Credit: Dr. Yuki Kurauchi
Many different countries have a tea culture, and Japanese Matcha tea is growing in popularity around the world. In Japan, Matcha has a long history of being used for various medicinal purposes. It has been suspected to have various beneficial effects to health, but relatively little scientific evidence supported that claim. Now, a group of Japanese researchers from Kumamoto University has shown that anxious behavior in mice is reduced after consuming Matcha powder or Matcha extract. Its calming effects appear to be due to mechanisms that activate dopamine D1 receptors and serotonin 5-HT1A receptors, both of which are closely related to anxious behavior.
Matcha is the finely ground powder of new leaves from shade-grown (90% shade) Camellia sinensis green tea bushes. The tea (and food flavoring) is enjoyed around the world. In Japan, historical medicinal uses for Matcha included helping people relax, preventing obesity, and treatment of skin conditions. The researchers, therefore, sought to determine its various beneficial effects.
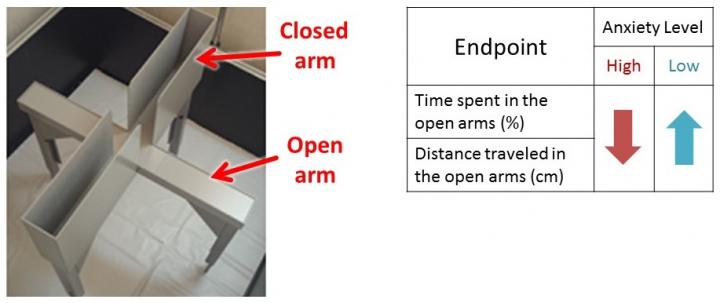
The “elevated plus maze” test is an elevated, plus-shaped, narrow platform with two walled arms that provide safety for the test subject, typically a mouse. It is used as an anxiety test for rodents with the idea that animals experiencing higher anxiety will spend more time in the safer walled-off areas. Using this test, researchers found that mouse anxiety was reduced after consuming Matcha powder or Matcha extract. In addition, when the anxiolytic activity of different Matcha extracts were evaluated, a stronger effect was found with the extract derived using 80% ethanol in comparison to the extract derived from only hot water. In other words, a poorly water-soluble Matcha component has stronger anxiolytic effects than a component that is easily soluble in water. A behavioral pharmacological analysis further revealed that Matcha and Matcha extracts reduce anxiety by activating dopamine D1 and serotonin 5-HT1A receptors.
“Although further epidemiological research is necessary, the results of our study show that Matcha, which has been used as medicinal agent for many years, may be quite beneficial to the human body,” said study leader, Dr. Yuki Kurauchi. “We hope that our research into Matcha can lead to health benefits worldwide.”
###
This research was published in the “Journal of Functional Foods” on 6 June 2019.
[Source]
Kurauchi, Y. et al., 2019. Anxiolytic activities of Matcha tea powder, extracts, and fractions in mice: Contribution of dopamine D1 receptor- and serotonin 5-HT1A receptor-mediated mechanisms. Journal of Functional Foods, 59, pp.301-308. Available at: http://dx.
Media Contact
J. Sanderson & N. Fukuda
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




