A molecule found in the venomous toadfish Thalassophryne nattereri has proved capable of controlling lung inflammation and could be the basis for a more effective asthma drug. The research was supported by FAPESP and conducted by scientists at Butantan Institute in São Paulo, Brazil. An article describing the results is published in the journal Cells.
Credit: Mônica Lopes-Ferreira/CeTICS
A molecule found in the venomous toadfish Thalassophryne nattereri has proved capable of controlling lung inflammation and could be the basis for a more effective asthma drug. The research was supported by FAPESP and conducted by scientists at Butantan Institute in São Paulo, Brazil. An article describing the results is published in the journal Cells.
A welter of fish species live in freshwater, seawater and a mixture of the two, and some of them are venomous. They have spines or stingers connected to venom glands, which are a kind of pouch full of molecules, large and small, that are toxins. For these fish, venom is a defensive weapon against predators.
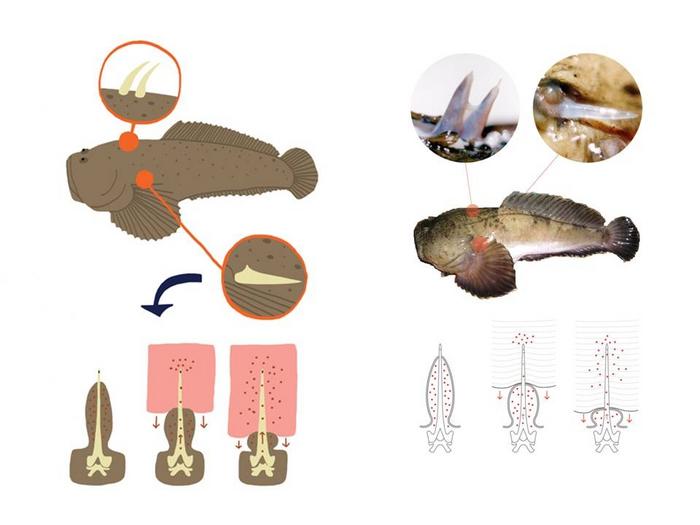
T. nattereri is a case in point. It is a small fish that inhabits calm shallow coastal waters in North and Northeast Brazil. Fishermen call it niquim, an Indigenous word for fish. Its venom apparatus consists of two dorsal and two lateral spines covered by a membrane connected to the venom glands at the base of the fins. When the spine penetrates the victim, the integumentary sheath enclosing the gland presses out the venom into the duct. When stepped on or touched, the animal defends itself by injecting venom, causing intense pain, wounds that swell, and potentially necrosis.
“We started studying the venom of T. nattereri in 1996 because we wanted to analyze its toxins in order to develop a treatment for people injured in accidents,” said Mônica Lopes-Ferreira, a biologist at the Center for Research on Toxins, Immune Response and Cell Signaling (CeTICS), one of the Research, Innovation and Dissemination Centers (RIDCs) funded by FAPESP.
“We were surprised to discover a small molecule, a peptide, that our studies here at the laboratory showed to have anti-inflammatory properties. An entirely novel molecule no one had ever discovered,” said Lopes-Ferreira, who has a PhD in immunology from the University of São Paulo (USP) and postdoctoral studies in biochemistry and pharmacology at Butantan Institute.
According to the article, mice treated with TnP (T. nattereri peptide) displayed no airway hyperreactivity or lung remodeling. The TnP acted systemically on secondary lymphoid organs and locally on the lungs, inhibiting production of cytokines Th2 and Th17. It also prevented hyperplasia of mucus-producing cells and decreased the thickening and deposition of sub-epithelial collagen. “Our results showed TnP to be a candidate molecule for treatment of airway remodeling associated with inflammatory diseases such as asthma,” the authors write.
“Many diseases cause inflammation. We chose asthma to test TnP using animal models in the laboratory and concluded that it was safe and efficacious. It improved the lung inflammation caused by asthma. This is a Brazilian discovery and we’ve taken care to protect it by filing for a patient,” Lopes-Ferreira said. “We now mean to continue with the research. The more we discover, the more we’ll know about the diseases TnP can treat. It will also be very important to partner with a pharmaceutical company that wants to invest in TnP so that a medical drug can be developed.”
A study supported by FAPESP and reported in October 2016 found that T. nattereri has a molecule with potential action against sclerosis. The results of the study, which was also conducted under the aegis of CeTICS, were published in the journal Toxicon.
About São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP)
The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) is a public institution with the mission of supporting scientific research in all fields of knowledge by awarding scholarships, fellowships and grants to investigators linked with higher education and research institutions in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. FAPESP is aware that the very best research can only be done by working with the best researchers internationally. Therefore, it has established partnerships with funding agencies, higher education, private companies, and research organizations in other countries known for the quality of their research and has been encouraging scientists funded by its grants to further develop their international collaboration. You can learn more about FAPESP at www.fapesp.br/en and visit FAPESP news agency at www.agencia.fapesp.br/en to keep updated with the latest scientific breakthroughs FAPESP helps achieve through its many programs, awards and research centers. You may also subscribe to FAPESP news agency at http://agencia.fapesp.br/subscribe.
Journal
Cells
DOI
10.3390/cells12060924
Article Title
The Anti-Inflammatory Peptide TnP Is a Candidate Molecule for Asthma Treatment
Article Publication Date
17-Mar-2023




