Credit: Department of Molecular Neuroscience,TMDU
Tokyo, Japan — Migraines affect millions of people worldwide, often lasting days and severely disrupting lives. More than simply super-intense headaches, some migraines actually result from pathological excitation of neurons in the brain. A new study in mice led by Kohichi Tanaka at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) shows that susceptibility to migraines could be related to a molecular transporter that normally works to prevent excessive excitation of neurons.
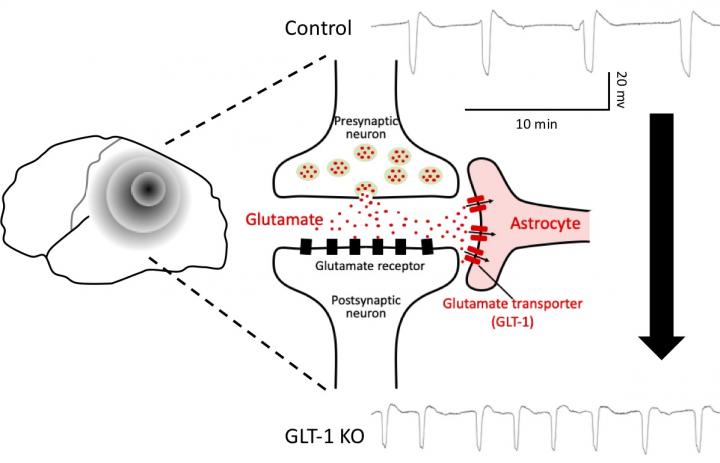
Neurons in the brain communicate with each other by passing along molecules called neurotransmitters. After a neurotransmitter takes care of business, it is transported away from the synapse–the space between two neurons–so that it cannot be used over and over again. This process is called reuptake, and is one of many ways in which over-excitation of neurons in the brain is prevented. Migraines are related to a condition called cortical depression, in which a large wave of hyperactivity spreads across the brain, followed by a wave of inhibition, or depressed brain activity. Tanaka and his team hypothesized that susceptibility to cortical spreading depression is related to disrupted transport of glutamate, the most common excitatory neurotransmitter.
In turns out that mammals have four molecules that transport glutamate, and three of them are in the cerebral cortex. To determine which of these, if any, is related to cortical spreading depression, the researchers created three strains of knockout mice, each of which lacked one of the three cortical glutamate-transporter genes. They found that when mice lacked the GLT-1 transporter, cortical spreading depression occurred more frequently and spread more quickly than in control mice or in the other knockout mice.
“We know that 90% of glutamate is transported by GLT-1 back into astrocytes, not neurons,” says Tanaka. “Our findings thus highlight another important function of glial cells in the brain as they support neuronal function.”
To confirm their findings, the team then measured the amount of glutamate outside of cells using a platinum-iridium electrode coated with glutamate oxidase. When glutamate oxidase interacts with glutamate, it creates a negative current that can be detected by the electrode very quickly, allowing almost real-time measurements of glutamate concentration in the region.
“A fast biosensor is critical,” explains Tanaka, “because cortical spreading depression only lasts about 5 minutes, and the changes in glutamate concentration could never be found using conventional methods that take minutes to hours of sampling.” When testing the three knockout mice, only the GLT-1 knockout mice produced current that differed from that of the control mice. This means that the greater and faster accumulation of glutamate outside of neurons resulted from impaired uptake by astrocytes.
“Abnormal glutamate reuptake by astrocytes is just one way overexcite neurons,” says Tanaka. “Nevertheless, if GLT-1 proves to be disrupted in people who have migraines, drug therapy that acts to increase glial reuptake of glutamate could be a reasonable therapeutic approach.”
###
The article, “Glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 determines susceptibility to spreading depression in the mouse cerebral cortex,” was published in Glia at DOI: 10.1002/glia.23874.
Media Contact
Kohichi TANAKA
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




