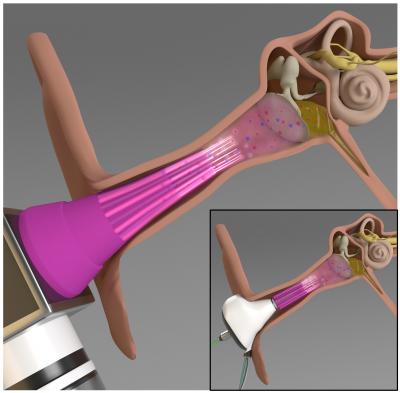
Middle ear infections, also known as otitis media, affect more than 80% of the children in the U.S. In a new study, researchers have designed a miniaturized 3D-printed device to inactivate Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a common bacterium that causes the infection.
The device–a microplasma jet array–generates plasma, which is composed of charged particles and reactive molecules that have been previously shown to inactivate various pathogens. “This is the first time anyone has tried treating middle ear infections using plasma technology,” said Jungeun Won, a graduate student in the Boppart lab. “Usually, the treatment involves using antibiotics or surgical intervention.”
The problem with using antibiotics is two-fold. First, antibiotics are ineffective in more than 30% of the patients with acute infections. Second, their use can lead to increased antibiotic resistance because the bacteria form biofilms–aggregates that attach to the surface of the ear.
“Biofilms are very dense, making it difficult for the antibiotics to penetrate,” said Helen Nguyen (IGOH), an Ivan Racheff Professor in Civil and Environmental Engineering. “Our idea was that if we could disrupt the structure of the biofilm, we could increase the penetration of the antibiotics.”
The researchers tested the microplasma jet array by building a model of the middle ear. They used an excised rat eardrum and tested the antimicrobial effects of the microplasma on the bacteria that were located behind the eardrum.
“We used different duration times for the treatment and found that 15 minutes and longer was effective in inactivating the bacteria,” Won said. “We also monitored the tissue to see if we had created any holes or ruptures, but we didn’t find any obvious physical damage.”
“We think that the microplasma disrupts the biofilm by disturbing the bacterial cell membrane,” Nguyen said. “So far, we only have indirect measurements supporting our idea, but we will look into it in the future.”
Although the thickness of the rat eardrum is 30% lower than that of a human, which is about the width of a hair strand, the results suggest that the microplasma treatment could be used to treat middle ear infections in humans.
“Middle ear infections and the over-prescription of antibiotics to treat these are major clinical challenges that are in need of new treatment technologies and solutions,” said Stephen Boppart, Grainger Distinguished Chair in Engineering, who is also a medical doctor.
The researchers are now designing a smaller, earbud-shaped jet array for treatments that will allow longer exposure times. They will also test the devices on animal models using biofilms of the other bacteria that cause middle ear infections, including, but not limited to, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Moraxella catarrhalis, to test whether the treatment is also effective with these bacteria. Additionally, the researchers will closely monitor the tissues of the middle ear to ensure that there is no structural and functional tissue damage from the plasma technology.
###
The study was carried out in collaboration with the labs of J. Gary Eden, Intel Alumni Endowed Chair Emeritus in Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Stephen Boppart, a Grainger Distinguished Chair in Engineering, with appointments in the Departments of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Bioengineering.
The study “Inactivation and sensitization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by microplasma jet array for treating otitis media” was published in npj Biofilms and Microbiomes and can be found at 10.1038/s41522-021-00219-2. The work was funded by the National Science Foundation, the U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research, and the National Institutes of Health.
Media Contact
Ananya Sen
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.