Neuroscience
Neural membrane’s structural instability may trigger multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is one of the most devastating neurodegenerative diseases. It affects some 2.5 million people worldwide. It has no...
Scientists find new path in brain to ease depression
CHICAGO — Northwestern Medicine scientists have discovered a new pathway in the brain that can be manipulated to alleviate depression....
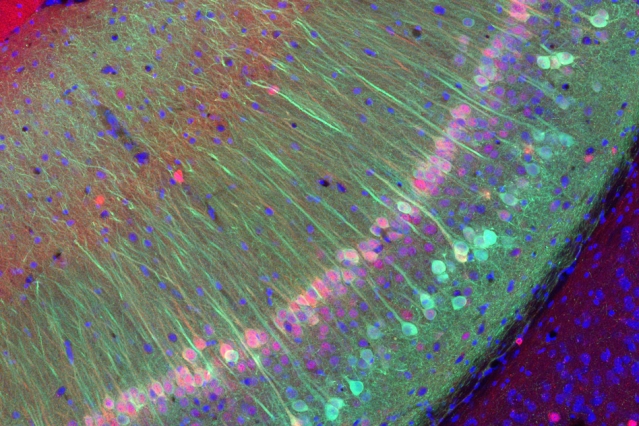
Key players responsible for learning and memory formation uncovered
Researchers from Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience, Duke University, and collaborators have identified a novel signaling system controlling neuronal...
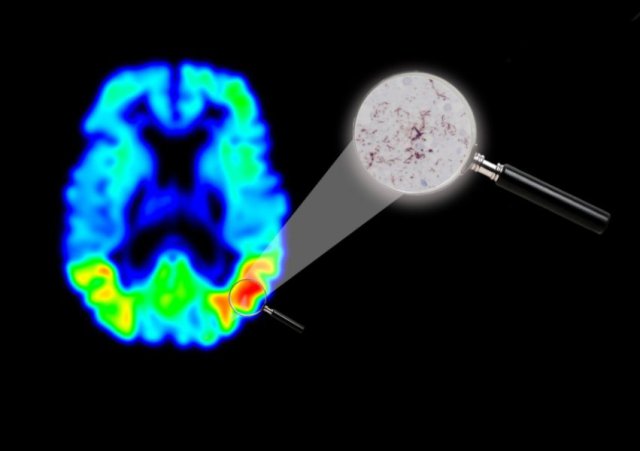
New imaging technique in Alzheimer’s disease opens up possibilities for new drug development
Tau PET is a new and promising imaging method for Alzheimer’s disease. A case study from Lund University in Sweden...
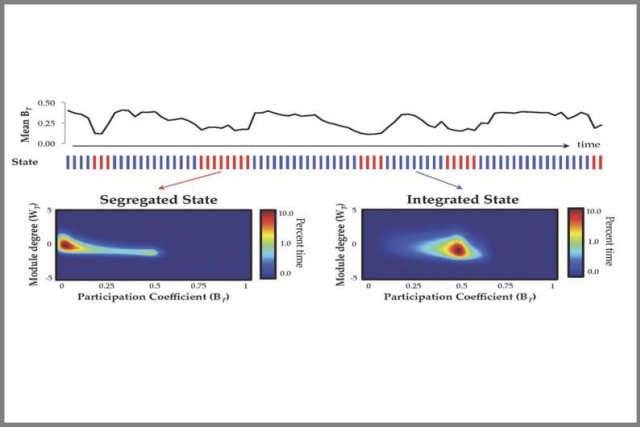
How a fluctuating brain network may make us better thinkers
For the past 100 years, scientists have understood that different areas of the brain serve unique purposes. Only recently have...
Zika infects neural cells related to skull formation, affecting their function
Cranial neural crest cells — which give rise to the bones and cartilage of the skull — are vulnerable to...
Breakthrough in mapping nicotine addiction could help researchers improve treatment
A scientific blueprint to end tobacco cravings may be on the way after researchers crystallized a protein that holds answers...
How the brain makes new memories while preserving the old
Columbia scientists have developed a new mathematical model that helps to explain how the human brain’s biological complexity allows it...
Keeping your synapses sharp: How spermidine reverses age-related memory decline
Synapses, connecting the neurons in our brains, continuously encode new memories, but the ability to form new memories (“learning”) diminishes...
Brain diseases manifest in the retina of the eye
Diseases of the central nervous system (CNS) may manifest as pathological changes in the retina of the eye. Research from...
New treatment strategy could cut Parkinson’s disease off at the pass
Researchers at Johns Hopkins report they have identified a protein that enables a toxic natural aggregate to spread from cell...
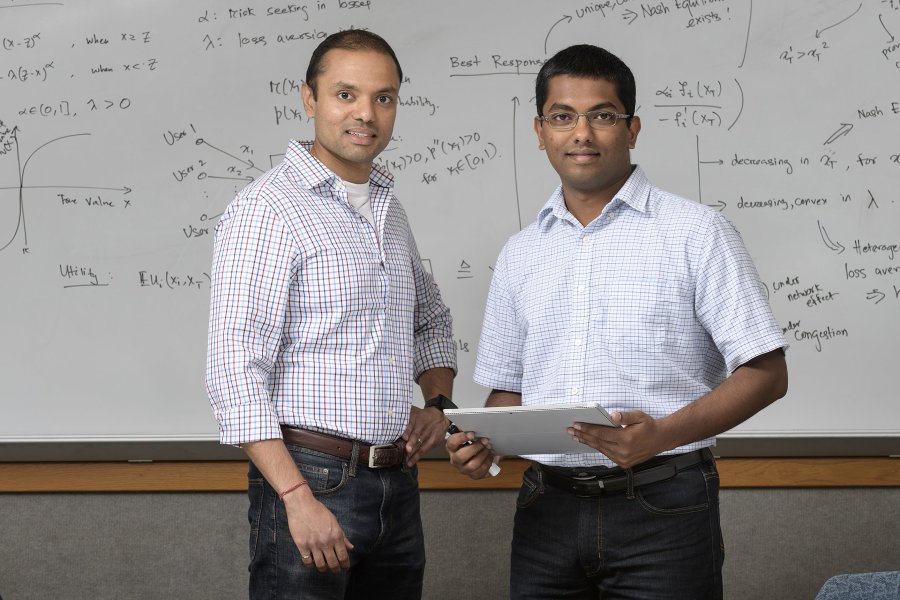
Game theory research reveals fragility of common resources
New research in game theory shows that people are naturally predisposed to over-use “common-pool resources” such as transportation systems and...
Brain disruptions similar across many emotional disorders
Researchers have long known that emotional disorders have a lot in common. Many often occur together, like depression and social...
Scientists identify neurons devoted to social memory
Mice have brain cells that are dedicated to storing memories of other mice, according to a new study from MIT...
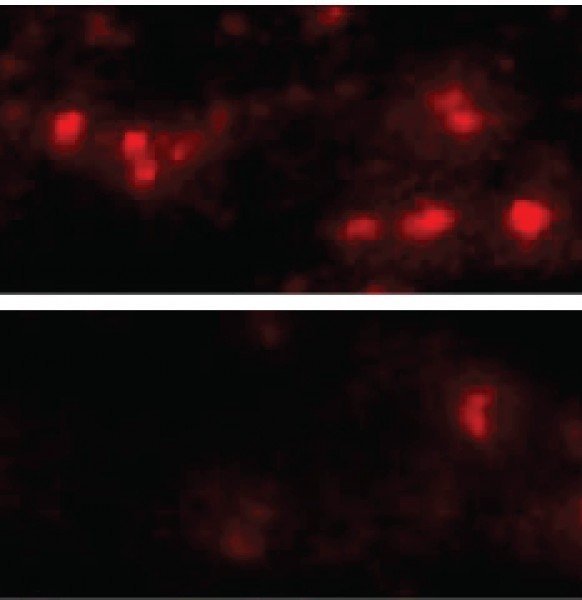
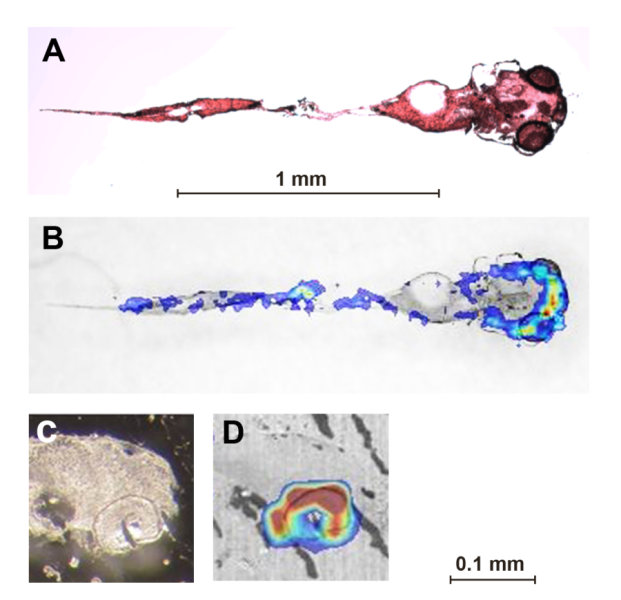
Cocaine accumulation in fish eyes
A study by Eawag and Zurich University researchers using a new imaging method has revealed that, surprisingly, cocaine accumulates in...
Alcohol shown to act in same way as rapid antidepressants
Can having a few drinks help people with clinical depression feel better? Yes. At least in terms of biochemistry. In...
Rest and well-being: World’s largest survey
Over two thirds (68 per cent) of the public would like more rest, according to the world’s largest ever survey...
How the brain decides between effort and reward
Every action we take involves a cost to us in physical energy, yet studies about decision-making have tended to look...
Brain’s biological clock stimulates thirst before sleep
The brain’s biological clock stimulates thirst in the hours before sleep, according to a study published in the journal Nature...
Depression in pregnancy increases risk of mental health problems in children
Depression in pregnancy increases the risk of behavioural and emotional problems in children, says a new review published in The...