Researchers have identified a yet unknown bacterial cell-cell communication system.
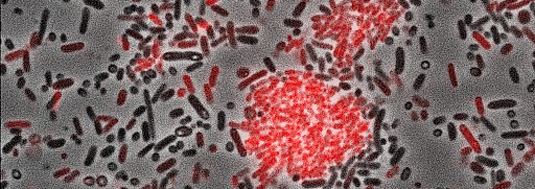
The micrograph shows the bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens. The cells labeled in red produce the aggregation factor. (Source: Ralf Heermann, LMU)
In nature, bacteria are no mavericks but live in close association with neighboring bacteria. They have evolved specific cell-cell communication systems that allow them to detect the presence of others and even to build up cooperative networks.
LMU microbiologist PD Dr. Ralf Heermann and Professor Helge Bode of the Goethe-University in Frankfurt have just reported the discovery of a previously unknown bacterial “language”. Their findings are detailed in the latest issue of the journal “Nature Chemical Biology”. “Our results demonstrate that bacterial communication is much more complex than has been assumed to date,” Heermann says.
The bacterial communication system that is currently best understood uses N-acylhomoserine lactones (AHLs) as signals. These compounds are made by enzymes that belong to the group of LuxI-family synthases. Transmitting cells secrete the signal and neighboring cells recognize the concentration via a LuxR-type receptor. Signal perception changes the pattern of gene expression in the receiving cells, which results in alterations in their functional properties or behavior. However, many bacteria have LuxR receptors but lack any LuxI homolog, so that they cannot produce AHLs. These receptors are referred to as LuxR solos.
A new class of bacterial signaling molecules
Ralf Heermann and Helge Bode have now discovered a type of ligand that binds to LuxR solos. As model system, they chose the species Photorhabdus luminescens, a pathogenic bacterium that is lethal to insects.
“We have identified a new class of bacterial signaling molecules, which are produced by a previously unknown biochemical route,” explains Helge Bode, Merck Professor of Molecular Biotechnology at Goethe-Universität Frankfurt. It turns out that a LuxR solo of this bacterium responds to compounds called alpha-pyrones, specifically to photopyrones. Furthermore, the researchers have identified the pyrone synthase (PpyS) that catalyzes the biosynthesis of photopyrones. The pyrone-based signaling system allows the bacteria to recognize one another, whereupon they produce a surface factor that causes cell clumping. Heermann and Bode assume that this collective behavior makes the cells less vulnerable to the insect’s innate immune system, and then allows them to kill their victims by the production of various of toxins.“ P. luminescens is a useful model organism, because it is related to many human pathogens, including coliform bacteria such as enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) and well as plague bacteria,” Heermann points out.
The new findings are also of more general interest because communication systems of bacterial pathogens offer promising targets for antimicrobial drugs. Thus, agents that interfere with bacterial “small talk” could inhibit the production of toxins or prevent the formation of biofilms. Since those drugs would only prevent the expression of pathogenic traits, rather than killing bacteria as antibiotics do, the danger of drug resistances would be enormously diminished.
Story Source:
The above story is reprinted from materials provided by Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich.