In the heart there are two different subtypes of beta-adrenergic receptors – beta1 and beta2 – which are activated by the stress hormones adrenaline and noradrenaline. They both trigger the strongest stimulation of the heart rate and pumping capacity that we know of. The two subtypes are highly similar biochemically, but differ substantially in terms of their functional and therapeutic relevance.
Both receptor types can stimulate the heart in the short term, yet when the beta1 receptor is activated over a prolonged period of time, it has a range of effects that are not seen with beta2. Beta1 can elicit a number of persistent changes and is endowed with the ability to initiate – oftentimes detrimental – growth of the heart muscle cells by activating various genes.
Recent studies by researchers at the Universities of Würzburg and Erlangen, the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (MDC) in Berlin, and the ISAR Bioscience Institute in Munich-Planegg have now shed light on the mechanisms behind these different effects. The research teams have published the results of their work in the current issue of the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA.
Special ligands and new microscopy methods
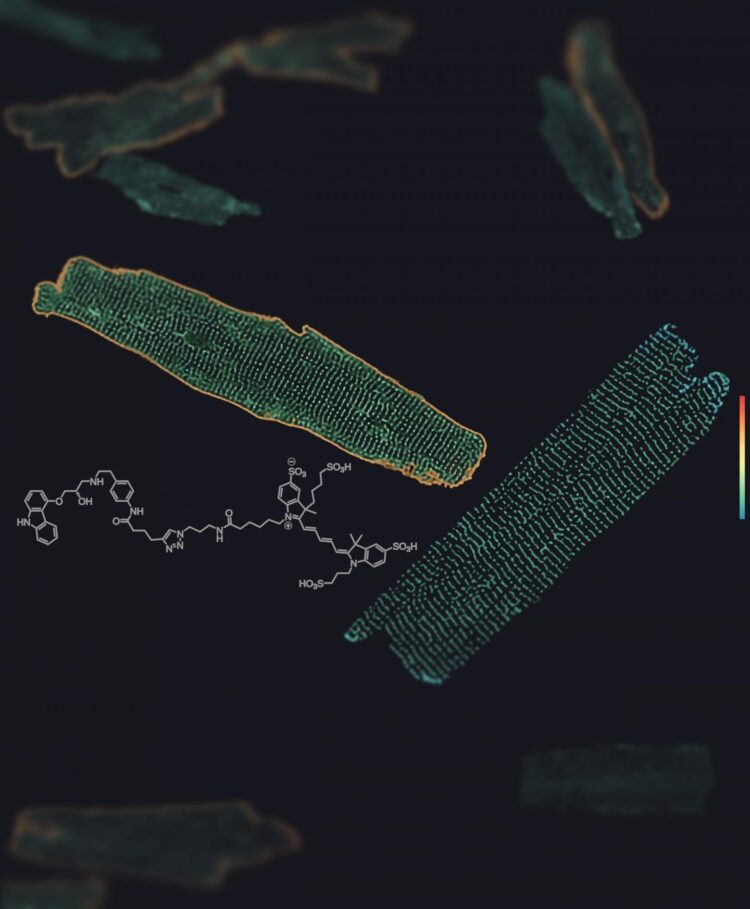
“Using a fluorescent ligand synthesized at the University of Erlangen and novel highly sensitive microscopy methods, we were able to show for the first time where these receptors are located on heart muscle cells,” explains Professor Martin Lohse of the Institute of Pharmacology and Toxicology at the Julius Maximilians University of Würzburg (JMU). He is co-lead author of the study along with Dr. Paolo Annibale, who is acting head of the MDC’s Receptor Signaling Lab. “The endogenous receptors are expressed at relatively low levels,” explains Annibale. “To detect their movement, it was necessary to use a form of spectroscopy based on the analysis of the signal’s minute fluorescence fluctuations.”
This revealed that beta1 receptors are found on the entire surface of heart muscle cells, while beta2 receptors are exclusively found in specific structures in these cells called T-tubules. Through invaginations of the cell surface, these tubules create a pipe-like network that runs through the entire interior of heart muscle cells. “One of the research focuses of our team at the MDC is the relationship between receptor function and subcellular localization,” adds Annibale. “So the biophysical environment of T-tubules, which have curved membranes, is of particular interest to us.”
Not all heart muscle cells have beta1 receptors
Another surprising finding of the study is that not all heart muscle cells have these receptors. “There are apparently different types or states of heart muscle cells, so not all cells respond to adrenaline,” Lohse said. Until now, it was assumed that heart muscle cells in the large chambers were all the same.
New target for heart failure therapy
It has been known for many years that in chronic heart failure, too much adrenaline and noradrenaline circulate in the bloodstream and stimulate the heart to such an extent that it causes changes in the heart and its cells to grow. This initially compensates for heart failure, but in the long run the excessive growth damages the heart. Therefore, based in part on earlier findings by the Würzburg team, blocking beta receptors has become the accepted therapy for chronic heart failure.
The new findings now show why beta1 receptors play a much greater role in producing these adverse effects than beta2 receptors. Beta1 receptors are localized on the entire cell surface, enabling them to have a more diverse impact than beta2 receptors. The new knowledge about the differential localization and distinct functional effects of beta1 and beta2 receptors in the heart could possibly be exploited to develop better therapies for chronic heart failure. These would selectively inhibit the harmful effects of beta receptors (such as heart muscle cell growth), while at the same time activating the beneficial effects (such as stimulation of heart function).
###
Media Contact
Martin Lohse
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.