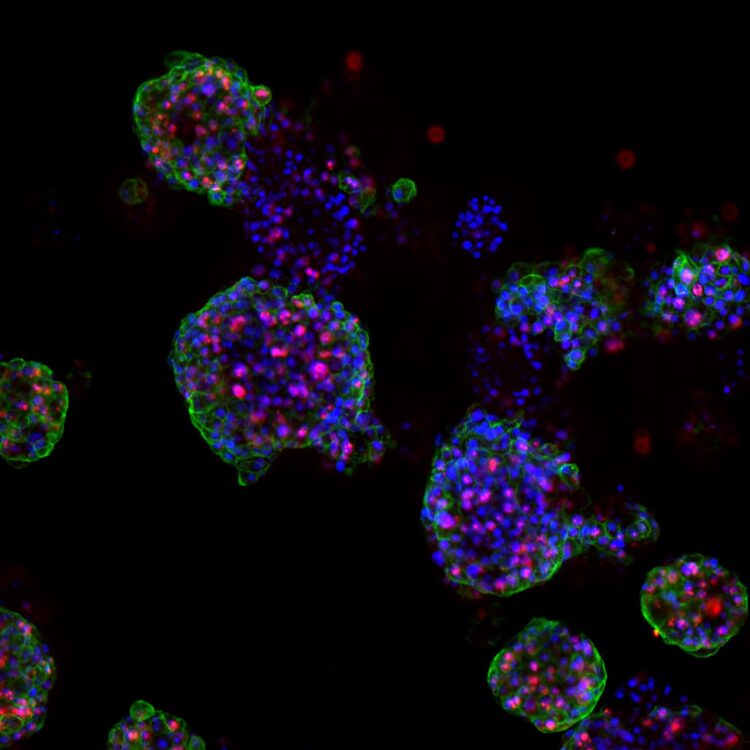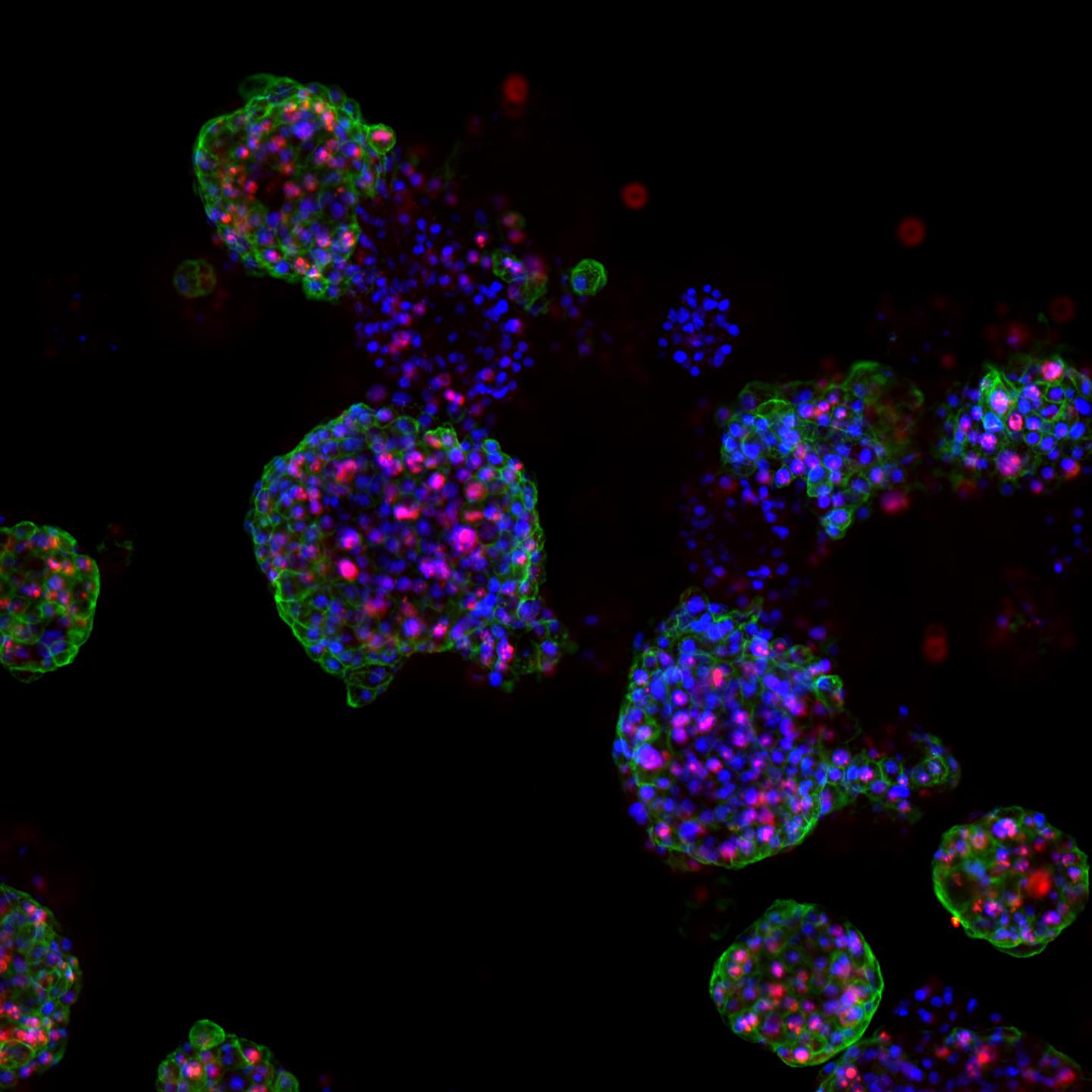
Credit: Marianna Kruithof-de Julio and Marta De Menna
In the EU alone, 78,800 men died of prostate cancer last year. While tumors discovered at an early stage can often be completely removed by surgery and radiation therapy, the prospects of successful treatment are reduced if the cancer has further metastasized. At present, physicians cannot predict drug response or therapy resistance in patients.
Three-dimensional structures
The team led by PD Dr. Marianna Kruithof-de Julio at the Urology Research Laboratory at the Department for BioMedical Research (DBMR) of the University of Bern and Inselspital Bern, has developed a new strategy for the generation of prostate cancer organoids that can contribute to assess therapy response, their work is published in the latest issue of Nature Communications. Drs Sofia Karkampouna and Federico La Manna, the two lead co-authors of the paper, spent over one and a half year in optimizing and efficient protocol for the generation of the patient derived organoids and their detailed characterization. Moreover, in collaboration with the NEXUS Personalized Health Technologies, they have meticulously developed a medium-throughput screen for drug testing.
The researchers led by PD Dr. Kruithof-de Julio have demonstrated that patient-derived organoids retain relevant characteristics of the prostate carcinoma from which they have been originated: not only are they characterized by the same genetic mutations, but they also exhibit similar gene activity patterns.
Paving the way for personalized medicine
PD Dr. Kruithof-de Julio and her collaborators first generated a novel early stage, patient derived xenograft that is treatment naïve, then tested 74 different drugs on organoids from this and other experimental tumor models – identifying 13 compounds that reduced prostate cancer cell viability.
The researchers then tested the efficacy of these compounds on organoids from five prostate cancer patients – two with early-stage tumors and three with advanced metastatic tumors. Interestingly, among the hits ponatinib, so far approved for the treatment of leukemia, proved to be particularly effective in reduction of organoid viability and tumor growth in vivo.
However, for PD Dr. Kruithof-de Julio, the significance of these results lies not only in the drug repurposing but more importantly in promoting an approach that the medical community can undertake. “Our results pave the way for personalized medicine. In our study we only analyzed data from five patients retrospectively,” says Kruithof-de Julio. “But we clearly showed that the method would be in principle feasible. Growing the organoids and drug testing can be accomplished in two weeks, a time frame that is compatible with clinical decision making. In collaboration with the Urology Department of the Inselspital, led by Prof Thalmann, we have now already been able to prove this in several cases.”
“In my clinical activity, I am regularly confronted by tumors that do not respond to therapy or for which we do not know which therapy to use”, says Thalmann. “This is a further step in the direction of individualized medicine, where we might be able to tailor the treatment to the tumor during the course of the disease and better understand its biology.” With this approach, the researchers hope to treat patients more efficiently with less side effects and diminished costs.
###
Media Contact
MARIANNA KRUITHOF-DE JULIO
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.