion aurorae share common mechanisms across planetary systems, despite temporal, spatial and energetic scales varying by orders of magnitude,” said YAO Zhonghua, first author of the study.
“What we see in the Juno data is this beautiful chain of events. We knew that the auroral ions are stored in the magnetosphere, originated from the volcanic activities of Jupiter’s moon Io. In the magnetosphere, now we see the magnetic compression happen, the electromagnetic ion cyclotron wave triggered, the ions, and then a pulse of ions traveling along the field line. A few minutes later, XMM sees a burst of X-rays,” said William Dunn from University College London, who co-led the study.
It is noteworthy that Jupiter’s X-ray auroral flares are often correlated with ultraviolet auroral flares, which are the most common auroral form. Indeed, the study of the latter may benefit from the wealth of Hubble Space Telescope data acquired through this research. “The discovery of Jupiter’s X-ray processes may have implications for our understanding of stunning ultraviolet auroral flares,” said Denis Grodent from the University of Liege, a co-author of the study.
###
Media Contact
YAO Zhonghua
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




