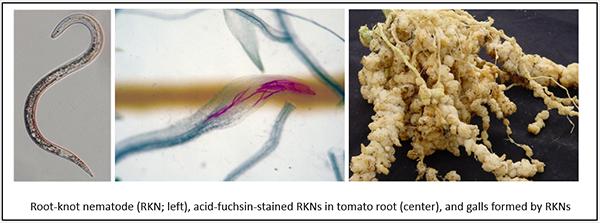
Credit: Taketo Fujimoto, Hiroshi Abe, Takayuki Mizukubo, and Shigemi Seo
Root-knot nematodes (RKNs, Meloidogyne spp.) infect a broad range of plants, including several agriculturally important species such as cotton, soybean and corn, as well as various vegetables and ornamentals. These parasites cause roots to develop galls that result in severe plant damage and, ultimately, important crop losses. Growers currently use synthetic nematicides to manage RKNs; however, these compounds are detrimental to the microbial diversity of soil and harmful for the environment. Thus, it is necessary to develop alternative sustainable control methods.
“We have been seeking natural compounds that activate plant defense systems and do not have direct nematicidal activity using the combination of RKNs and their host plants,” explained Shigemi Seo, researcher at the National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences of Japan. “We were most excited to discover that phytol, a chlorophyll constituent, has an inhibitory effect on the root invasion by a certain harmful plant nematode without killing it. We did not expect this molecule to be involved in RKN resistance.”
“We noticed that plant leaves discolored yellow or pale green when their roots were parasitized by RKNs and confirmed a decrease in chlorophyll content in such leaves. We hypothesized that chloroplast-related compounds would accumulate in RKN-parasitized roots and induce the host defense against RKNs. We analyzed root metabolites and found accumulation of phytol, a constituent of chlorophyll. When phytol was applied to plant roots, RKN invasion of the roots was inhibited. This inhibition was not due to the direct nematicidal activity of phytol, since this compound did not kill RKNs,” added Seo.
Even though phytol has been known for several years as a constituent of chlorophyll and is a ubiquitous compound present in almost all photosynthetic organisms, its role as a plant defense-signaling molecule remained unexplored. “Phytol may be a promising material for eco-friendly agrochemicals for the control of RKNs. We are currently investigating its effects on not only other plant parasitic nematodes but also other pathogenic microorganisms.”
For more information about this study, read “Phytol, a Constituent of Chlorophyll, Induces Root-Knot Nematode Resistance in Arabidopsis via the Ethylene Signaling Pathway” in the MPMI journal.
###
Media Contact
Juan S. Ramirez-Prado
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




