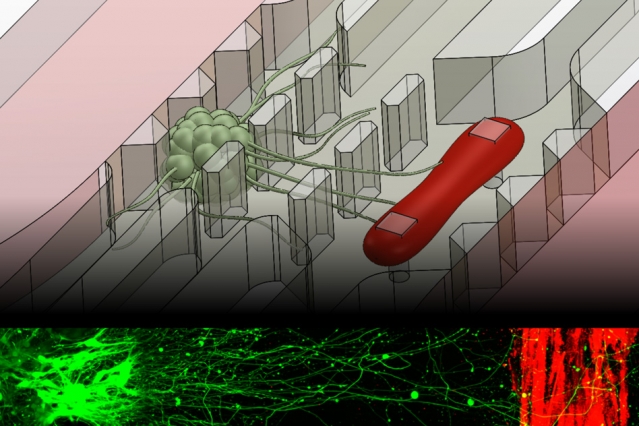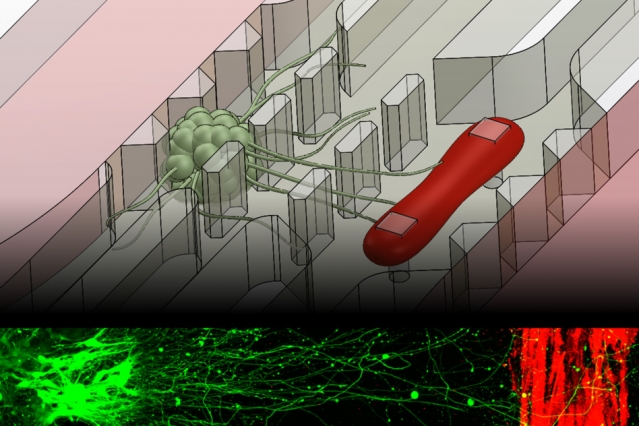
MIT engineers have developed a microfluidic device that replicates the neuromuscular junction — the vital connection where nerve meets muscle. The device, about the size of a U.S. quarter, contains a single muscle strip and a small set of motor neurons. Researchers can influence and observe the interactions between the two, within a realistic, three-dimensional matrix.
The researchers genetically modified the neurons in the device to respond to light. By shining light directly on the neurons, they can precisely stimulate these cells, which in turn send signals to excite the muscle fiber. The researchers also measured the force the muscle exerts within the device as it twitches or contracts in response.
The team’s results, published online today in Science Advances, may help scientists understand and identify drugs to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), more commonly known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, as well as other neuromuscular-related conditions.
“The neuromuscular junction is involved in a lot of very incapacitating, sometimes brutal and fatal disorders, for which a lot has yet to be discovered,” says Sebastien Uzel, who led the work as a graduate student in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering. “The hope is, being able to form neuromuscular junctions in vitro will help us understand how certain diseases function.”
Uzel’s coauthors include Roger Kamm, the Cecil and Ida Green Distinguished Professor of Mechanical and Biological Engineering at MIT, along with former graduate student and now postdoc Randall Platt, research scientist Vidya Subramanian, former undergraduate researcher Taylor Pearl, senior postdoc Christopher Rowlands, former postdoc Vincent Chan, associate professor of biology Laurie Boyer, and professor of mechanical engineering and biological engineering Peter So.
Closing in on a counterpart
Since the 1970s, researchers have come up with numerous ways to simulate the neuromuscular junction in the lab. Most of these experiments involve growing muscle and nerve cells in shallow Petri dishes or on small glass substrates. But such environments are a far cry from the body, where muscles and neurons live in complex, three-dimensional environments, often separated over long distances.
“Think of a giraffe,” says Uzel, who is now a postdoc at the Wyss Institute at Harvard University. “Neurons that live in the spinal cord send axons across very large distances to connect with muscles in the leg.”
To recreate more realistic in vitro neuromuscular junctions, Uzel and his colleagues fabricated a microfluidic device with two important features: a three-dimensional environment, and compartments that separate muscles from nerves to mimic their natural separation in the human body. The researchers suspended muscle and neuron cells in the millimeter-sized compartments, which they then filled with gel to mimic a three-dimensional environment.
A flash and a twitch
To grow a muscle fiber, the team used muscle precursor cells obtained from mice, which they then differentiated into muscle cells. They injected the cells into the microfluidic compartment, where the cells grew and fused to form a single muscle strip. Similarly, they differentiated motor neurons from a cluster of stem cells, and placed the resulting aggregate of neural cells in the second compartment. Before differentiating both cell types, the researchers genetically modified the neural cells to respond to light, using a now-common technique known as optogenetics.
Kamm says light “gives you pinpoint control of what cells you want to activate,” as opposed to using electrodes, which, in such a confined space, can inadvertently stimulate cells other than the targeted neural cells.
Finally, the researchers added one more feature to the device: force sensing. To measure muscle contraction, they fabricated two tiny, flexible pillars within the muscle cells’ compartment, around which the growing muscle fiber could wrap. As the muscle contracts, the pillars squeeze together, creating a displacement that researchers can measure and convert to mechanical force.
In experiments to test the device, Uzel and his colleagues first observed neurons extending axons toward the muscle fiber within the three-dimensional region. Once they observed that an axon had made a connection, they stimulated the neuron with a tiny burst of blue light and instantly observed a muscle contraction.
“You flash a light, you get a twitch,” Kamm says.
Judging from these experiments, Kamm says the microfluidic device may serve as a fruitful testing ground for drugs to treat neuromuscular disorders, and could even be tailored to individual patients.
“You could potentially take pluripotent cells from an ALS patient, differentiate them into muscle and nerve cells, and make the whole system for that particular patient,” Kamm says. “Then you could replicate it as many times as you want, and try different drugs or combinations of therapies to see which is most effective in improving the connection between nerves and muscles.”
On the flip side, he says the device may be useful in “modeling exercise protocols.” For instance, by stimulating muscle fibers at varying frequencies, scientists can study how repeated stress affects muscle performance.
“Now with all these new microfluidic approaches people are developing, you can start to model more complex systems with neurons and muscles,” Kamm says. “The neuromuscular junction is another unit people can now incorporate into those testing modalities.”
This research was funded, in part, by the National Science Foundation.
Story Source:
The above post is reprinted from materials provided by MIT NEWS
The post Replicating the connection between muscles and nerves appeared first on Scienmag.