Credit: Kanazawa University
Most lung cancers are of a type called non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). This type of cancer is relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, so NSCLC therapies are usually based on drug treatment. Alectinib is a drug commonly used for treating patients with NSCLC. It addresses a gene rearrangement known as ALK that occurs in 3 to 5% of NSCLC patients (alectinib belongs to a class of drugs called ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors). It has been unclear, however, whether there is a correlation between the use of alectinib and the poorer prognosis in ALK-NSCLC patients in which secondary cancer mutations are observed — the latter are known to occur with a frequency of about 25%. Now, Azusa Tanimoto from Kanazawa University and colleagues have investigated this correlation. They found that such secondary mutations reduce the efficacy of alectinib, but they also suggest how to overcome this issue.
The researchers looked at data on 124 NSCLC patients who were treated with ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors, including alectinib, and who had tested positive for the ALK gene rearrangement. Out of these, for 31 patients, a secondary gene rearrangement known as TP53 mutation was detected. Tanimoto and colleagues looked at whether there is a correlation between alectinib use and TP53 mutations in this group of patients.
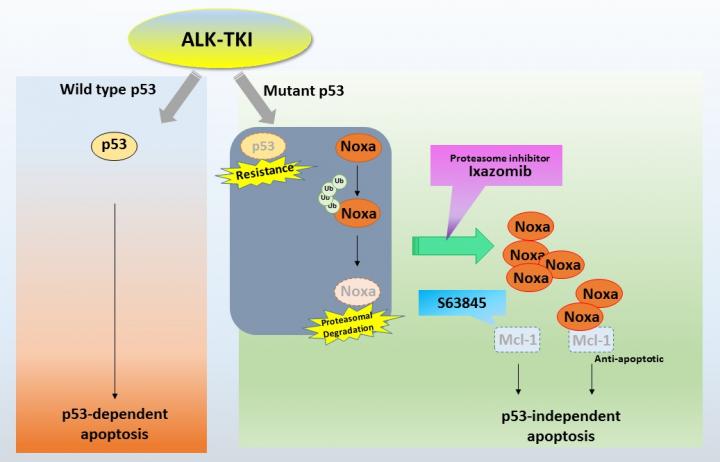
The data showed that the cancer’s progression-free survival was significantly poorer in patients with TP53 mutations who received alectinib treatment. (The same conclusion was obtained for other treatments with other ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors.) The resistance to the drugs is linked to the loss of normal p53 function in ALK-rearranged NSCLC; p53 refers to a set of proteins that are known to play a role in preventing cancer formation.
The scientists then investigated how to overcome the adverse effect of alectinib when secondary TP53 mutations occur. Based on their insights into the biochemical mechanisms at play, they proposed to combine alectinib with another drug: ixazomib. The latter is a drug from the class of proteasome inhibitors, which block the action of proteasomes, which in turn break down proteins. Experiments in mice showed promising results: general tumor shrinkage, and complete regression of 3 out of 8 tumors.
The findings of Tanimoto and colleagues show that the combined use of a proteasome inhibitor and alectinib restores the latter’s unfavorable efficacy in ALK-rearranged NSCLC. The scientists further conclude: “Based on these [clinical and preclinical] data, this combination therapy is needed to be validated in … clinical trials.”
[Background]
NSCLC
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) and small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) are the two types of lung cancer. 85% of all lung cancers are of the NSCLC type. NSCLCs are less sensitive to chemotherapy than SCLCs, making drug treatment of the highest importance.
Alectinib is a drug used for treating NSCLC, normally with good efficiency. However, in certain scenarios where gene alterations occur, the drug has an adverse effect, as now shown by Azusa Tanimoto from Kanazawa University and colleagues. Tanimoto and colleagues further show that in such situations, combining alectinib with another drug (of the proteasome-inhibitor type) restores its efficacy.
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
A tyrosine kinase inhibitor is a drug inhibiting (that is, preventing or reducing the activity of) a specific tyrosine kinase. A tyrosine kinase is a protein (enzyme) involved in the activation of other proteins by signaling cascades. The activation happens by the addition of a phosphate group to the protein (phosphorylation); it is this step that a tyrosine kinase inhibitor inhibits. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors are used as anticancer drugs. One such drug is alectinib, used to treat NSCLC.
###
Media Contact
Hiroe Yoneda
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




