Volume 11, Issue 23 of @Oncotarget reported that the authors have previously established that mi R-151a functions as an onco-mi R in non-small cell lung cancer cells by inducing partial EMT and enhancing tumor growth.
Credit: Correspondence to – Irene Munk Pedersen – [email protected]
Volume 11, Issue 23 of @Oncotarget reported that the authors have previously established that mi R-151a functions as an onco-mi R in non-small cell lung cancer cells by inducing partial EMT and enhancing tumor growth.
Here, the authors identify anti-mi R-151a as a molecule that promotes endothelial cell contacts and barrier properties, suggesting that mi R-151a regulates cell-cell junctions.
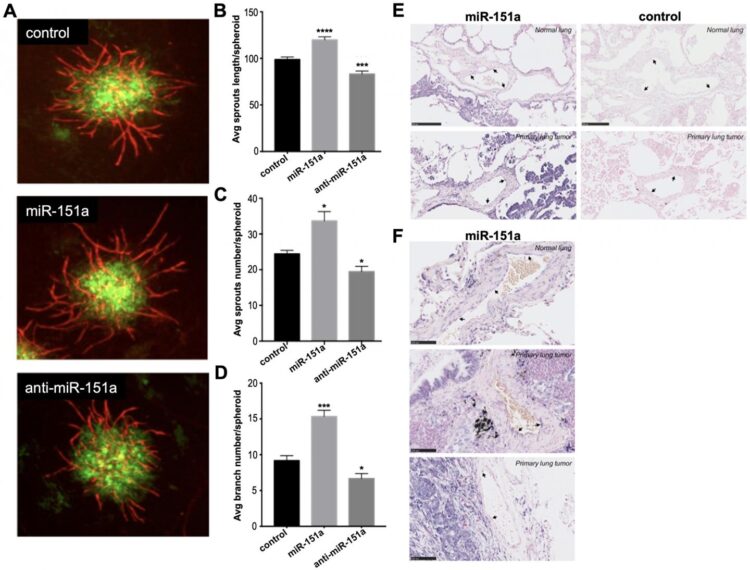
They find that induced mi R-151a expression enhances endothelial cell motility and angiogenesis and these functions depend on mi R-151a-induced Slug levels.
Moreover, The authors show that mi R-151a overexpression enhances tumor-associated angiogenesis in 3D vascularized tumor spheroid assays.
Their results suggest that mi R-151a plays multi-faceted roles in the lung, by regulating multiple functions in distinct cell types.
Dr. Irene Munk Pedersen from The University of California as well as The Scintillon Institute said, “Angiogenesis, or the growth of new networks of blood vessels from existing vessels, is an important natural process used for growth, healing, and reproduction.“
“The authors find that anti-mi R-375 and anti-mi R-151a strengthen cell-cell contact and endothelial cell barrier in primary lung endothelial cells, relative to control samples”
Proper regulation of angiogenesis is essential not only for developing an adult’s healthy organs to support growth and metabolism but also for disease progression since abnormal vessel growth and/or function are hallmarks of cancer, ischemic and chronic inflammatory diseases.
Slug and Snail may regulate a distinct but overlapping set of genes and therefore Snail may compensate for Slug in the Slug-knock-out context.
There is a need to characterize the repertoire of master mi R regulators in normal and diseased microenvironments to further understand how to restore the delicate balance of cell homeostasis when it has been lost.
The authors find that anti-mi R-375 and anti-mi R-151a strengthen cell-cell contact and endothelial cell barrier in primary lung endothelial cells, relative to control samples.
The Munk Pedersen Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Priority Research Paper, “Our results show that increased miR-151 expression, significantly promotes endothelial cell motility and angiogenesis in 2D and 3D models and that miR-151a-induced Slug expression is required for these endothelial cell properties. Our findings provide a new avenue to the understanding of the processes in the lung niche environment, and may facilitate the development of potential therapeutics against lung cancer.“
Media Contact
Ryan James Jessup
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.