Credit: Copyright 2021, Hisano et al., Shinshu University
Lysophospholipids are phospholipids that have just one fatty acid chain, and in recent years, the role of lysophospholipids in physiology and pathophysiology has attracted attention. Lysophosphatidylethanolamine (LPE) is a type of lysophospholipid that are reportedly present in the brain that consist of many species with different fatty acid chain lengths and degrees of unsaturation. The latest studies in animal models have reported elevated levels of LPE in the brain after traumatic brain injury and cerebral ischemia. Fluctuations in LPE concentration have also been reported in the plasma of patients with major depression and Alzheimer’s disease. Although these reports suggest the involvement of LPE in brain function, the role of LPE in the brain has remained unclear.
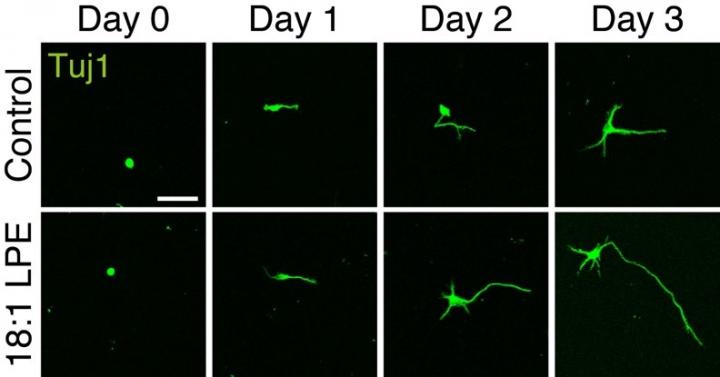
Therefore, a team of doctors led by Shinshu University’s Institute for Biomedical Sciences first analyzed the composition of LPE species in the mouse brain using mass spectrometry and decided to investigate the role of 18: 1 LPE in nerve cells, which is abundant in the brain. As a result, it was clarified that 18: 1 LPE has a function of promoting neurite outgrowth of cerebral cortical neurons. Furthermore, it was revealed that 18: 1 LPE protects neurons from cell death due to glutamate toxicity. These results suggested that LPE plays an important role in brain function. This is the first elucidation of the role of LPE in neurons of the central nervous system. Glutamate toxicity is considered to be a major cause of nerve cell death due to acute diseases such as brain damage and cerebral ischemia, and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Therefore, our finding is expected to contribute to the development of treatment for these nerve damage.
Corresponding author of the study Dr. Takeshi Uemura states, “the study confirmed that 18: 1 LPE, which is one of the LPE species most abundant in the brain, has a function of promoting neurite outgrowth and protecting against neuronal cell death due to glutamate toxicity. It is suggested that LPE plays an important role in brain function.”
The research group would like to further elucidate the physiological importance of LPE in the brain. Since there are other LPE species that are abundant in the brain besides 18: 1 LPE, the research group will investigate how other LPE species work in the brain. They will work with animal models to confirm whether symptoms such as nerve damage are improved by administration of LPE.
From a molecular biology perspective, it is important to clarify the receptor of LPE. The group believe that identifying specific receptors for individual LPEs and clarifying their signal transduction pathways will be the key to elucidating the physiological and pathophysiological roles of LPEs in the brain. The research group at Shinshu University’s Institute for Biomedical Sciences hopes to lead the development of neuroprotective and therapeutic agents for cranial nerve damage targeting LPE and its receptors.
###
Media Contact
Hitomi Thompson
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




