Credit: The University of Copenhagen
Proteins are found throughout our cells and regulate a lot of biological processes that are important forour survival. But some of them also regulate processes that can make us sick. Now, an international research team, with researchers from the University of Copenhagen at the forefront, has achieved a much better understanding of one such protein.
In a new study, the researchers discovered how the protein PP2A works at the molecular level, and how it inhibits the development of tumours in mice. The new results have been published in the scientific journal, the EMBO Journal.
‘We call PP2A a household protein because it is found almost everywhere. In everything living – from simple yeast cells to complex cells in humans. PP2A removes phosphate groups on other proteins, and now we have found these proteins and how PP2A, via one of these proteins, inhibits cancer development’, says Jakob Nilsson, Professor at the Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Protein Research.
Turned-Off Enzyme
According to the researchers, there is a great deal of interest from both the academic research community and from the pharmaceutical industry for the protein PP2A because it is well-known that PP2A is a so-called tumour suppressor that suppresses tumours. But precisely which proteins PP2A regulates in order to inhibit cancer have so far not been known. Now, the researchers have gained detailed insight into this.
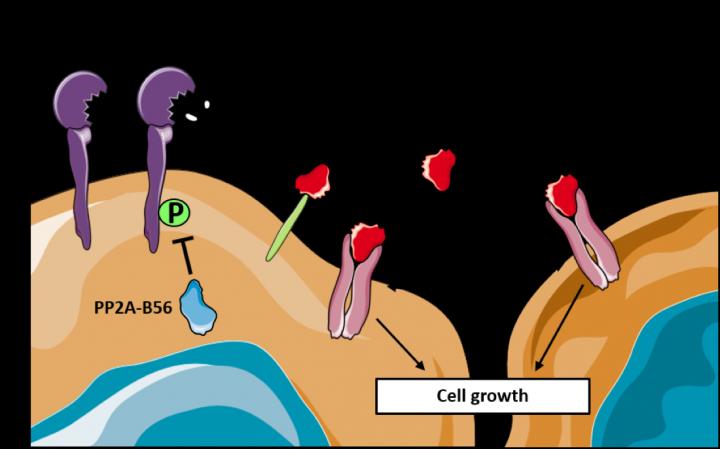
‘The new thing about our study is that we show how PP2A selects the phosphate groups that shall be removed from other proteins. And then at the same time, we show that PP2A turns off an enzyme named ADAM17. This shutdown of ADAM17 results in inhibition of tumour growth in mice’, explains Associate Professor Marie Kveiborg from the Biotech Research and Innovation Centre.
The researchers have used advanced methods to show that PP2A can turn off the activity of ADAM17 on the outside of the cell by removing phosphate groups from the part of ADAM17 that is located inside the cell.
The Function is Inhibited
Normally, ADAM17 sits as a pair of molecular scissors in the cell’s outer membrane and cleaves other proteins from the cell surface – for example, growth factors that will then stimulate cell growth. But that function ceases when PP2A removes the phosphate groups from ADAM17.
The researchers already knew from previous studies that ADAM17 stimulates a variety of cancers, including breast and bowel cancer. But this is the first time that PP2A has been shown to actively turn off ADAM17 activity.
Going forward, the researchers hope that their new cancer discovery will also apply to human tumoursFor now, the next step for the researchers is to clarify whether substances that activate PP2A can be used to regulate ADAM17 activity. In addition, the researchers also want to look at how PP2A regulates other proteins that may be important for the understanding of its tumour suppressor function.
###
Media Contact
Mathias Traczyk
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




