Credit: Yuri Kovalev
Astrophysicists from the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, the Lebedev Physical Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences (LPI RAS), and NASA have found an error in the coordinates of active galactic nuclei measured by the Gaia space telescope, and helped correct it. The findings, published in The Astrophysical Journal, also serve as an independent confirmation of the astrophysical model of these objects.
“One of the key results of our work is a new and fairly unexpected way of indirectly studying the optical emission from the central regions of active galactic nuclei. There is a lot that direct optical observations cannot show us. But radio telescopes proved useful in complementing the picture,” commented Alexander Plavin, a researcher at MIPT’s relativistic astrophysics lab and a doctoral student at LPI RAS.
While the precision of the coordinates obtained by Earth-based optical telescopes is quite limited, orbital observatories such as Gaia offer a way around this. Launched in 2013, it receives signals from relatively remote cosmic sources and retrieves their coordinates with a superior precision.
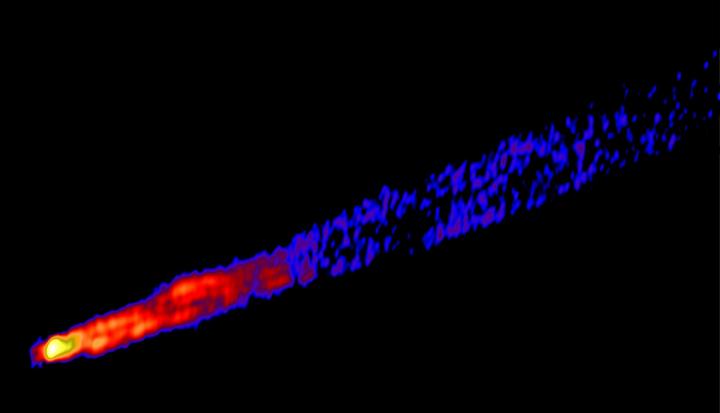
Before Gaia, the most precise coordinates were measured by radio telescope arrays (figure 1). These are systems of telescopes that can pick up a low-frequency signal — that is, radio waves — with a decent resolution. That way rather detailed images can be produced, but the objects’ positions in space are determined with somewhat less precision than that of Gaia.
The MIPT-LPI team found that, for all its precision, Gaia is not infallible, too. A comparison between the data from Gaia and radio telescopes (for example, figures 2-3) revealed a systematic error in the orbital observatory’s measurements of an entire class of celestial objects, called active galactic nuclei. As a result, the most accurate space maps are those that rely on orbital observations backed by Earth-based telescopes, whose radio data enable the coordinates to be corrected.
An active galactic nucleus is a compact and very bright region at the center of a galaxy. The emission spectra of AGNs differ from those of the stars, which raises the question about what object is at the center. The current consensus is that AGNs harbor black holes absorbing the matter of their host galaxies. In addition to the galactic disk, the bright nucleus, and a dust cloud around it, such systems can include powerful outflows of matter known as jets. Depending on the nature of the jet, an AGN may be classified as a quasar, a blazar, or otherwise.
Yuri Kovalev, who heads the astrophysics labs at MIPT and LPI RAS, explained: “We hypothesized that the jet may be responsible for the systematic error in the coordinates of the active galactic nuclei measured by Gaia. This indeed proved to be the case. It turned out that if an object has a sufficiently long jet, Gaia perceives the source to be much farther along the jet direction than the radio telescopes.”
The effect cannot be written off as random, because the offset was in the direction of the jet, and a statistically significant error was only observed for the AGNs with the longest “tails.” Namely, those whose jets were orders of magnitude larger than the size of the galaxies themselves. The magnitude of the offset was comparable to the length of the jets.
Since last year, Gaia has also been providing information on the visible “colors” of the galaxies. This has enabled the researchers to determine the individual coordinates and contributions to the emission spectrum of the various parts of the galaxy: the source, disk, jet, and stars. The coordinate shifts proved to be primarily due to the jets being long and the accretion disks being small. That said, measuring stellar emission has almost no effect on the precision with which the position of a galaxy is determined.
These findings led the authors to conclude that astrophysical effects related to long jets are capable of confusing the Gaia orbital observatory. This means that it cannot be regarded as a fully credible independent source of data on quasar coordinates. To obtain better data, the space telescope needs to be backed with ground-based radio observations (figure 3).
“In the future, by combining observation results, we can see the structure of the central disk-jet system in a quasar in minute detail — with subparsec resolution [where a parsec is an astronomical unit of distance equal to about 3 ¼ light years]. Direct optical telescope observations yield no such images, yet we can get them!” Plavin added.
The findings are independent evidence in support of the unified AGN model. It explains the behavior of the various kinds of AGNs in terms of their orientation in space relative to the observer, rather than in terms of their inner workings.
Being able to precisely measure the positions of celestial objects outside our galaxy is important from a practical standpoint: It is their positions that serve as the best reference for the most punctual coordinate systems, including those underlying GPS and its Russian counterpart GLONASS.
###
This research was supported by the Russian Science Foundation.
Media Contact
Varvara Bogomolova
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




