Study continues with rheumatoid arthritis patients
Credit: Anne Roivainen
The preliminary trial results of a novel radiopharmaceutical for PET imaging of inflammation developed at the University of Turku, Finland, have been published. The compound, which targets the vascular adhesion protein 1 (VAP-1) that regulates inflammatory cell traffic, is the first radiopharmaceutical that has been developed completely in Finland and has advanced to clinical trials. In the study that started with healthy volunteers, the radiopharmaceutical was found to be well tolerated and safe.
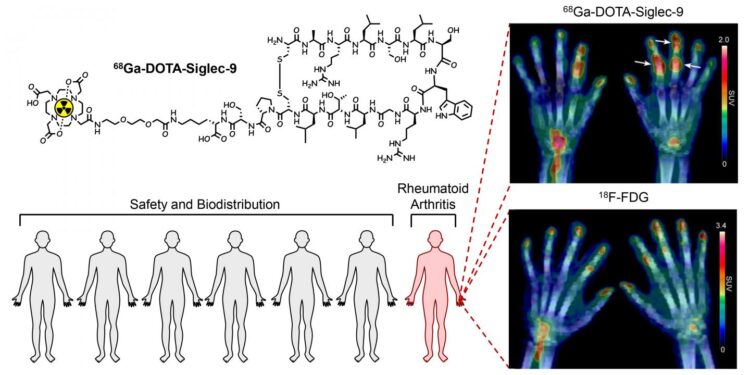
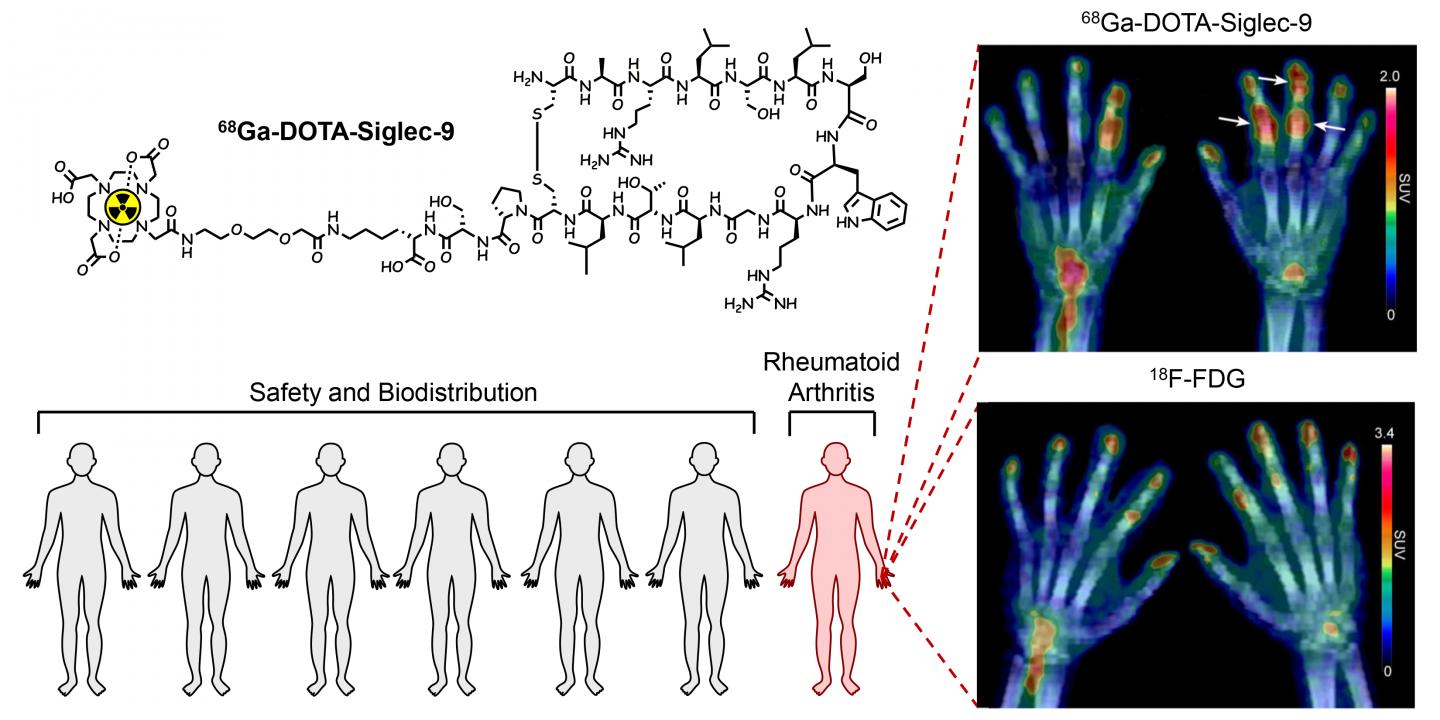
The radiopharmaceutical is 68Ga-labelled Siglec-9 peptide.
“The dose of the radiopharmaceutical used in PET imaging is thousands of times lower when compared with the regular drugs. Studies with new radiopharmaceuticals are therefore safer than the usual drug research studies,” explain Researchers Riikka Viitanen and Olli Moisio from the Turku PET Centre.
The study also included the imaging of a patient with early rheumatoid arthritis. The inflamed joints were clearly visible in the PET images, and the radiopharmaceutical seems to effectively target inflamed tissue.
“Our radiopharmaceutical is a product of long-term preclinical research work, and it is rewarding to see results that match our expectations. The research results are promising, but all novel radiopharmaceuticals must fulfil strict medical and statistical criteria before they can be considered for general research use. Therefore, we will continue the study with voluntary rheumatoid arthritis patients,” says the leader of the research group, Professor Anne Roivainen from the University of Turku.
“This study is unique and has long, innovative history in the University of Turku. Now, it has been proven that the new radiopharmaceutical works in humans, rejoices Academician of Science,” Professor Sirpa Jalkanen.
The purpose of the new radiopharmaceutical is to advance both the diagnostics of inflammatory diseases and drug development with molecular imaging. The research field is rapidly developing, and the Turku PET Centre, research institute of the University of Turku, Åbo Akademi University, and Turku University Hospital is one of the field’s leading research centres in Europe.
###
The study was funded by the Academy of Finland, Hospital District of Southwest Finland (ERVA funding), Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation, Sigrid Jusélius Foundation, Business Finland, Finnish Cultural Foundation, and Finnish Foundation for Cardiovascular Research.
The study was published in the Journal of Nuclear Medicine in April 2021.
Media Contact
Anne Roivainen
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.