New study finds presence of regulatory T cells enables partial recovery from paralysis
Credit: UCI School of Medicine
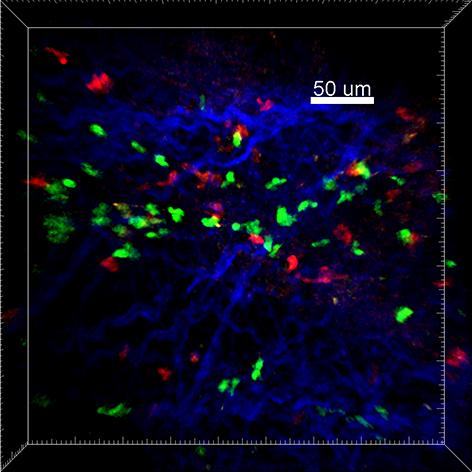
Irvine, CA – September 21, 2020 – In a new University of California, Irvine-led study, researchers have discovered how regulatory T cells (Treg) are instrumental in limiting the damage caused to the spinal cord in diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS).
Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the results of the study help explain how Treg cells prevent autoimmunity and dampen immune responses, specifically the negative effects of type 17 helper T cells (Th17) which are known to drive the progression of several autoimmune diseases.
This new study, which builds on recent research that identified pathogenic Th17 cells and their role in the progression of several autoimmune diseases, showed how the inhibition of Th17 cells by Treg cells enabled partial recovery from paralysis. This finding demonstrates how autoimmune diseases may be effectively targeted using Treg-based cellular therapies.
“We discovered a unique ‘repetitive scanning motility’ by which Treg cells (the good guys) dampen calcium signaling in pathogenic Th17 cells (the bad guys), and help to resolve neuroinflammation and limit reactivation of Th17 cells in the spinal cord,” explained Shivashankar Othy, PhD, lead author of the study with Amit Jairaman, PhD, both project scientists in the Cahalan Lab at UCI.
Senior author, Michael D. Cahalan, PhD, distinguished professor and chair of the Department of Physiology & Biophysics at the UCI School of Medicine, added, “Building on our years of expertise in immunoimaging and calcium signaling, this study highlights Th17 and Treg cell interactions, their motility characteristics, and intracellular signaling, thus providing new insights into the pathophysiology of MS. Our results illustrate how a regulatory T cell-based immunotherapy may be instrumental in limiting demyelination in MS.”
###
This research was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health.
About the UCI School of Medicine
Each year, the UCI School of Medicine educates more than 400 medical students, and nearly 150 doctoral and master’s students. More than 700 residents and fellows are trained at UCI Medical Center and affiliated institutions. The School of Medicine offers an MD; a dual MD/PhD medical scientist training program; and PhDs and master’s degrees in anatomy and neurobiology, biomedical sciences, genetic counseling, epidemiology, environmental health sciences, pathology, pharmacology, physiology and biophysics, and translational sciences. Medical students also may pursue an MD/MBA, an MD/master’s in public health, or an MD/master’s degree through one of three mission-based programs: the Health Education to Advance Leaders in Integrative Medicine (HEAL-IM), the Leadership Education to Advance Diversity-African, Black and Caribbean (LEAD-ABC), and the Program in Medical Education for the Latino Community (PRIME-LC). The UCI School of Medicine is accredited by the Liaison Committee on Medical Accreditation and ranks among the top 50 nationwide for research. For more information, visit som.uci.edu.
Media Contact
Anne Warde
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




