Credit: University of Bristol
New research by scientists at the University of Bristol explains how a ‘stop-start’ pattern of evolution, governed by environmental change, could explain why crocodiles have changed so little since the age of the dinosaurs.
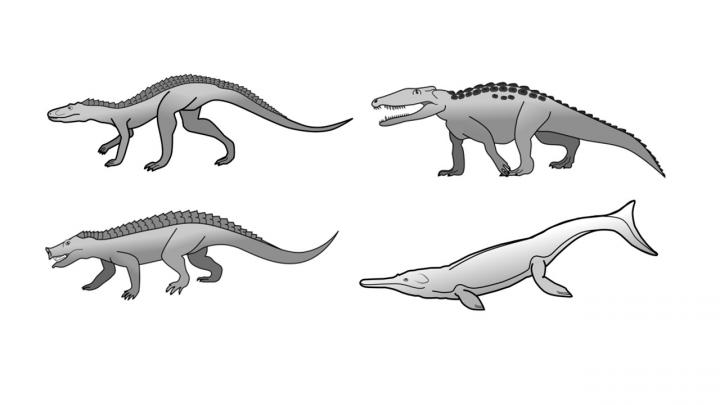
Crocodiles today look very similar to ones from the Jurassic period some 200 million years ago. There are also very few species alive today – just 25. Other animals such as lizards and birds have achieved a diversity of many thousands of species in the same amount of time or less.
Prehistory also saw types of crocodile we don’t see today, including giants as big as dinosaurs, plant-eaters, fast runners and serpentine forms that lived in the sea.
In the new research, published today in the journal Nature Communications Biology, the scientists explain how crocodiles follow a pattern of evolution known as ‘punctuated equilibrium’.
The rate of their evolution is generally slow, but occasionally they evolve more quickly because the environment has changed. In particular, this new research suggests that their evolution speeds up when the climate is warmer, and that their body size increases.
Lead author Dr Max Stockdale from the University of Bristol’s School of Geographical Sciences, said: “Our analysis used a machine learning algorithm to estimate rates of evolution. Evolutionary rate is the amount of change that has taken place over a given amount of time, which we can work out by comparing measurements from fossils and taking into account how old they are.
“For our study we measured body size, which is important because it interacts with how fast animals grow, how much food they need, how big their populations are and how likely they are to become extinct.”
The findings show that the limited diversity of crocodiles and their apparent lack of evolution is a result of a slow evolutionary rate. It seems the crocodiles arrived at a body plan that was very efficient and versatile enough that they didn’t need to change it in order to survive.
This versatility could be one explanation why crocodiles survived the meteor impact at the end of the Cretaceous period, in which the dinosaurs perished. Crocodiles generally thrive better in warm conditions because they cannot control their body temperature and require warmth from the environment.
The climate during the age of dinosaurs was warmer than it is today, and that may explain why there were many more varieties of crocodile than we see now. Being able to draw energy from the sun means they do not need to eat as much as a warm-blooded animal like a bird or a mammal.
Dr Stockdale added: “It is fascinating to see how intricate a relationship exists between the earth and the living things we share it with. The crocodiles landed upon a lifestyle that was versatile enough to adapt to the enormous environmental changes that have taken place since the dinosaurs were around.”
The next step for the team’s research is to find out why some types of prehistoric crocodile died out, while others didn’t.
###
Media Contact
Dr Max Stockdale
[email protected]




