Researchers explain how a new meteorological satellite can be an option to monitor land surfaces and climate change
Credit: Tomoaki Miura and Kazuhito Ichii
Satellite remote sensing has widely been used to monitor and characterize the spatial and temporal changes of the Earth’s vegetative cover. Satellites used in these analyses have conventionally been polar-orbiting satellites, which orbit from “pole to pole” and obtain only one to two images of the Earth per day. The utility of these polar-orbiting satellites has, however, often been limited because frequently occurring clouds block their view of the land surface.
New-generation geostationary satellites present an opportunity to observe land surfaces in a more efficient manner. Being in geostationary orbit, the Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI) sensor onboard Himawari-8, for example, can obtain multi-band color images over Japan every 10 minutes, increasing the chance of obtaining “cloud-free” observations. In a new study published in Scientific Reports, an international team of researchers, including Tomoaki Miura from University of Hawaii, Shin Nagai and Mika Takeuchi from Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology, Kazuhito Ichii from Chiba University, and Hiroki Yoshioka from Aichi Prefectural University, examined this possibility and the utility of Himawari-8 AHI geostationary satellite data for capturing seasonal vegetation changes in Central Japan.
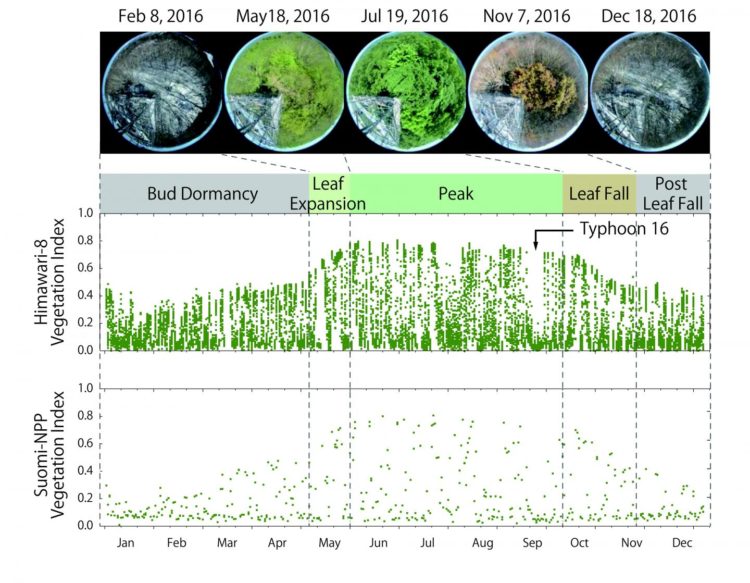
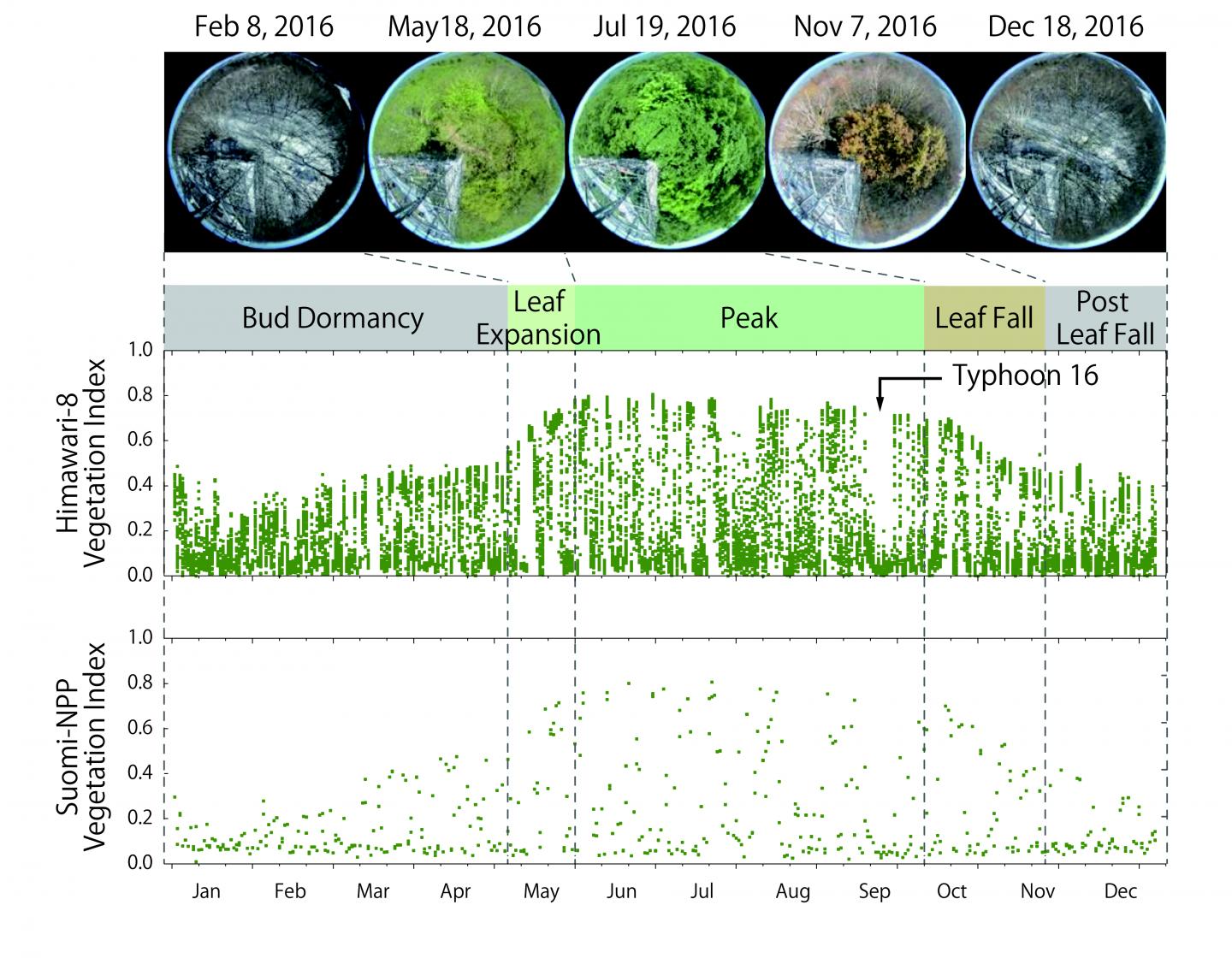
Their study found that Himawari-8 AHI acquired approximately 26 times more observations than the Suomi-National Polar-orbiting Partnership (S- NPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS), one of the latest polar-orbiting satellite sensors, for the year 2016. As a result, there were a larger number of days with “cloud-free” observations with Himawari-8 AHI than with S-NPP VIIRS. The study has demonstrated that the AHI geostationary sensor obtained one cloud-free observation data every 4 days, whereas the VIIRS polar-orbiting sensor was able to obtain one cloud-free observation every 7 to 16 days. Owing to this larger number of cloud-free observations, AHI “vegetation index,” a satellite measure of vegetation greenness, captured the temporal changes of vegetation from leaf expansion to leaf fall continuously throughout the growing season, corresponding to the observed vegetation phenology with in situ time-lapse digital images (Figure 1). There were, however, several periods where even AHI was unable to obtain cloud-free observations due to persistent cloud cover during summer-fall seasons.
“Detailed vegetation seasonal information from the Himawari-8 geostationary satellite can be useful for many applications such as short- term drought monitoring and assessing the impact of heavy rainfall events,” said Prof Miura, the lead author of the study. “This study has shown that the Himawari-8 meteorological satellite can be used to monitor land surface and vegetation. With new-generation geostationary satellites, we may begin to see various types of vegetation changes that could not be seen with previous satellites. The new findings contribute to understanding land-atmosphere carbon dioxide budgets,” said Prof Ichii of Chiba University, a co-author of this study.
The Himawari-8 AHI geostationary satellite also acquires multi-band color images over the tropical Southeast Asia region every 10 minutes. It is expected that AHI geostationary sensor data would contribute to improving our understanding of vegetation dynamics and the effect of climate change in this cloud-prone tropical region.
###
Funding information
This study was supported partially by a Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Invitational Fellowship (ID no. L18554 Tomoaki Miura and Shin Nagai) and the Center for Environmental Remote Sensing (CEReS) Joint Research Program.
Contact
Saori Tanaka
Research Administrator for Communications
Institute for Global Prominent Research, Chiba University [email protected]
+81 (0)43 290 3022
Tomoaki Miura
Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Management, University of Hawai?i at Mānoa
Email: [email protected]
Media Contact
Saori Tanaka
[email protected]
81-043-290-3022
Related Journal Article
http://dx.