Can you trust the map on your smartphone, or the satellite image on your computer screen?
So far, yes, but it may only be a matter of time until the growing problem of “deep fakes” converges with geographical information science (GIS). Researchers such as Associate Professor of Geography Chengbin Deng are doing what they can to get ahead of the problem.
Deng and four colleagues — Bo Zhao and Yifan Sun at the University of Washington, and Shaozeng Zhang and Chunxue Xu at Oregon State University — co-authored a recent article in Cartography and Geographic Information Science that explores the problem. In “Deep fake geography? When geospatial data encounter Artificial Intelligence,” they explore how false satellite images could potentially be constructed and detected. News of the research has been picked up by countries around the world, including China, Japan, Germany and France.
“Honestly, we probably are the first to recognize this potential issue,” Deng said.
Geographic information science (GIS) underlays a whole host of applications, from national defense to autonomous cars, a technology that’s currently under development. Artificial intelligence has made a positive impact on the discipline through the development of Geospatial Artificial Intelligence (GeoAI), which uses machine learning — or artificial intelligence (AI) — to extract and analyze geospatial data. But these same methods could potentially be used to fabricate GPS signals, fake locational information on social media posts, fabricate photographs of geographic environments and more.
In short, the same technology that can change the face of an individual in a photo or video can also be used to make fake images of all types, including maps and satellite images.
“We need to keep all of this in accordance with ethics. But at the same time, we researchers also need to pay attention and find a way to differentiate or identify those fake images,” Deng said. “With a lot of data sets, these images can look real to the human eye.”
To figure out how to detect an artificially constructed image, first you need to construct one. To do so, they used a technique common in the creation of deep fakes: Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks (CycleGAN), an unsupervised deep learning algorithm that can simulate synthetic media.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) are a type of artificial intelligence, but they require training samples — input — of whatever content they are programmed to produce. A black box on a map could, for example, represent any number of different factories or businesses; the various points of information inputted into the network helps determine the possibilities it can generate.
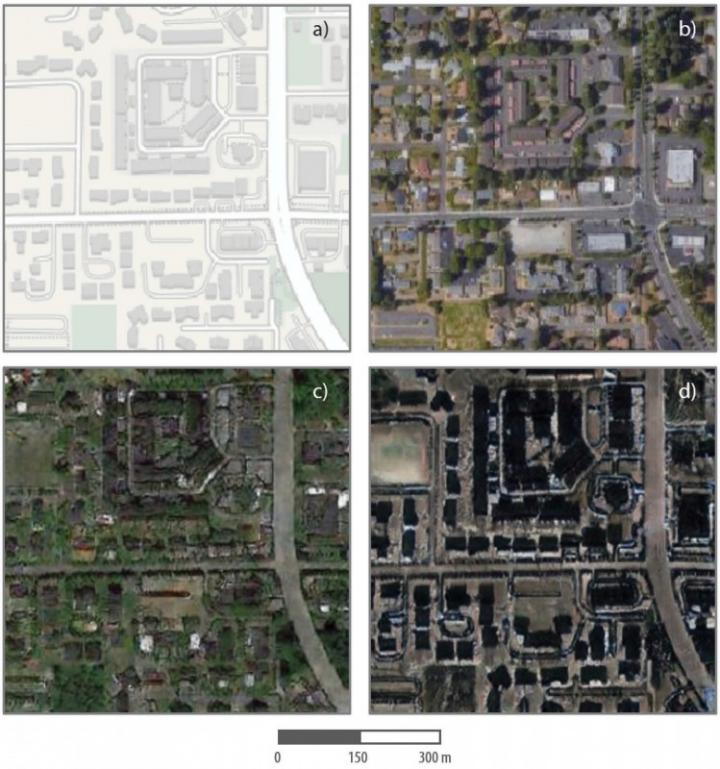
The researchers altered a satellite image of Tacoma, Washington, interspersing elements of Seattle and Beijing and making it look as real as possible. Researchers are not encouraging anyone to try such a thing themselves — quite the opposite, in fact.
“It’s not about the technique; it’s about how human being are using the technology,” Deng said. “We want to use technology for the good, not for bad purposes.”
After creating the altered composite, they compared 26 different image metrics to determine whether there were statistical differences between the true and false images. Statistical differences were registered on 20 of the 26 indicators, or 80%.
Some of the differences, for example, included the color of roofs; while roof colors in each of the real images were uniform, they were mottled in the composite. The fake satellite image was also dimmer and less colorful, but had sharper edges. Those differences, however, depended on the inputs they used to create the fake, Deng cautioned.
This research is just the beginning. In the future, geographers may track different types of neural networks to see how they generate false images and figure out ways to detect them. Ultimately, researchers will need to discover systematic ways to root out deep fakes and verify trustworthy information before they end up in the public view.
“We all want the truth,” Deng said.
###
Media Contact
John Brhel
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.