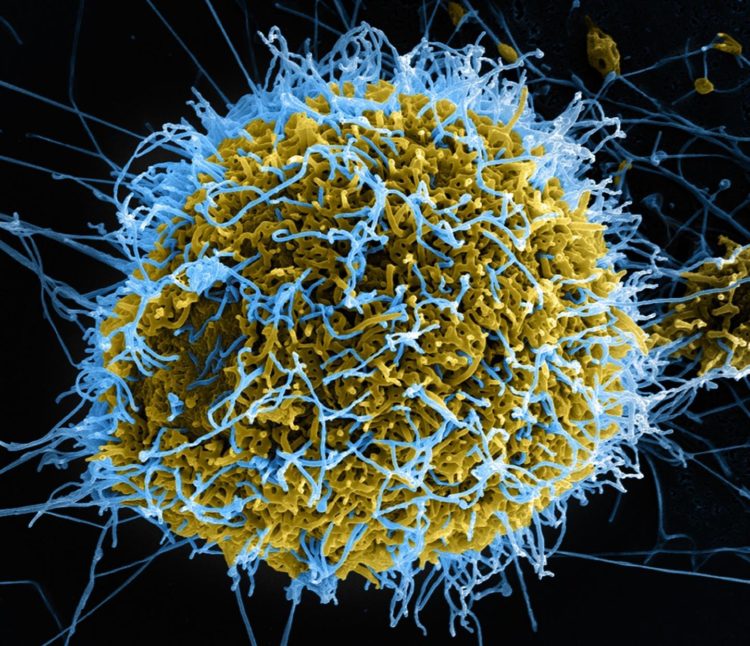
Credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
The situation is extraordinary: there have only ever been four declarations of public health emergencies of international concern in the past and now there are two at the same time. Whilst the risks associated with the novel coronavirus are still unclear, people in the Democratic Republic of the Congo are still battling with an outbreak of the deadly Ebola virus which has been ongoing since 2018 and has already claimed over 2000 lives. One issue is the precise characterisation of the pathogen because the ebolaviruses, like lots of viruses, appear in various genetic forms. Only the analysis of its genetic material provides the information necessary to develop specific tests for diagnosis and decide on efficient measures for controlling the outbreak. A German Center for Infection Research (DZIF) team at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin has now developed a test which accelerates the process of identifying the genetic makeup of the virus.
There have been multiple Ebola outbreaks in the last decades. Since 2013, at least eight countries have been affected and 30,000 people have contracted the virus. The origin of these outbreaks is often unclear and they are caused by various ebolavirus variants. “At the moment, it often takes months to develop the right tools to fully characterise the genetic material of the ebolavirus causing an outbreak” explains Professor Jan Felix Drexler, a scientist at the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF) and Charité. “However, this knowledge is crucial for developing specific diagnostic tests, identifying transmission chains and eventually controlling the outbreak.”
The scientists in Professor Drexler’s team have now developed a test which provides information about the genetic material of new ebolaviruses regardless of the species or the variant, that is, of the genetic makeup. The test is based on the commonly used polymerase chain reaction (PCR), using which the genetic material can be amplified in a manner that allows precise sequencing. The new test is compatible with various technical procedures such as high-throughput sequencing. It has been tested with four different ebolavirus species.
“In cases in which different regions and countries are affected by outbreaks of this kind in particular, it is necessary to establish whether the case in question relates to the spread of a previously known variant of the virus or a new outbreak,” explains the virologist. This is exactly what the new test can now determine in one process. “Both in the current outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and in future outbreaks, we may now be able to characterise the trigger more quickly and take appropriate effective measures to end the outbreak,” says the scientist.
###
Scientists from Charité and Marburg DZIF are involved in the current study within the framework of the DZIF working group on “Virus detection and preparedness” and have the use of a high-security laboratory which is equipped for research into highly contagious viruses. The research work was carried out in partnership with the rapidly deployable health expert group (SEEG) at the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) and, in addition to the DZIF, it also received funding from the EU and the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ). The establishment of the method in the GIZ global partner laboratories is currently being tested.
Media Contact
Dr. Jan Felix Drexler
[email protected]
49-304-505-25461
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.