Credit: ETH Zurich / Helma Wennemers
In recent years, the number of targeted cancer drugs has continued to rise. However, conventional chemotherapeutic agents still play an important role in cancer treatment. These include platinum-based cytotoxic agents that attack and kill cancer cells. But these agents also damage healthy tissue and cause severe side effects. Researchers at ETH Zurich have now identified an approach that allows for a more selective cancer treatment with drugs of this kind.
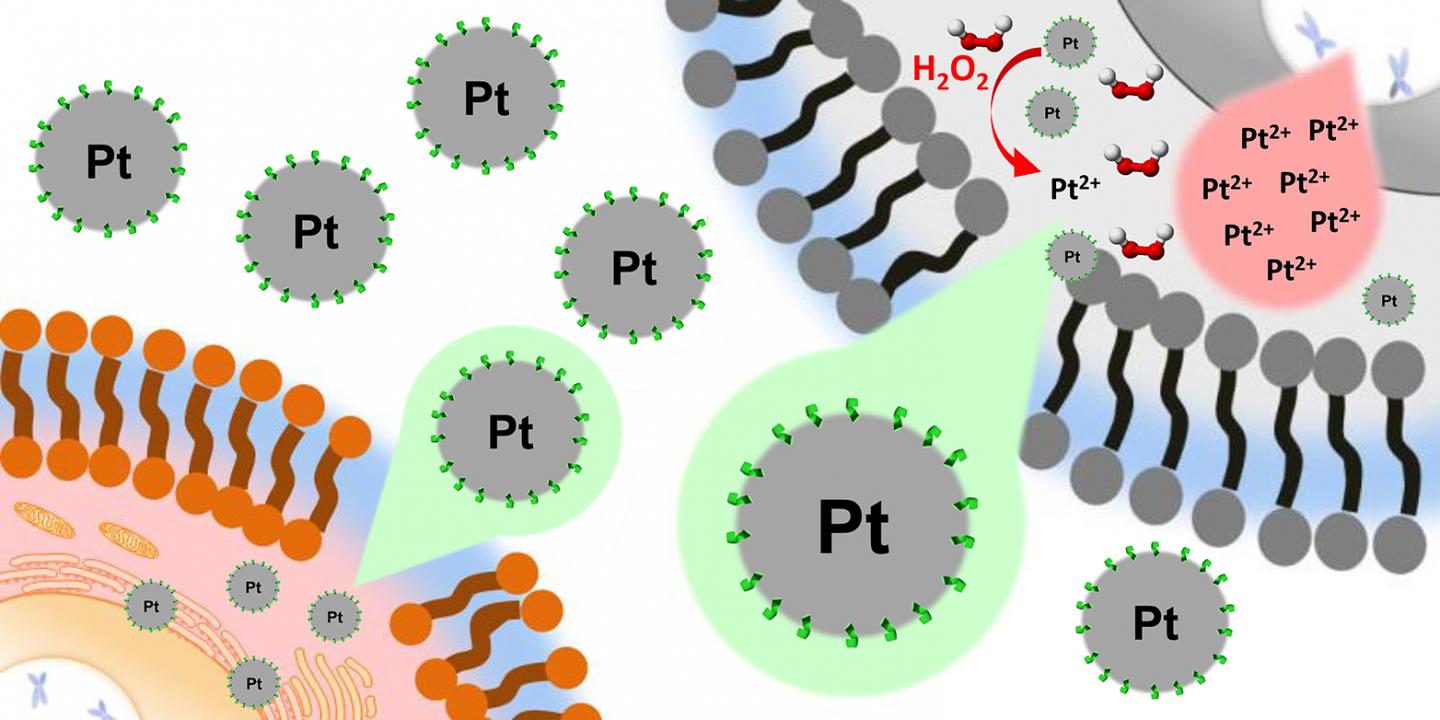
Platinum can be cytotoxic when oxidised to platinum(II) and occurs in this form in conventional platinum-based chemotherapeutics. Non-oxidised platinum(0), however, is far less toxic to cells. Based on this knowledge, a team led by Helma Wennemers, Professor at the Laboratory of Organic Chemistry, and Michal Shoshan, a postdoc in her group, looked for a way to introduce platinum(0) into the target cells, and only then for it to be oxidised to platinum(II). To this end, they used non-oxidised platinum nanoparticles, which first had to be stabilized with a peptide. They screened a library containing thousands of peptides to identify a peptide suitable for producing platinum nanoparticles (2.5 nanometres in diameter) that are stable for years.
Oxidised inside the cell
Tests with cancer cell cultures revealed that the platinum(0) nanoparticles penetrate into cells. Once inside the specific environment of liver cancer cells, they become oxidised, triggering the cytotoxic effect of platinum(II).
Studies with ten different types of human cells also showed that the toxicity of the peptide-coated nanoparticles was highly selective to liver cancer cells. They have the same toxic effect as Sorafenib, the most common drug used to treat primary liver tumours today. However, the nanoparticles are more selective than Sorafenib and significantly more so than the well-known chemotherapeutic Cisplatin. It is therefore conceivable that the nanoparticles will have fewer side effects than conventional medication.
Joining forces with ETH Professor Detlef Günther and his research group, Wennemers and her team were able to determine the platinum content inside the cells and their nuclei using special mass spectrometry. They concluded that the platinum content in the nuclei of liver cancer cells was significantly higher than, for instance, in colorectal cancer cells. The authors believe that the platinum(II) ions – produced by oxidation of the platinum nanoparticles in the liver cancer cells – enter the nucleus, and there release their toxicity.
“We are still a very long and uncertain way away from a new drug, but the research introduced a new approach to improve the selectivity of drugs for certain types of cancer – by using a selective activation process specific to a given cell type,” Wennemers says. Future research will expand the chemical properties of the nanoparticles to allow for greater control over their biological effects.
###
Reference
Shoshan MS, Vonderach T, Hattendorf B, and Wennemers H: Peptide-Coated Platinum Nanoparticles with Selective Toxicity against Liver Cancer Cells. Angewandte Chemie 2019, 58: 1, doi: 10.1002/anie.201813149 [http:dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201813149]
Media Contact
Helma Wennemers
[email protected]
41-446-333-777
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




