Researchers first to model COVID-19 completion vs. cessation study using machine learning
Credit: Florida Atlantic University/College of Engineering and Computer Science
In order to win the battle against COVID-19, studies to develop vaccines, drugs, devices and re-purposed drugs are urgently needed. Randomized clinical trials are used to provide evidence of safety and efficacy as well as to better understand this novel and evolving virus. As of July 15, more than 6,180 COVID-19 clinical trials have been registered through ClinicalTrials.gov, the national registry and database for privately and publicly funded clinical studies conducted around the world. Knowing which ones are likely to succeed is imperative.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University’s College of Engineering and Computer Science are the first to model COVID-19 completion versus cessation in clinical trials using machine learning algorithms and ensemble learning. The study, published in PLOS ONE, provides the most extensive set of features for clinical trial reports, including features to model trial administration, study information and design, eligibility, keywords, drugs and other features.
This research shows that computational methods can deliver effective models to understand the difference between completed vs. ceased COVID-19 trials. In addition, these models also can predict COVID-19 trial status with satisfactory accuracy.
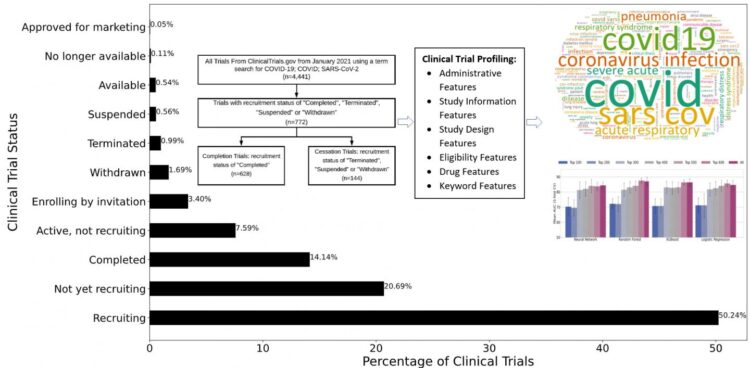
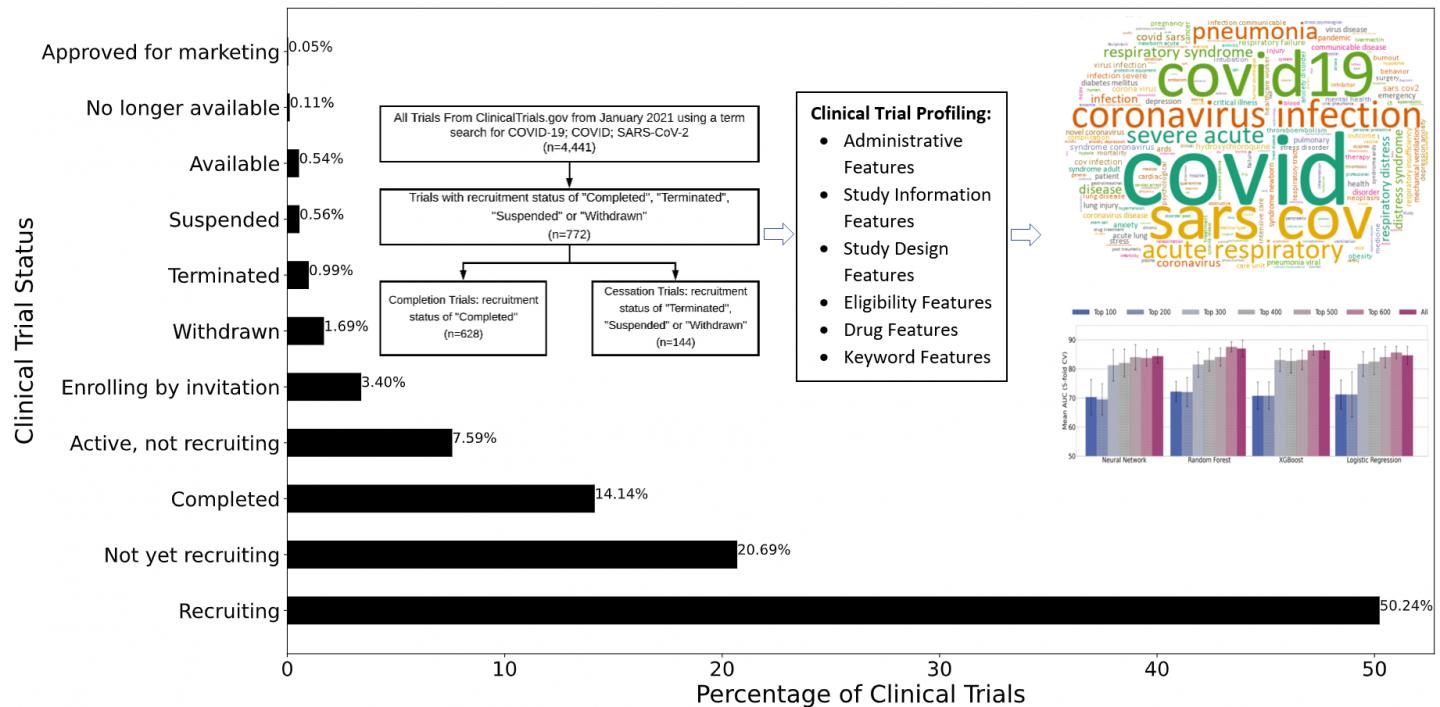
Because COVID-19 is a relatively novel disease, very few trials have been formally terminated. Therefore, for the study, researchers considered three types of trials as cessation trials: terminated, withdrawn, and suspended. These trials represent research efforts that have been stopped/halted for particular reasons and represent research efforts and resources that were not successful.
“The main purpose of our research was to predict whether a COVID-19 clinical trial will be completed or terminated, withdrawn or suspended. Clinical trials involve a great deal of resources and time including planning and recruiting human subjects,” said Xingquan “Hill” Zhu, Ph.D., senior author and a professor in the Department of Computer and Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, who conducted the research with first author Magdalyn “Maggie” Elkin, a second-year Ph.D. student in computer science who also works full-time. “If we can predict the likelihood of whether a trial might be terminated or not down the road, it will help stakeholders better plan their resources and procedures. Eventually, such computational approaches may help our society save time and sources to combat the global COVID-19 pandemic.”
For the study, Zhu and Elkin collected 4,441 COVID-19 trials from ClinicalTrials.gov to build a testbed. They designed four types of features (statistics features, keyword features, drug features and embedding features) to characterize clinical trial administration, eligibility, study information, criteria, drug types, study keywords, as well as embedding features commonly used in state-of-the-art machine learning. In total, 693 dimensional features were created to represent each clinical trial. For comparison purposes, researchers used four models: Neural Network; Random Forest; XGBoost; and Logistic Regression.
Feature selection and ranking showed that keyword features derived from the MeSH (medical subject headings) terms of the clinical trial reports, were the most informative for COVID-19 trial prediction, followed by drug features, statistics features and embedding features. Although drug features and study keywords were the most informative features, all four types of features are essential for accurate trial prediction.
By using ensemble learning and sampling, the model used in this study achieved more than 0.87 areas under the curve (AUC) scores and more than 0.81 balanced accuracy for prediction, indicating high efficacy of using computational methods for COVID-19 clinical trial prediction. Results also showed single models with balanced accuracy as high as 70 percent and an F1-score of 50.49 percent, suggesting that modeling clinical trials is best when segregating research areas or diseases.
“Clinical trials that have stopped for various reasons are costly and often represent a tremendous loss of resources. As future outbreaks of COVID-19 are likely even after the current pandemic has declined, it is critical to optimize efficient research efforts,” said Stella Batalama, Ph.D., dean, College of Engineering and Computer Science. “Machine learning and AI driven computational approaches have been developed for COVID-19 health care applications, and deep learning techniques have been applied to medical imaging processing in order to predict outbreak, track virus spread and for COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment. The new approach developed by professor Zhu and Maggie will be helpful to design computational approaches to predict whether or not a COVID-19 clinical trial will be completed so that stakeholders can leverage the predictions to plan resources, reduce costs, and minimize the time of the clinical study.”
###
The study was funded by the National Science Foundation awarded to Zhu.
About FAU’s College of Engineering and Computer Science:
The FAU College of Engineering and Computer Science is internationally recognized for cutting edge research and education in the areas of computer science and artificial intelligence (AI), computer engineering, electrical engineering, bioengineering, civil, environmental and geomatics engineering, mechanical engineering, and ocean engineering. Research conducted by the faculty and their teams expose students to technology innovations that push the current state-of-the art of the disciplines. The College research efforts are supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF), the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Department of Defense (DOD), the Department of Transportation (DOT), the Department of Education (DOEd), the State of Florida, and industry. The FAU College of Engineering and Computer Science offers degrees with a modern twist that bear specializations in areas of national priority such as AI, cybersecurity, internet-of-things, transportation and supply chain management, and data science. New degree programs include Masters of Science in AI (first in Florida), Masters of Science in Data Science and Analytics, and the new Professional Masters of Science degree in computer science for working professionals. For more information about the College, please visit eng.fau.edu.
About Florida Atlantic University:
Florida Atlantic University, established in 1961, officially opened its doors in 1964 as the fifth public university in Florida. Today, the University serves more than 30,000 undergraduate and graduate students across six campuses located along the southeast Florida coast. In recent years, the University has doubled its research expenditures and outpaced its peers in student achievement rates. Through the coexistence of access and excellence, FAU embodies an innovative model where traditional achievement gaps vanish. FAU is designated a Hispanic-serving institution, ranked as a top public university by U.S. News & World Report and a High Research Activity institution by the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. For more information, visit http://www.
Media Contact
Gisele Galoustian
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.